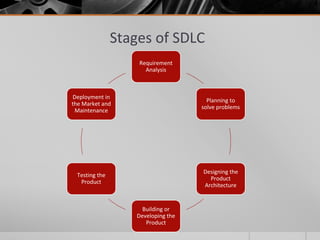
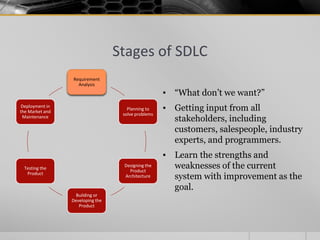
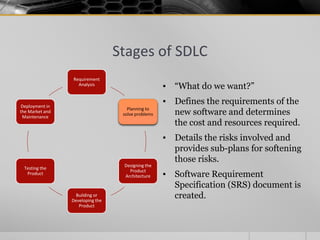
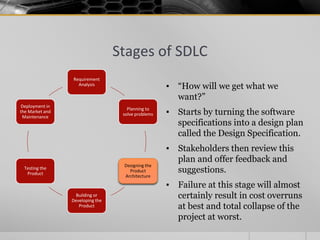
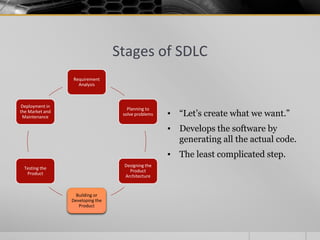
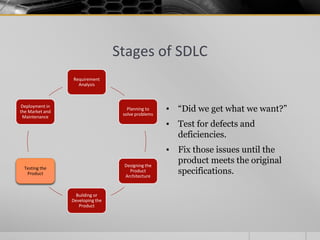
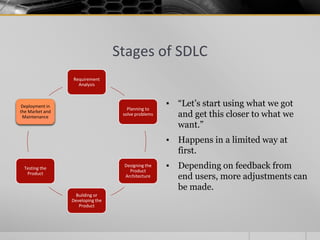
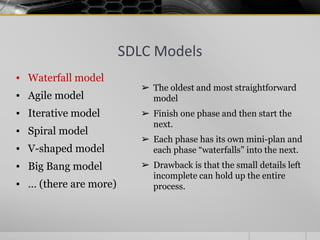
The document provides an overview of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), including definitions of software, software engineering, and key stages of the SDLC such as requirement analysis, design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance. It discusses various SDLC models, including waterfall, agile, iterative, spiral, and others, highlighting their characteristics, advantages, and drawbacks. The document emphasizes the systematic approach needed for successful software development and the importance of stakeholder engagement throughout the process.