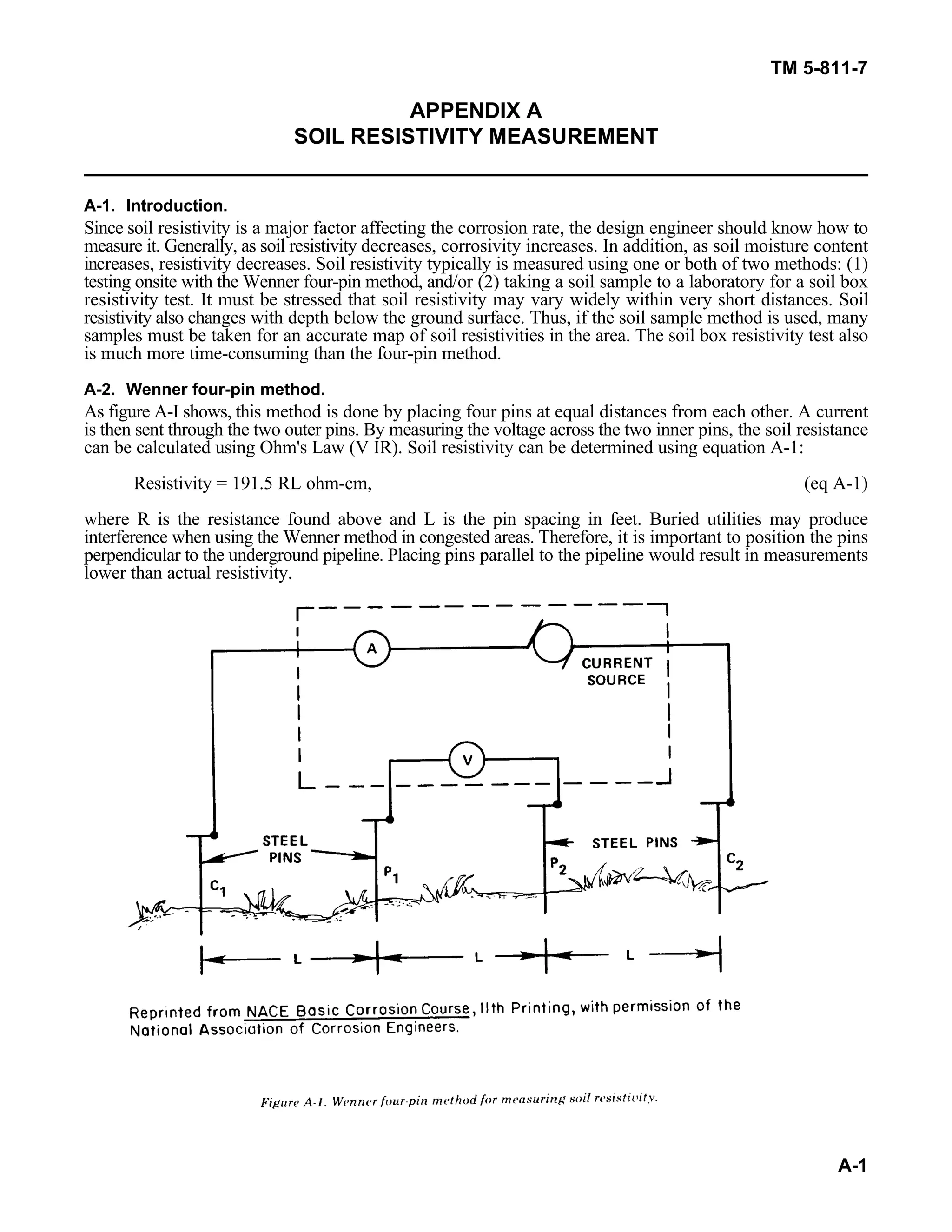
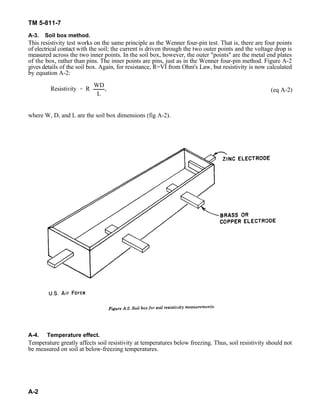
This document discusses methods for measuring soil resistivity, which is an important factor in determining corrosion rates. It describes two key methods: (1) the Wenner four-pin method, where four pins are placed in the soil in a line and current is passed between the outer pins to measure voltage between the inner pins and calculate resistivity; and (2) the soil box method, where a soil sample is placed in a metal box and contacts make measurements to determine resistivity using the sample's dimensions. Both methods apply Ohm's Law and equations to calculate resistivity from resistance measurements. Temperature also affects resistivity, so measurements should not be taken below freezing.