Ringkasan dokumen tersebut adalah:
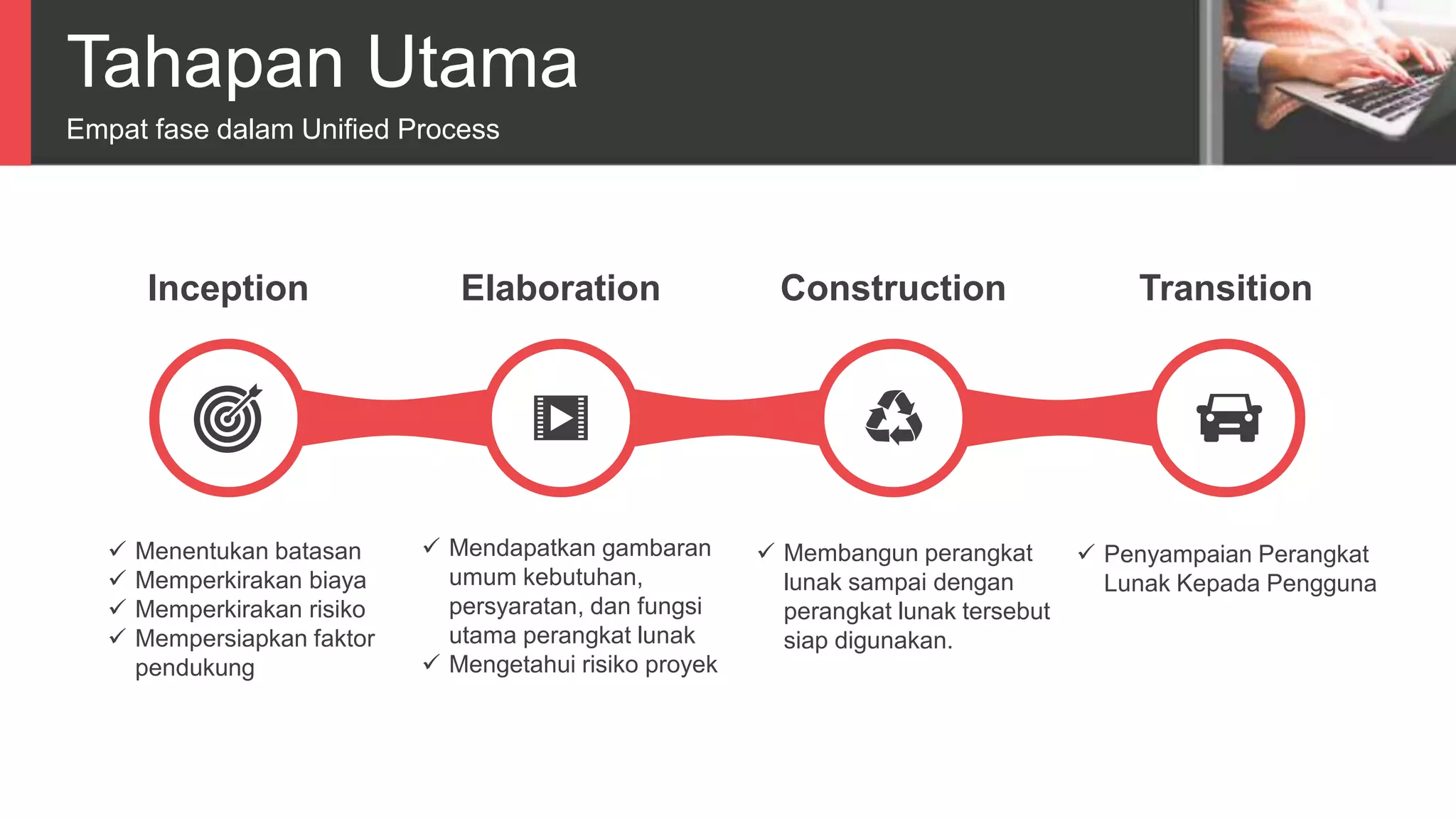
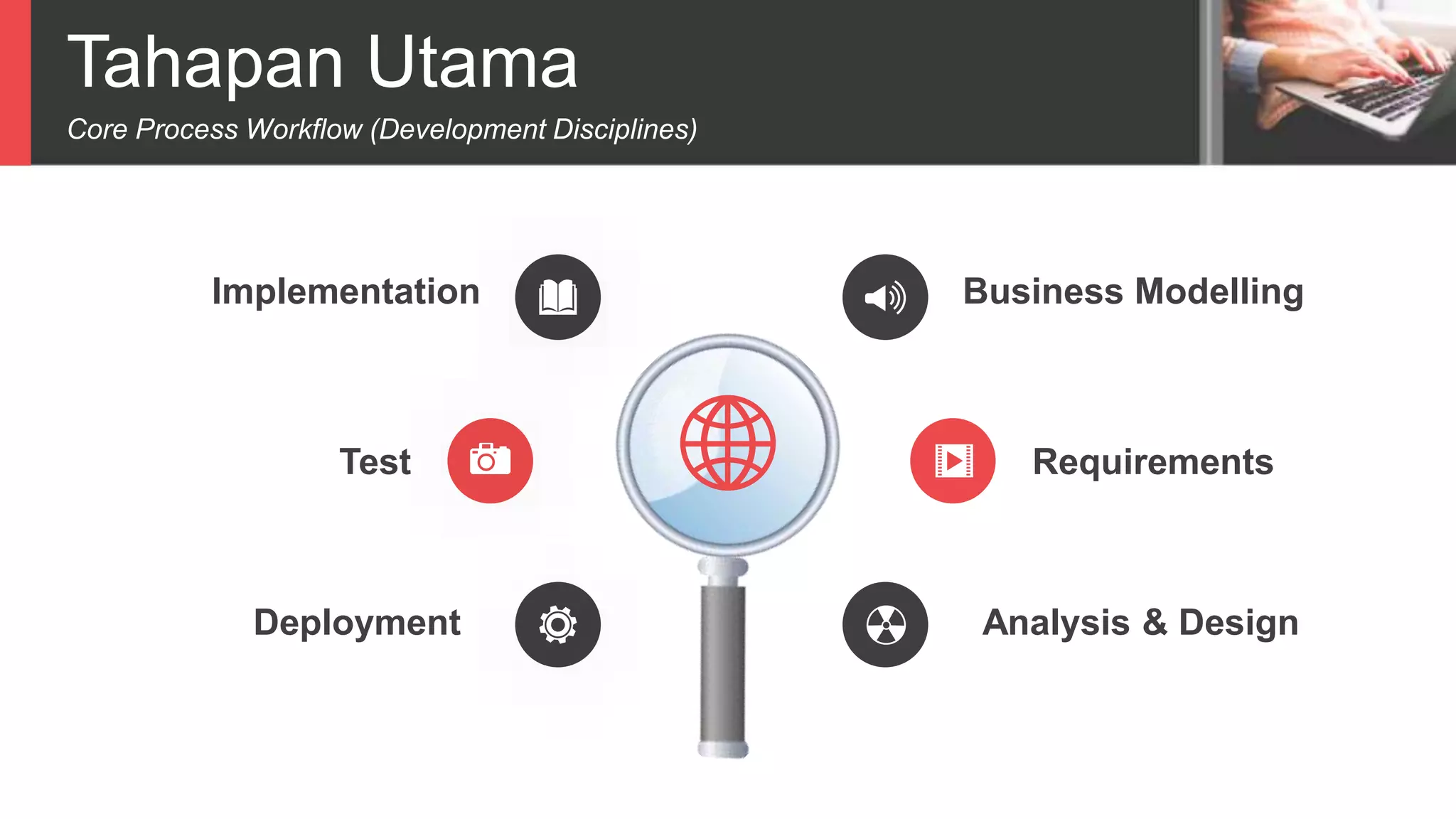
