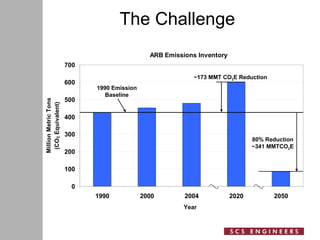
The document discusses the potential of solar power production on brownfield sites as a means to address environmental challenges and promote renewable energy. It highlights government initiatives, such as the Brightfields program, which aims to repurpose contaminated lands for solar energy generation, providing economic and sustainability benefits. Key considerations for implementing solar projects on these sites include site selection, engineering challenges, and the advantages of revitalizing underutilized properties.