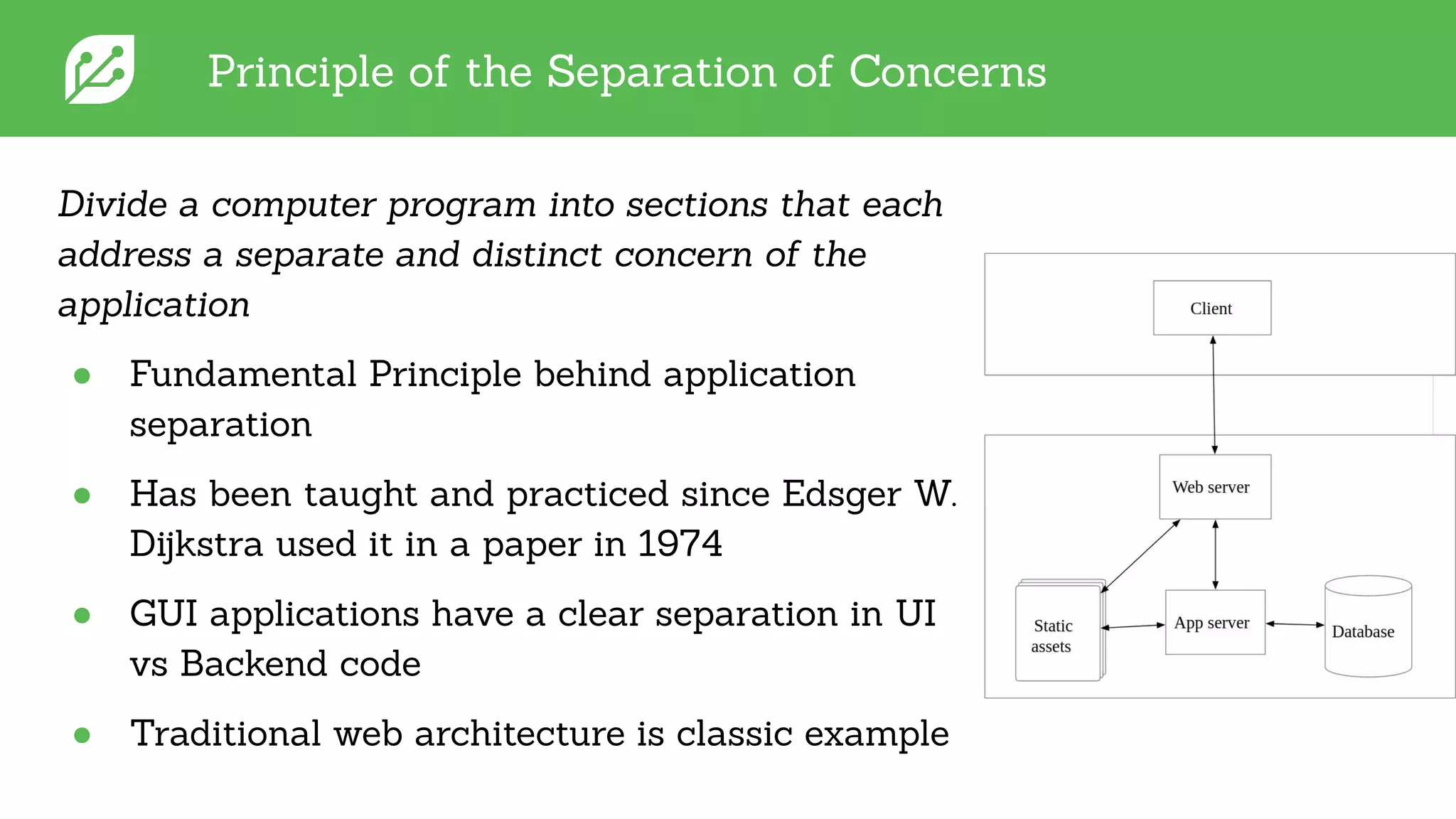
