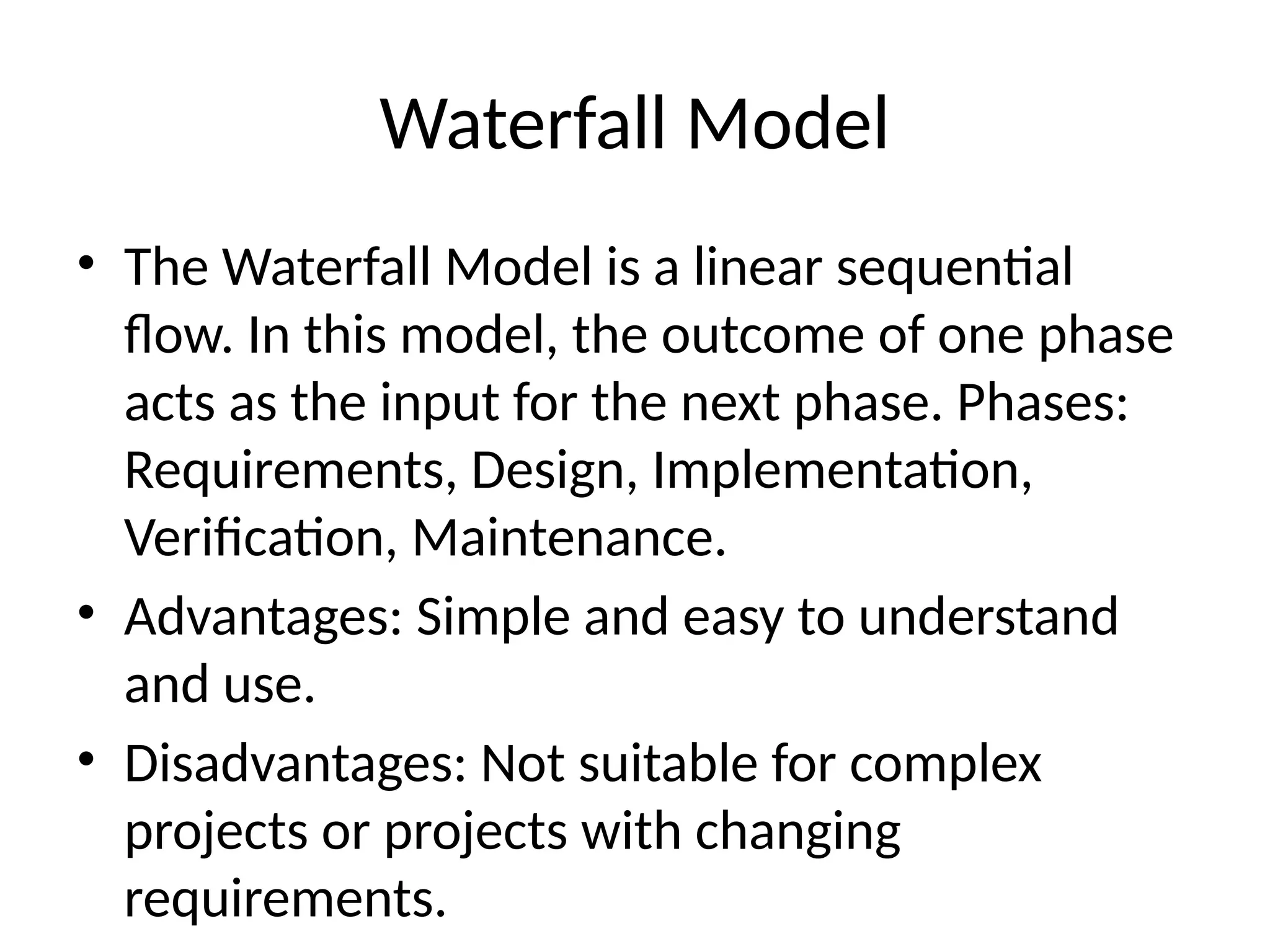
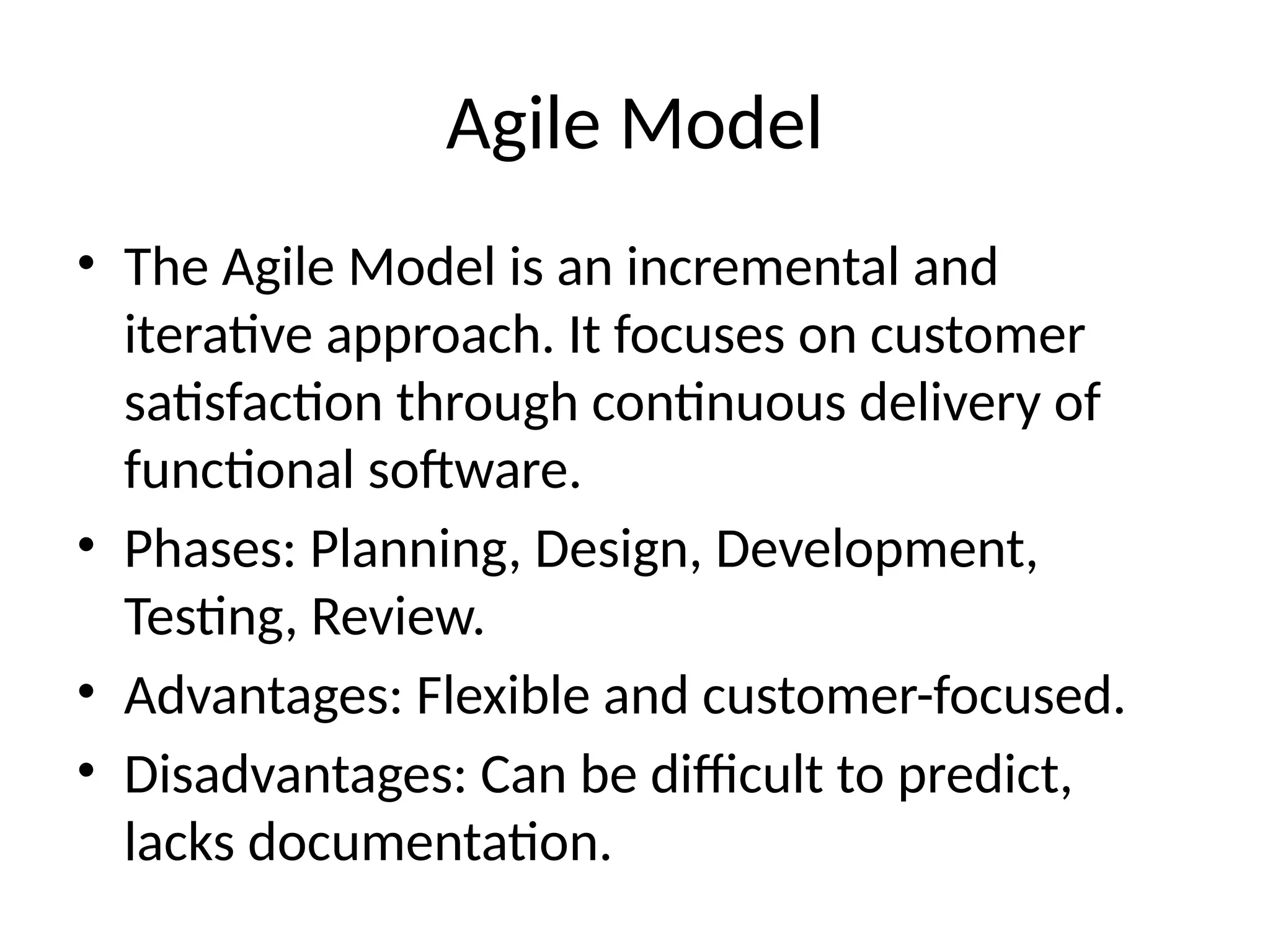
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a systematic process for building software that ensures quality and meets customer expectations. Various models such as Waterfall, Spiral, RAD, Iterative, and Agile have unique advantages and disadvantages that make them suitable for different project requirements and complexities. Understanding these models aids in selecting the most effective approach for successful software development.