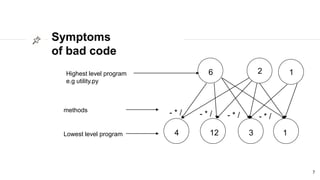
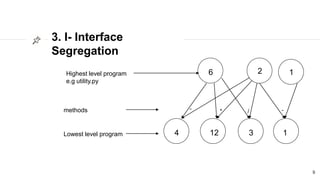
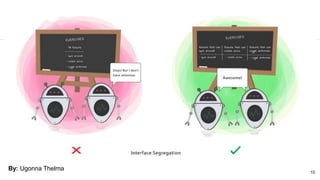
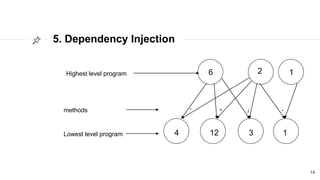
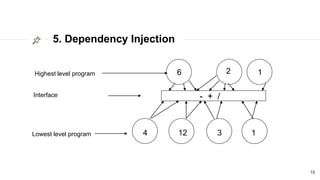
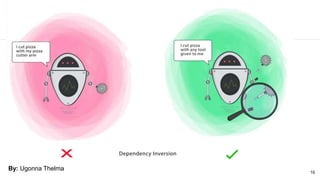
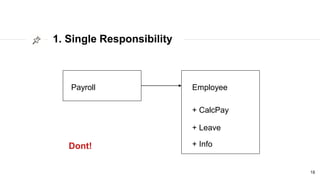
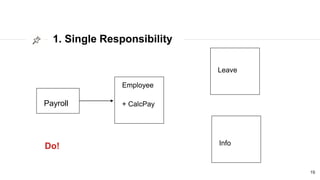
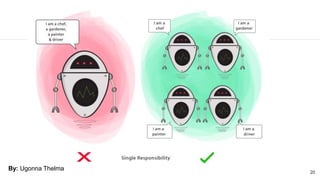
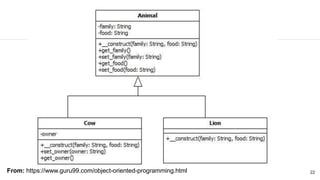
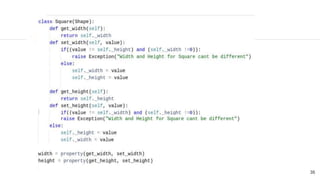
This document discusses the SOLID principles of object-oriented programming and agile design. It defines each principle: single responsibility, open/closed, Liskov substitution, interface segregation, and dependency inversion. For each principle, it provides an example of how to apply the principle to code through refactoring existing code. It also discusses object-oriented concepts like polymorphism that relate to the SOLID principles.















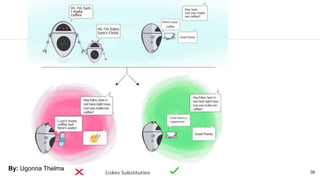
![36
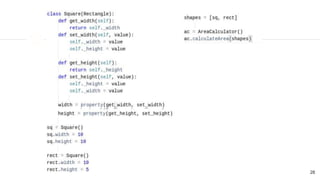
class AreaCalculator:
def calculateArea(self, shapes):
for shape in shapes:
print(f'Area : {shape.width * shape.height}')
square = Square()
square.height = 10
rectangle = Rectangle()
rectangle.width = 10
rectangle.height = 5
shapes = [square, rectangle]
ac = AreaCalculator()
ac.calculateArea(shapes)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solid-210619234506/85/S-O-L-I-D-Principles-of-OOP-and-Agile-design-36-320.jpg)