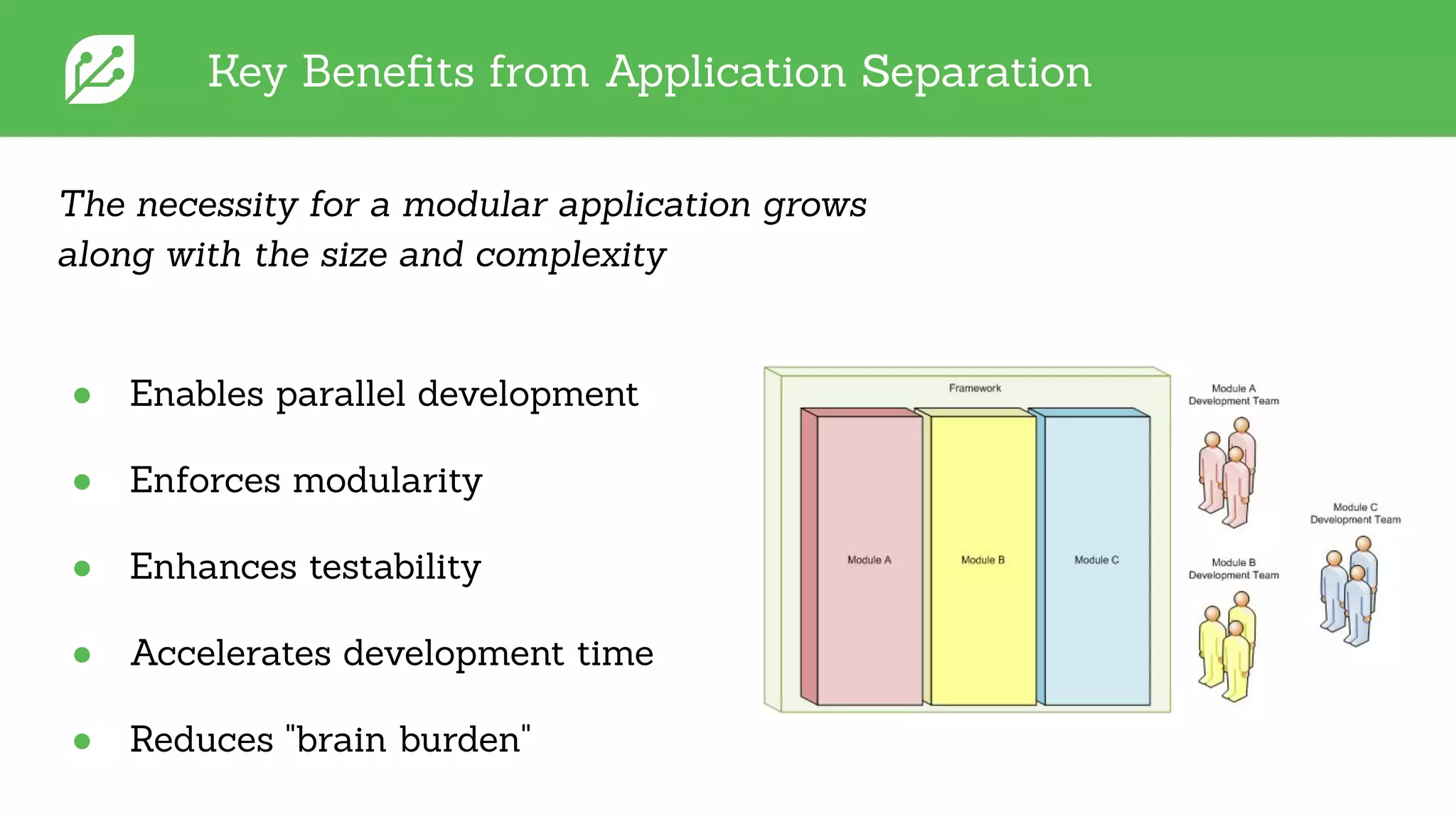