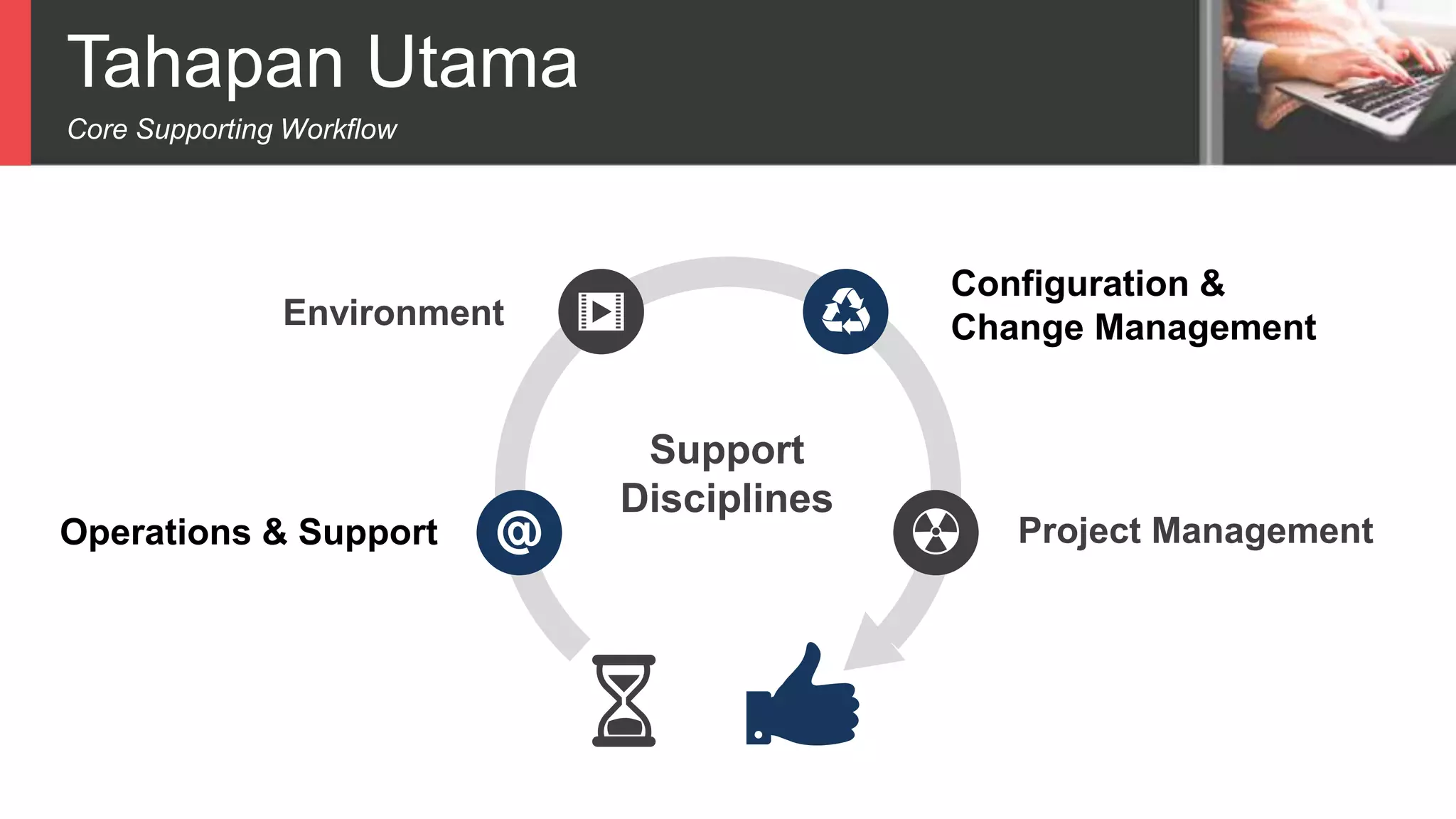
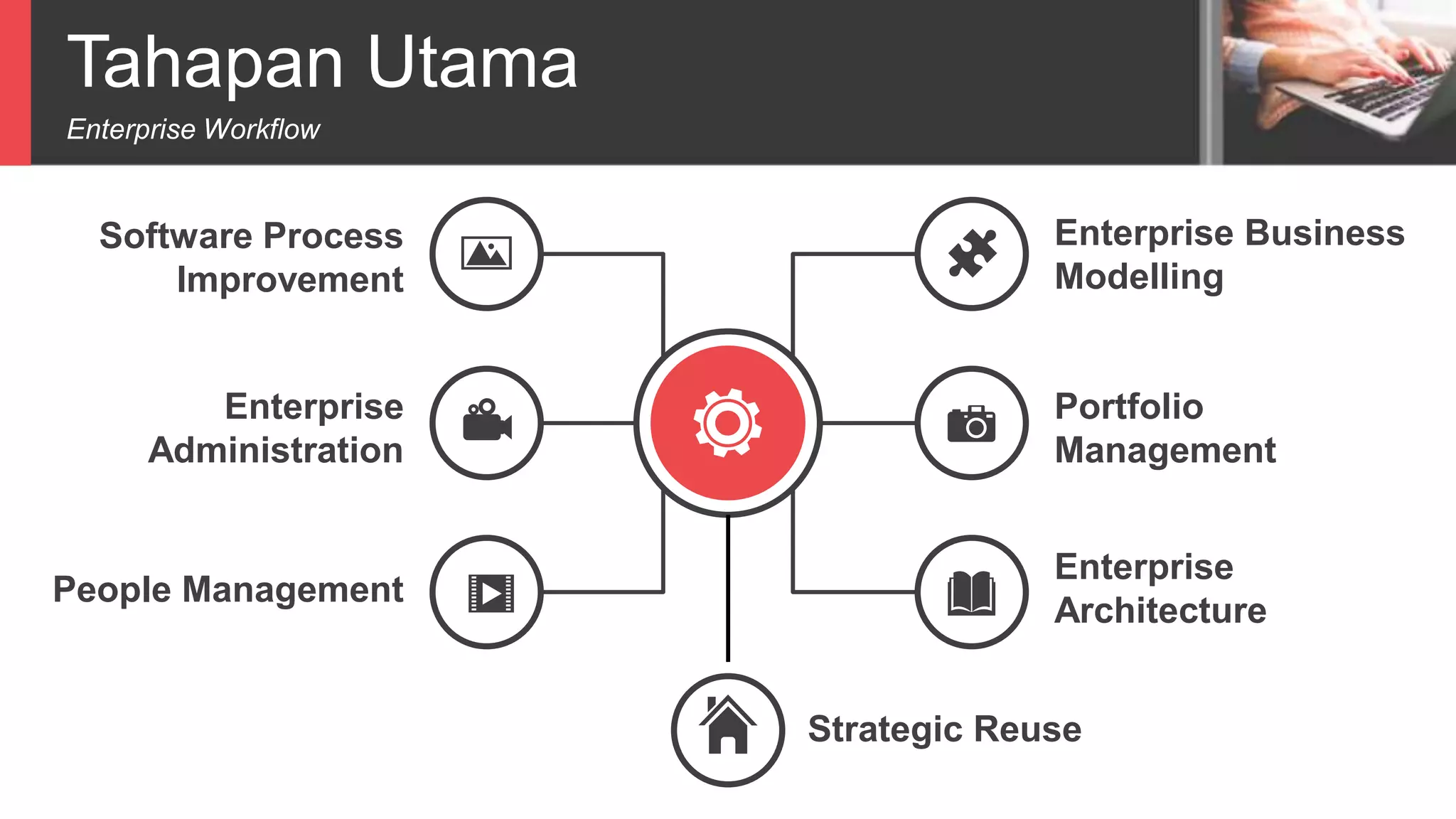
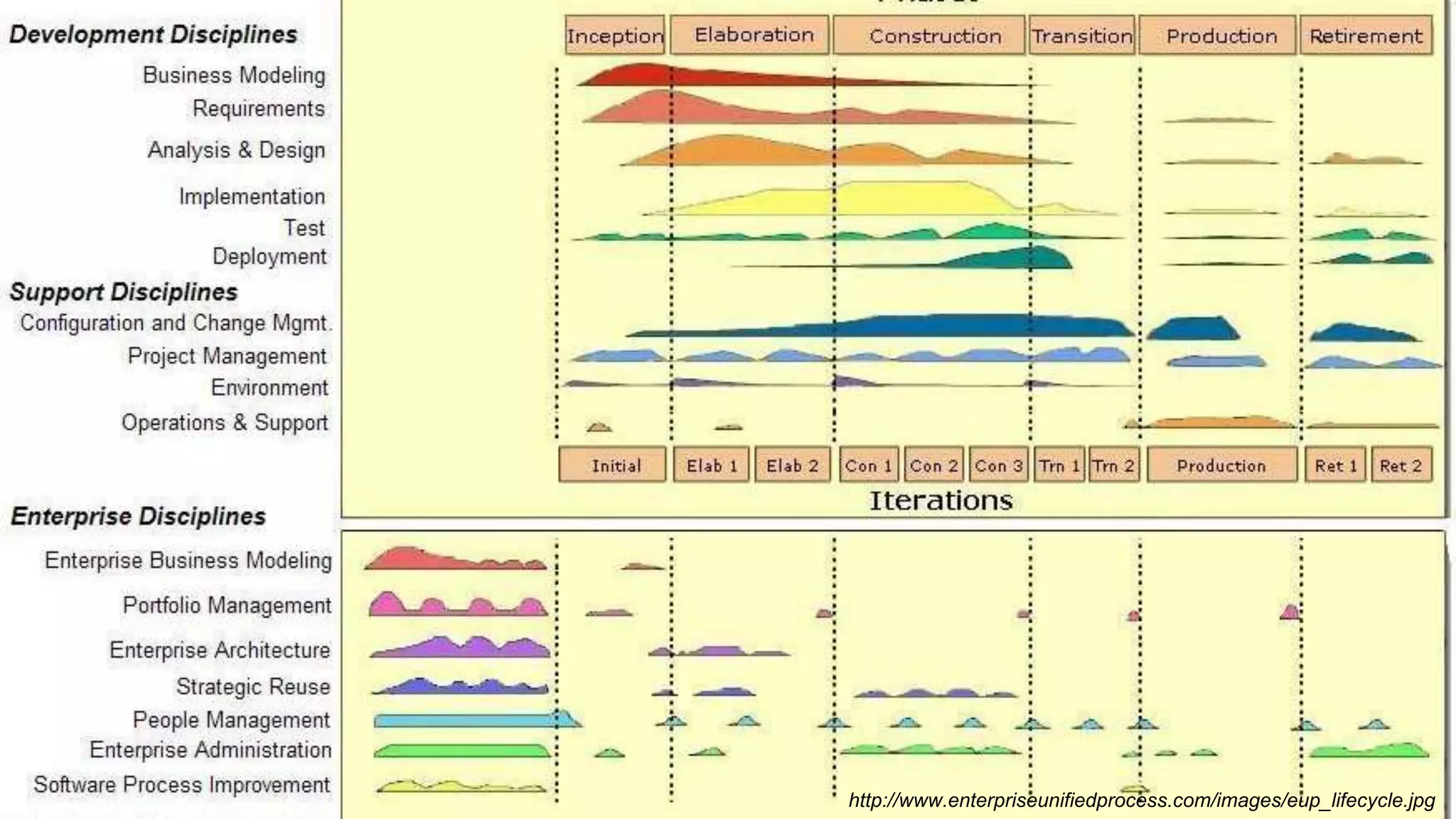
