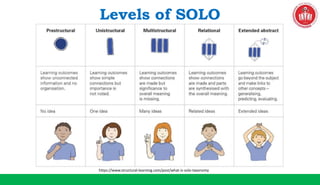
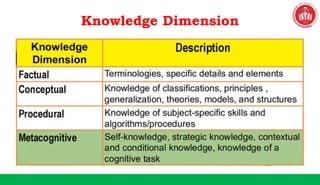
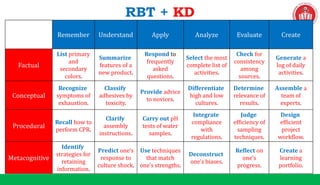
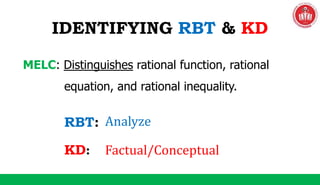
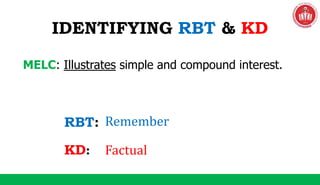
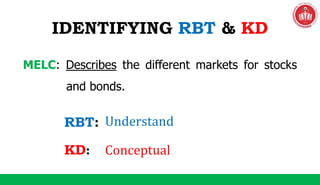
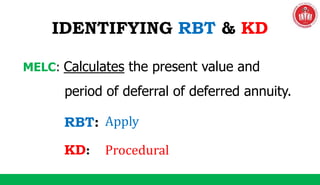
The document discusses the SOLO taxonomy, which is a framework for classifying the quality of student responses. It was developed by Biggs and Collis in 1982. The document explains that SOLO taxonomy is useful for helping learners reflect on their progress, for instructors to design learning experiences, and for implementing success criteria. It also notes that SOLO taxonomy provides feedforward and feedback and shows the difference between deep and surface understanding. The document then discusses the levels of SOLO taxonomy and provides a link for more information. It also introduces and explains the revised Bloom's taxonomy, including its knowledge dimension with the categories of factual, conceptual, procedural, and metacognitive knowledge. The document provides examples of how to identify the cognitive