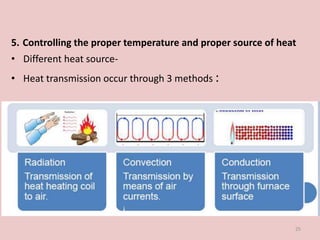
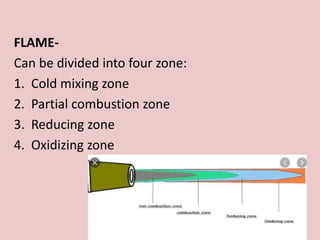
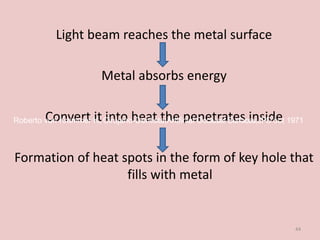
Soldering and welding are processes to join metal components. Soldering involves melting a filler metal below the melting points of the components being joined. Welding directly melts the components together without a filler. Common types of soldering include soft, hard, and brazing based on the filler metal temperature. Welding techniques include spot welding, laser welding, and tungsten inert gas welding. Key factors for a strong joint include clean surfaces, proper temperature, timing, and gap width between components. Defects like porosity or distortion can weaken the joint if processes are not followed correctly.