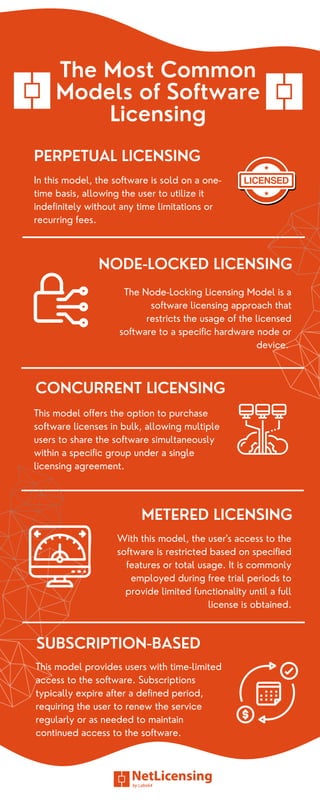
Software licensing is a contractual agreement that defines the permissible usage of software programs, categorizing them into open-source and proprietary licenses. Each license outlines the rights and responsibilities of developers and users, ensuring legal compliance and protecting intellectual property. Key models include perpetual, concurrent, node-locked, and subscription-based licensing, facilitating efficient asset management and fostering positive developer-user relationships.