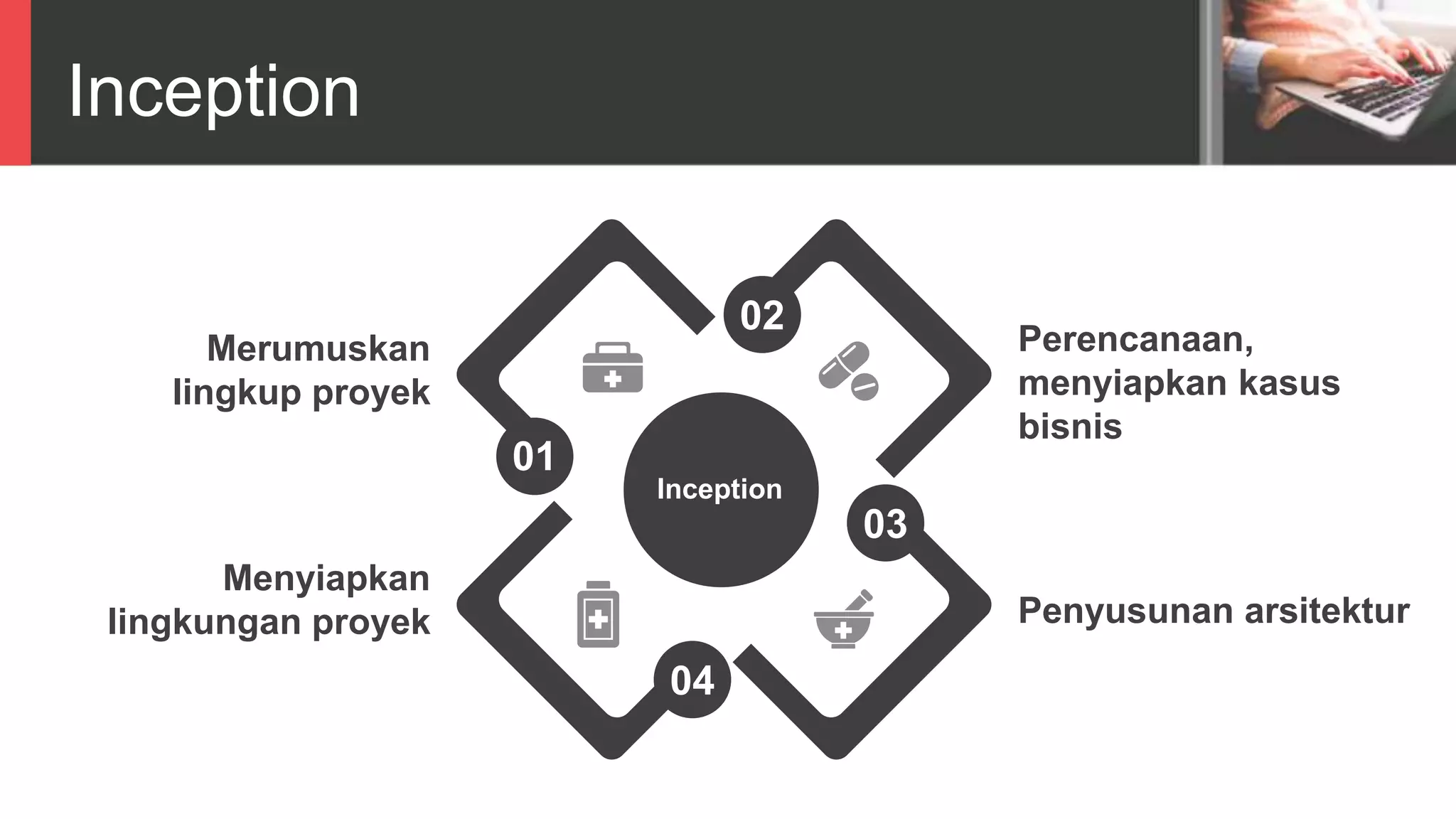
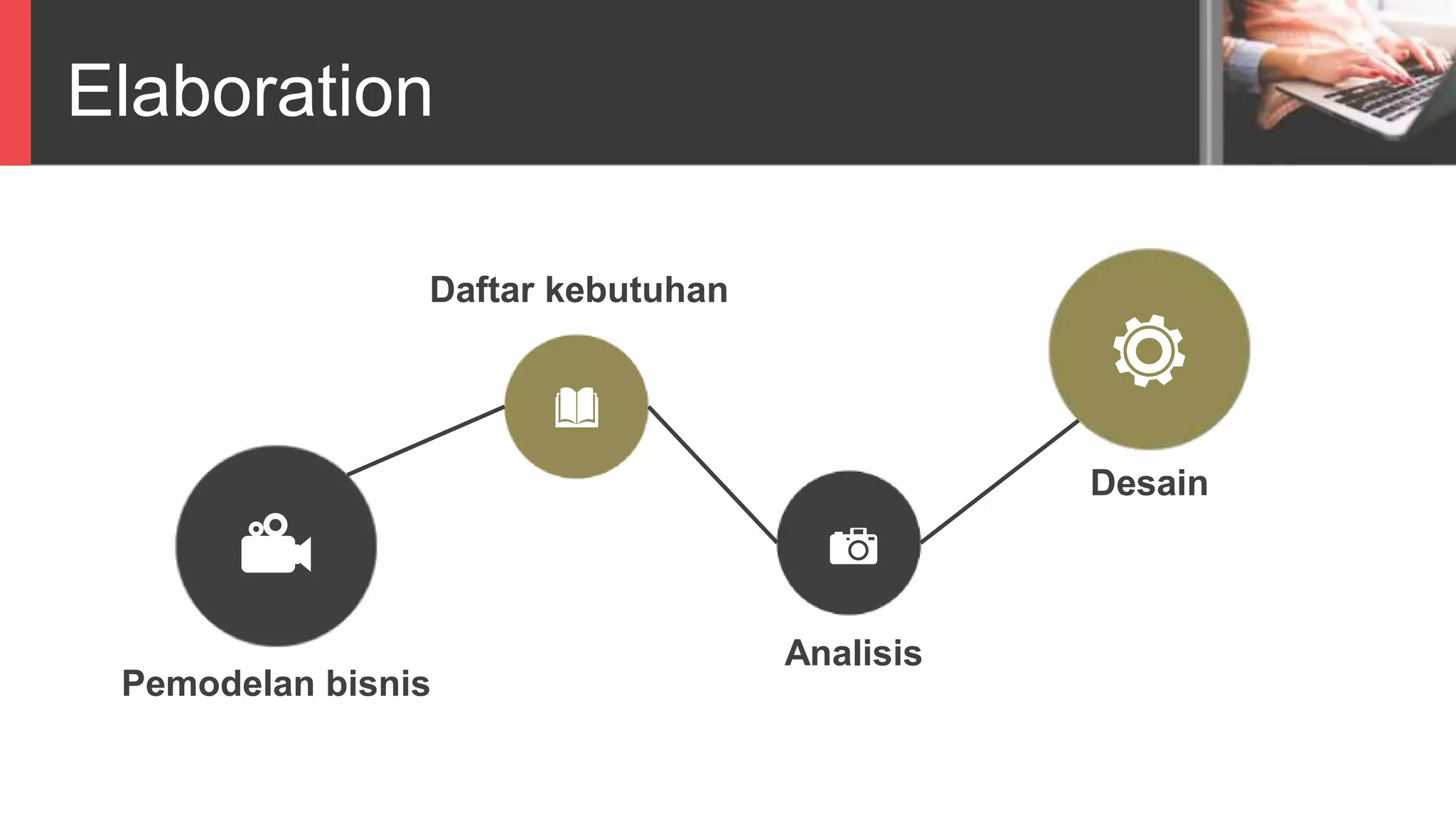
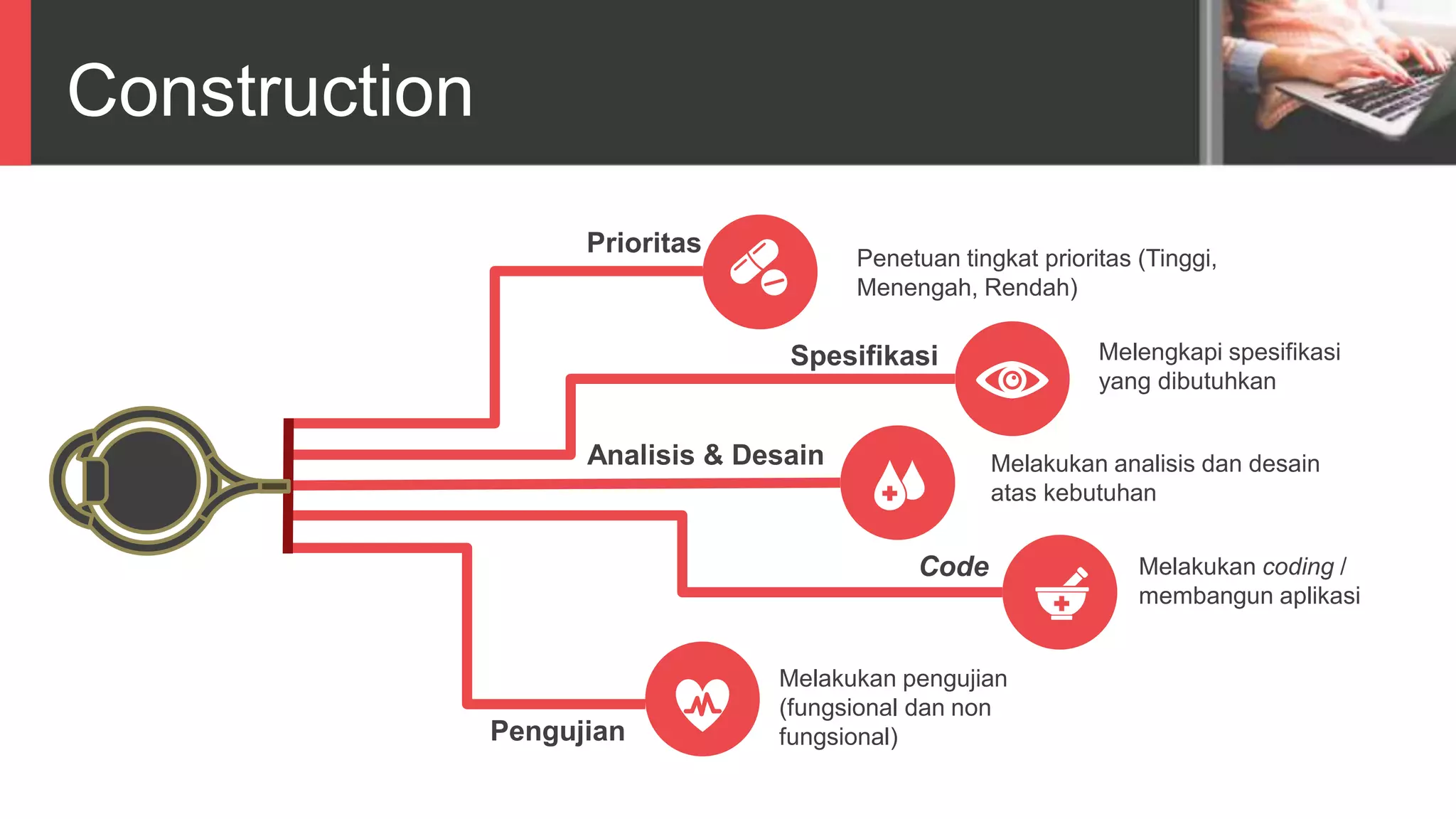
