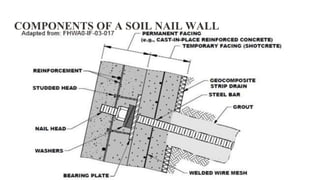
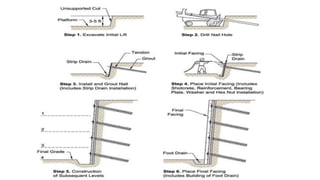
Soil nailing is a technique used to reinforce soil by inserting steel bars or nails into the ground to increase tensile and shear strength. It is commonly used for stabilizing existing slopes or excavations. The first uses of soil nailing were in Germany in 1975 and France in 1972. Key components are excavation, drilling nail holes, installing and grouting nails, constructing temporary shotcrete facing, and building a permanent facing. Proper drilling, grouting, and shotcreting equipment is needed, along with steel reinforcements and cementitious grout. Design considerations include strength limits, heights, nail spacing, ground properties, and drainage. Advantages are suitability for confined spaces and quick installation, while disadvantages include restrictions around







![Driven soil Nail
● These soil nails are relatively
small in diameter [19 to 25 mm
(¾ to 1 in.)] and are mechanically
driven into the ground.
● They are usually spaced
approximately 1 to 1.2 m (3 to 4
ft) apart.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soilnailing-210630065410/85/Soil-nailing-8-320.jpg)