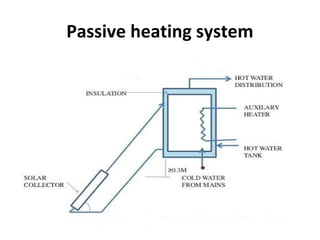
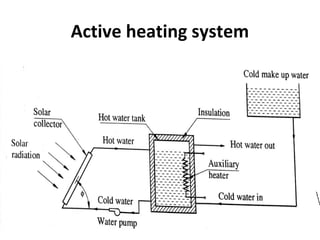
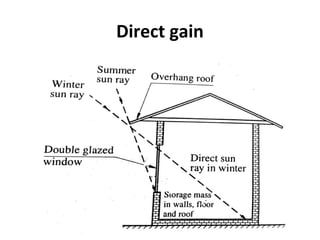
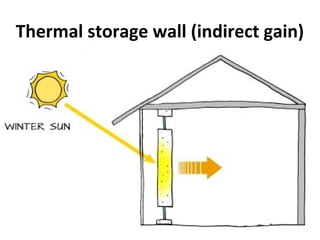
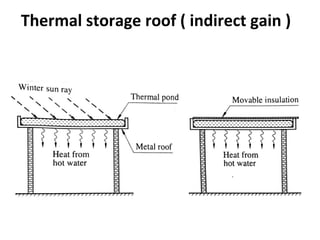
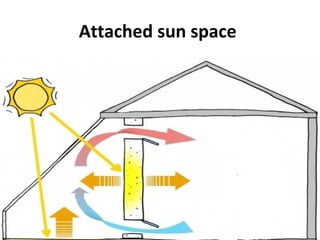
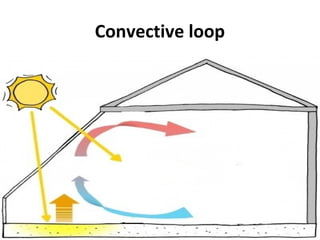
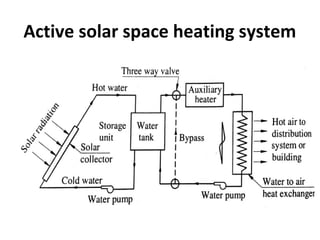
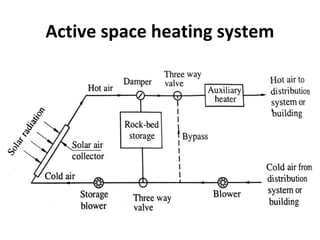
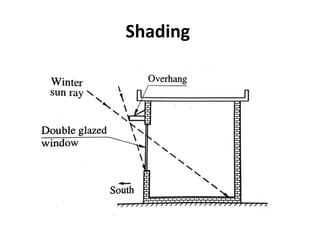
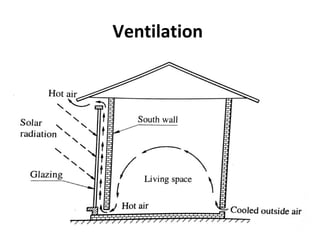
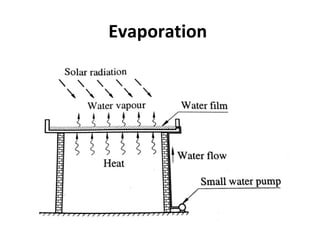
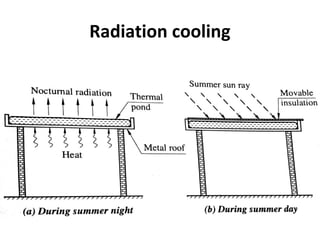
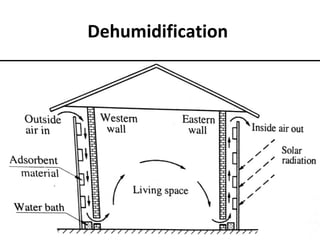
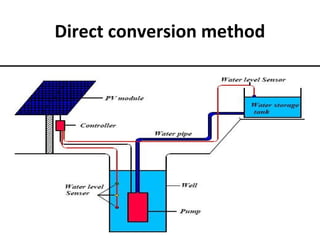
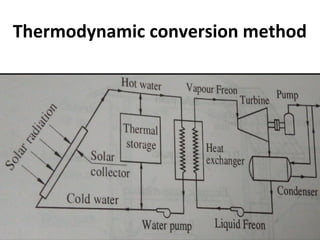
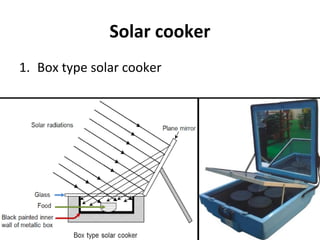
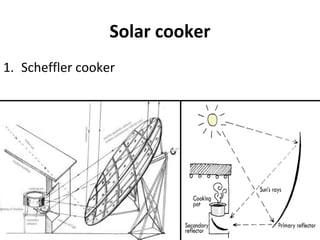
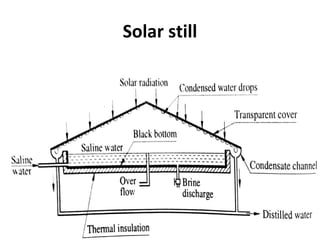
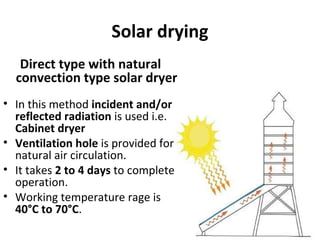
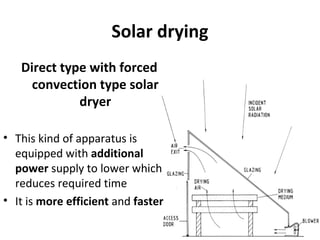
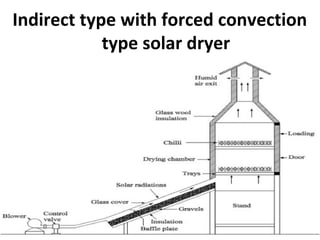
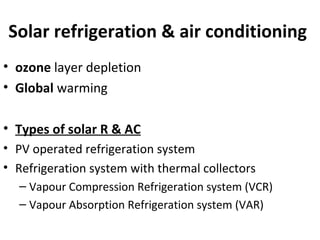
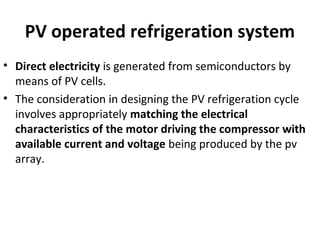
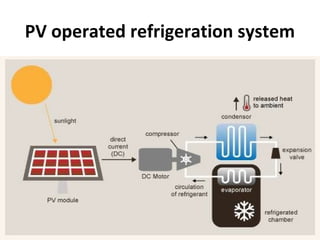
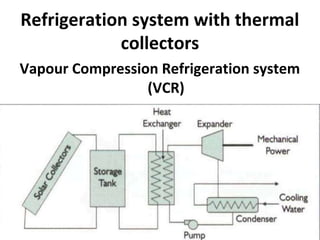
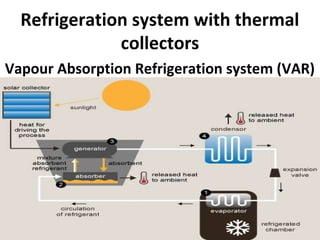