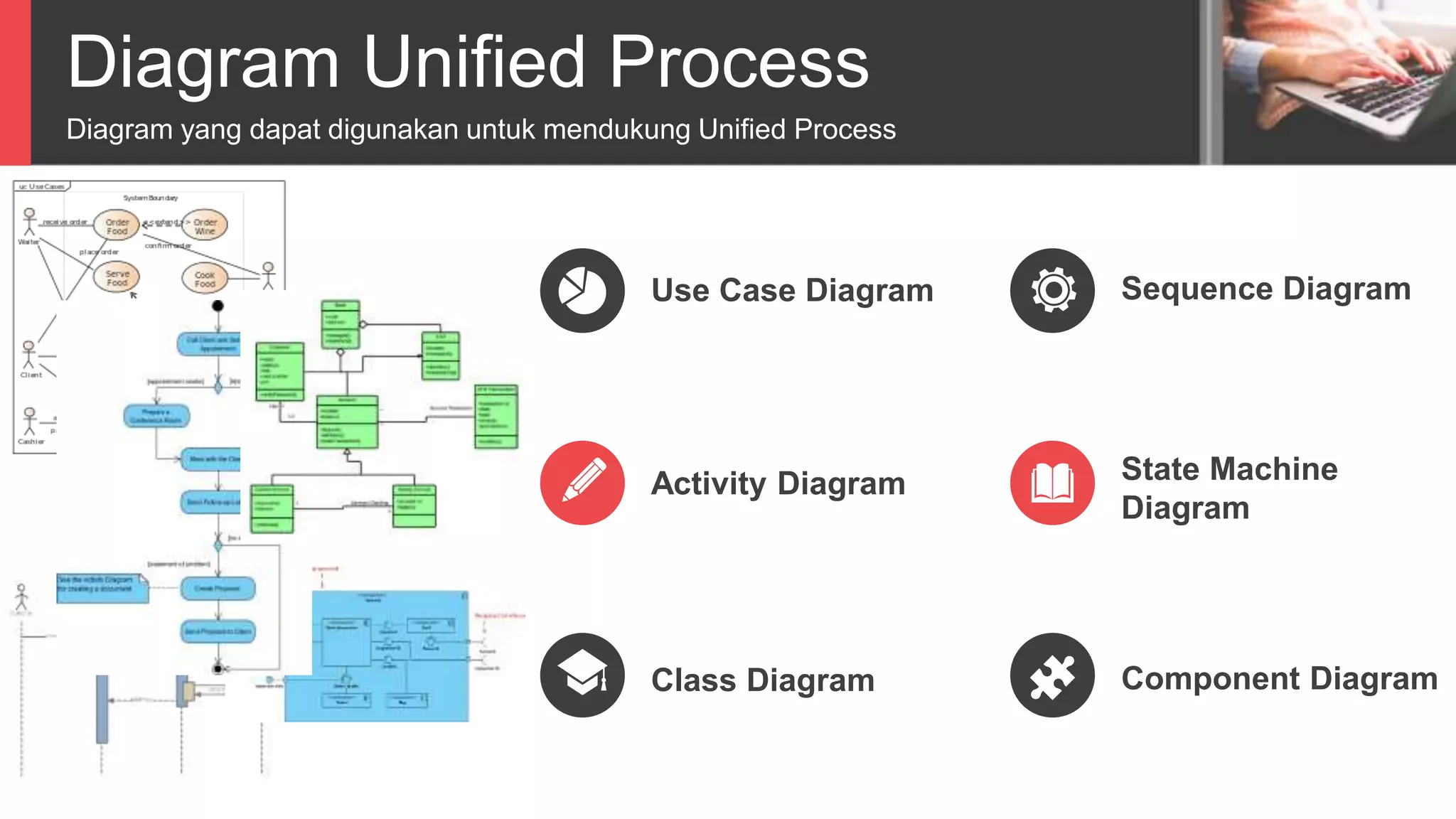
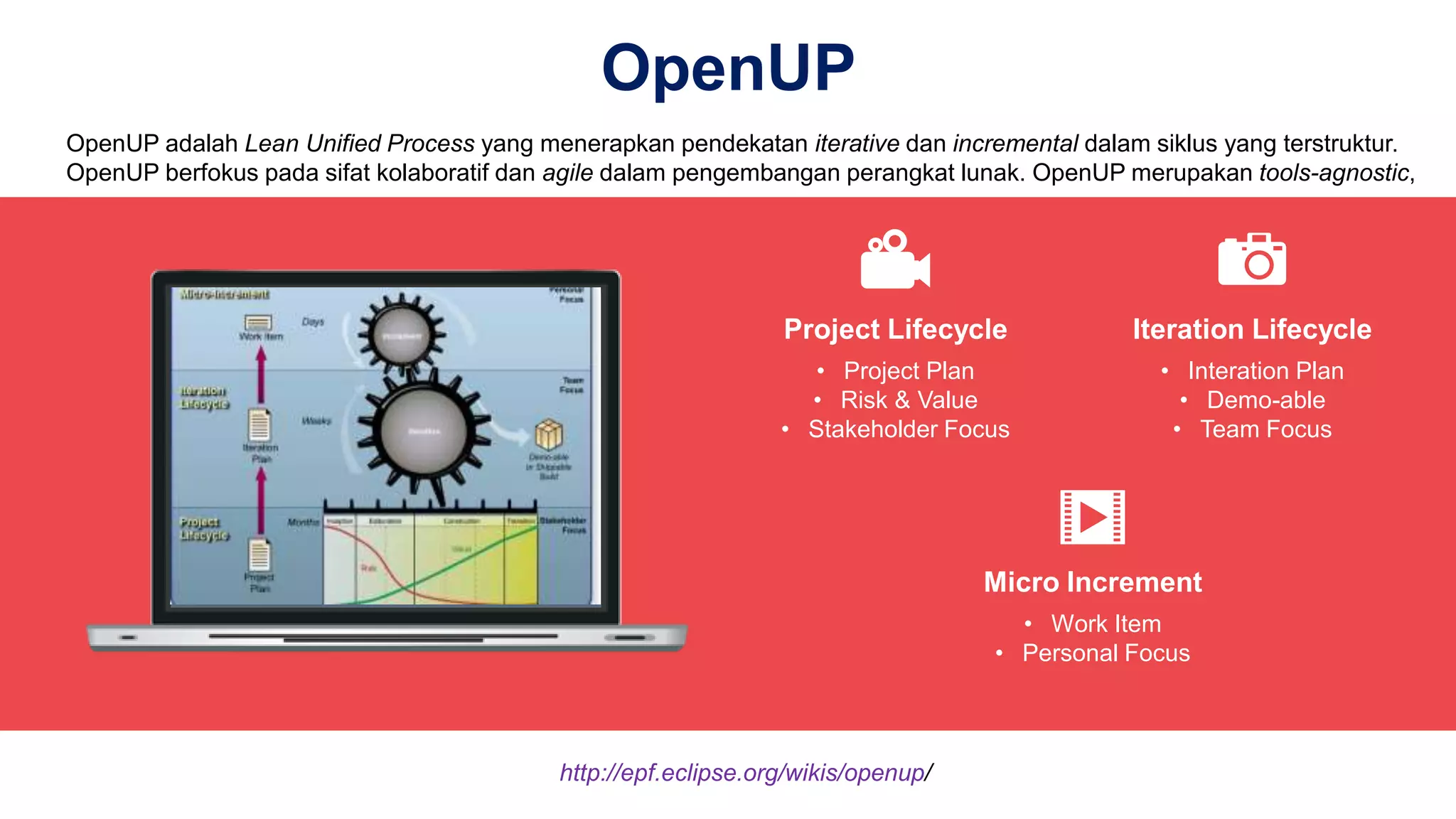
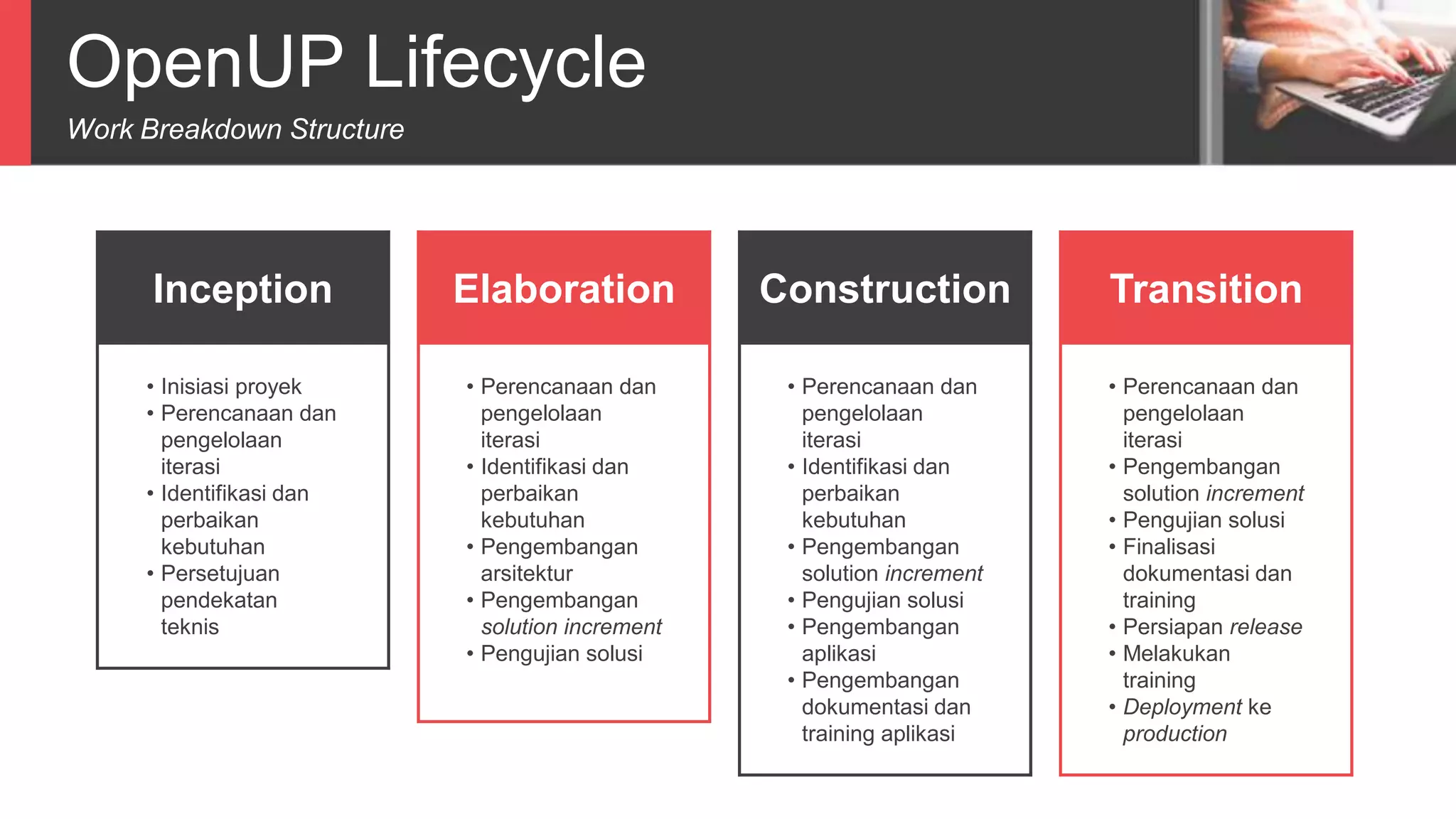
