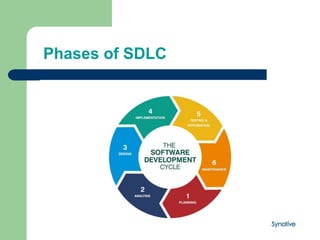
The document outlines the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), detailing its phases: planning, analysis, design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance. Each phase encompasses specific activities aimed at delivering high-quality software products efficiently while meeting client needs. The SDLC serves as a structured approach ensuring effective management and continuous improvement of software applications.