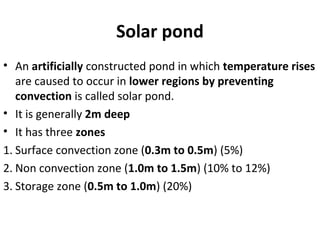
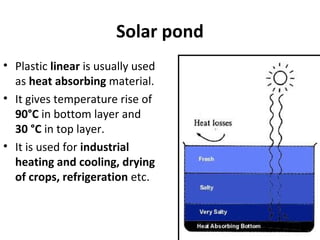
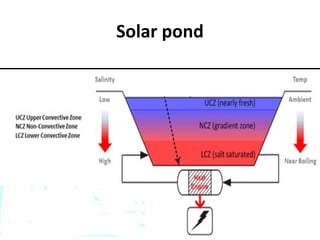
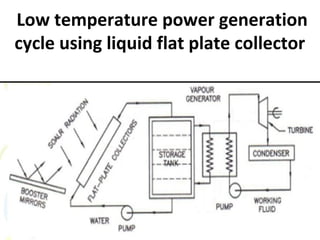
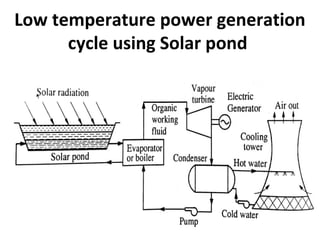
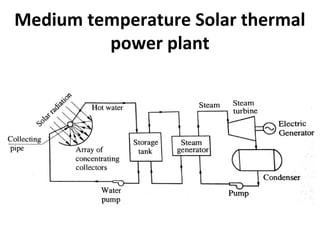
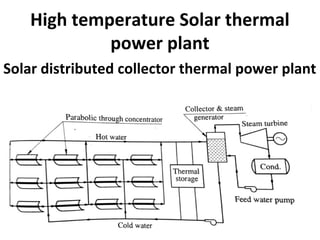
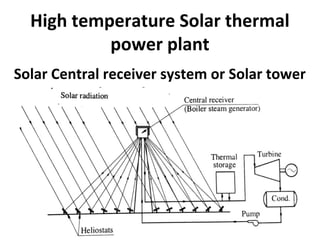
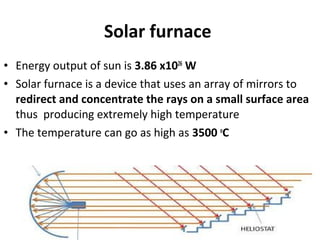
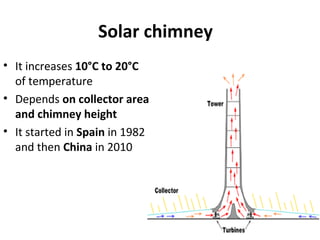
Solar energy can be stored and utilized in various ways for applications such as water heating, space heating and cooling, pumping, cooking, drying, and power generation. Some key storage methods include thermal, electrical, chemical, and mechanical storage. Solar water heaters use collectors to absorb solar radiation and transfer heat to water for storage. Active solar space heating systems use pumps to circulate fluid through collectors and transfer heat. Other applications like solar cookers, dryers, and stills use solar energy for heating. Larger scale uses include solar ponds, power plants using photovoltaics or concentrating solar thermal technologies, and solar chimneys for power generation.