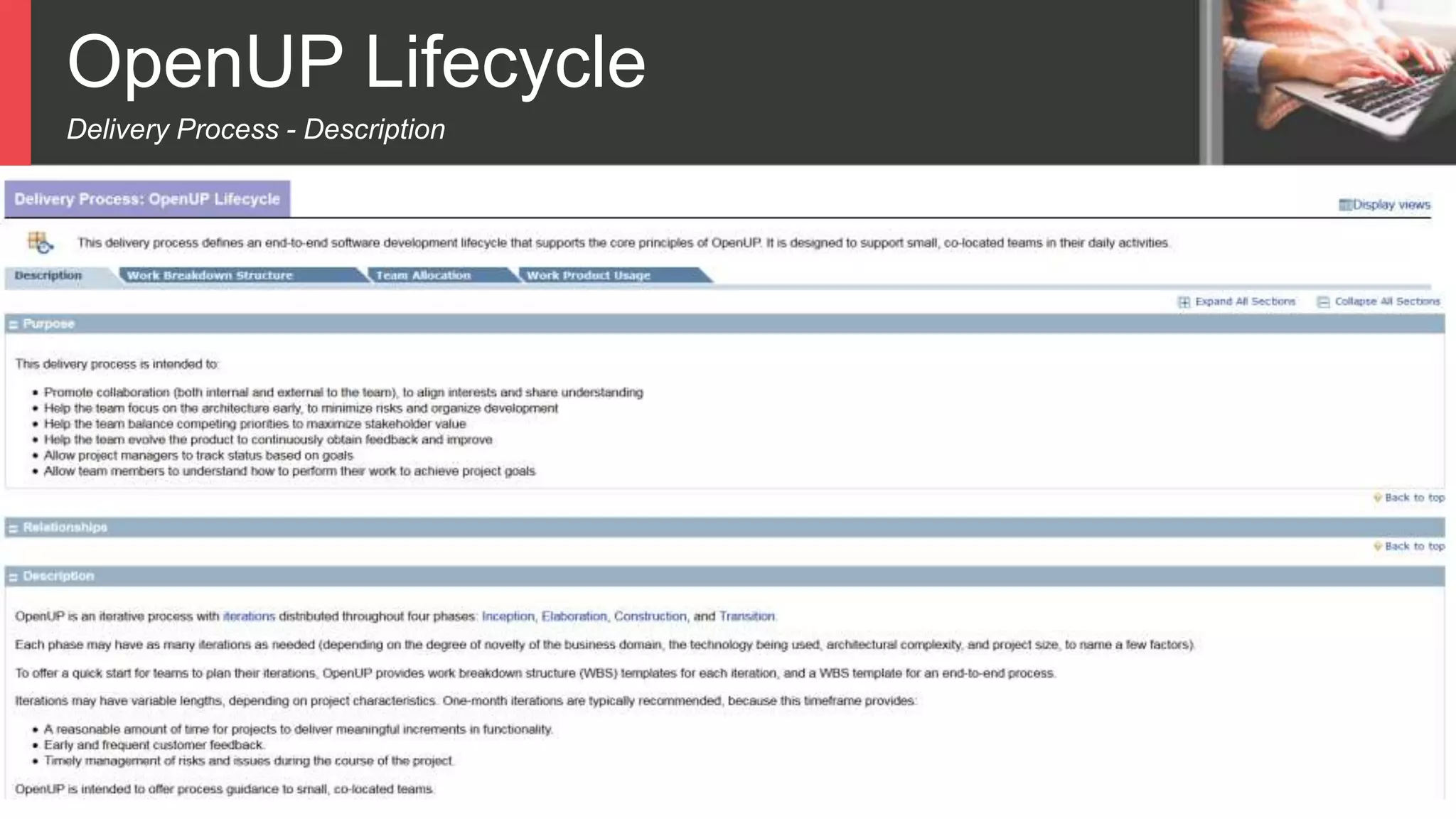
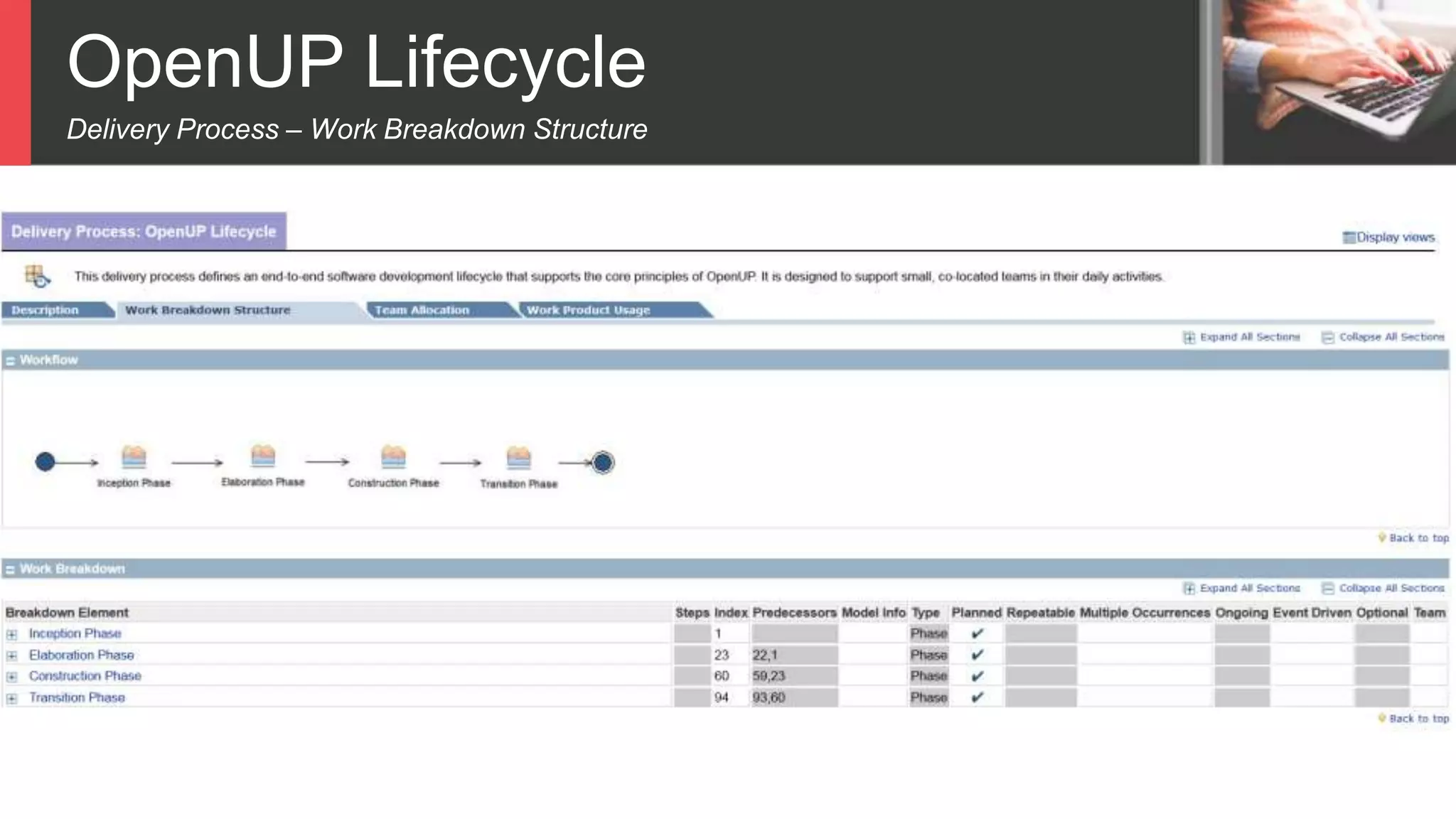
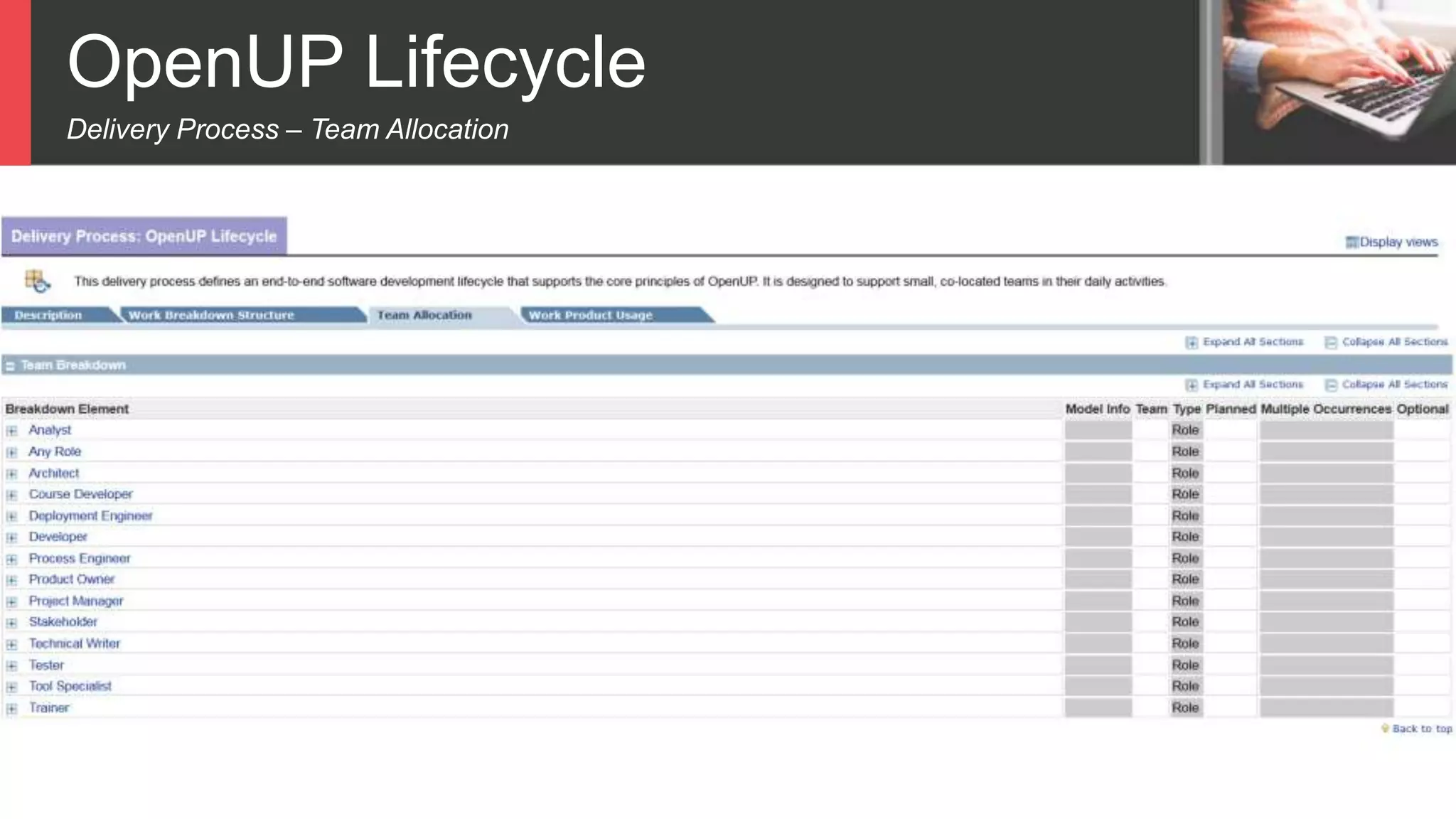
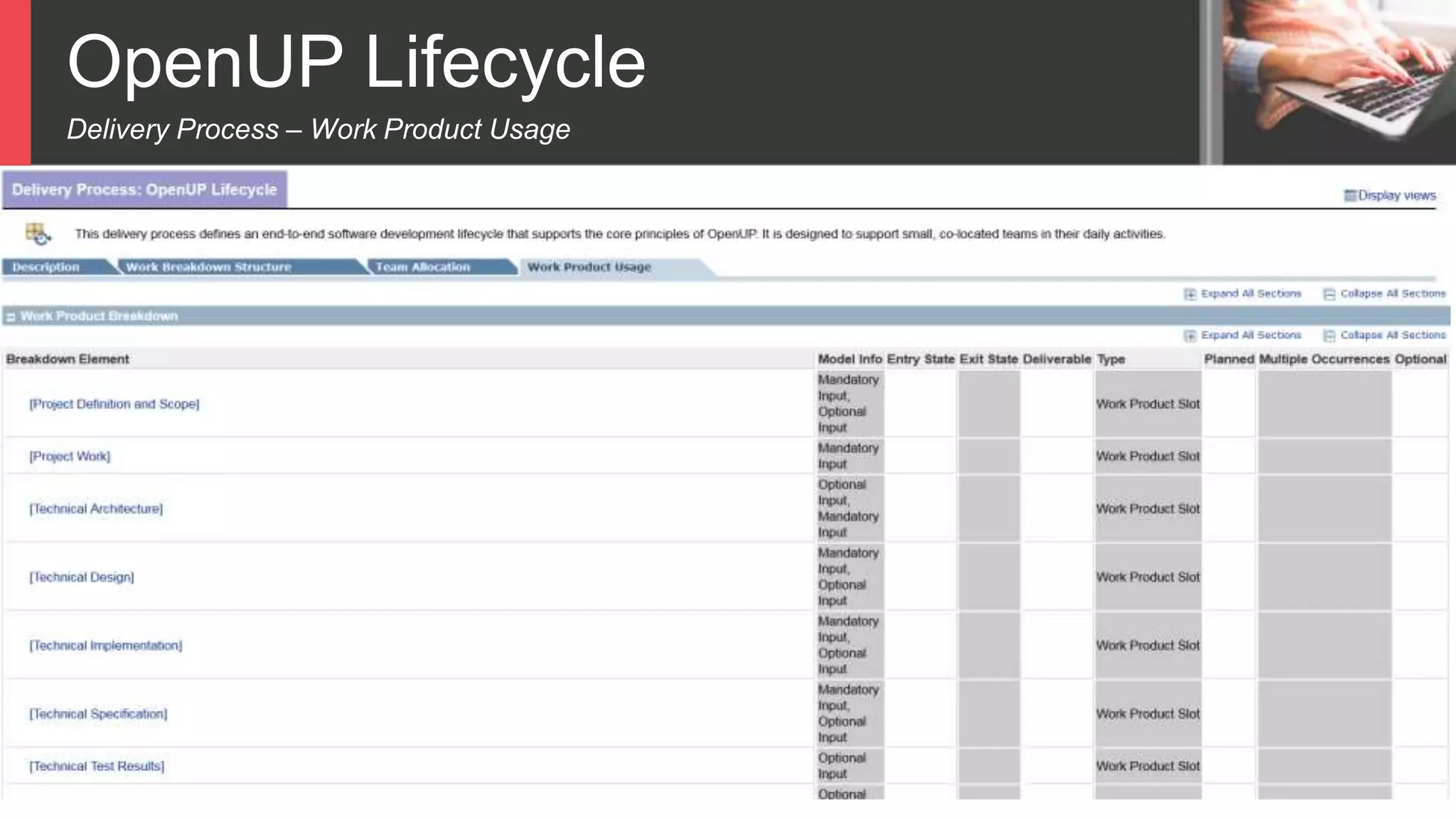
Dokumen tersebut membahas tentang Unified Process sebagai metode pengembangan perangkat lunak berbasis use case dan UML. Unified Process memiliki empat tahapan utama yaitu inception, elaboration, construction, dan transition. Dokumen juga menjelaskan penerapan Unified Process melalui OpenUP yang menerapkan pendekatan iterative dan incremental.