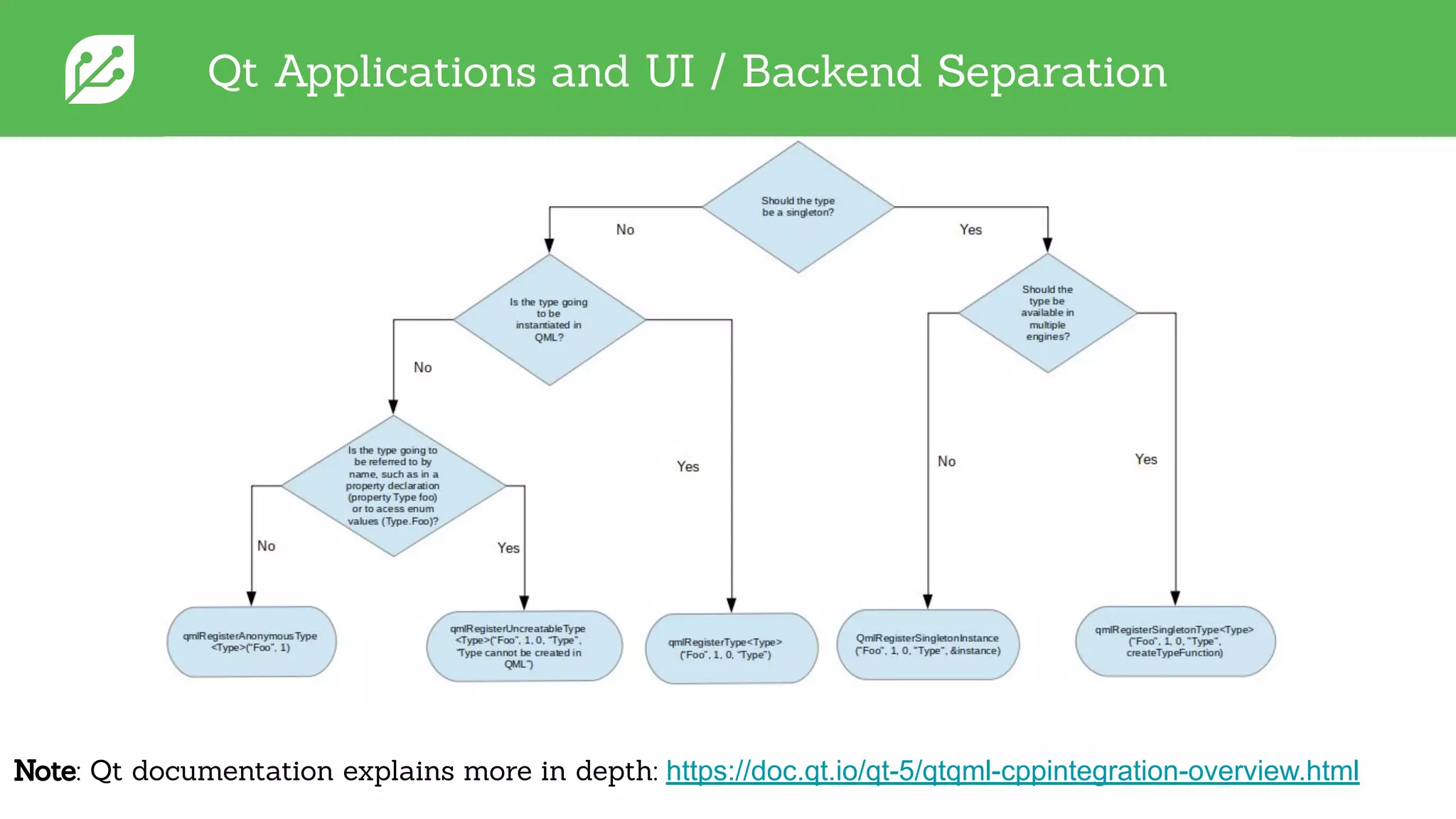
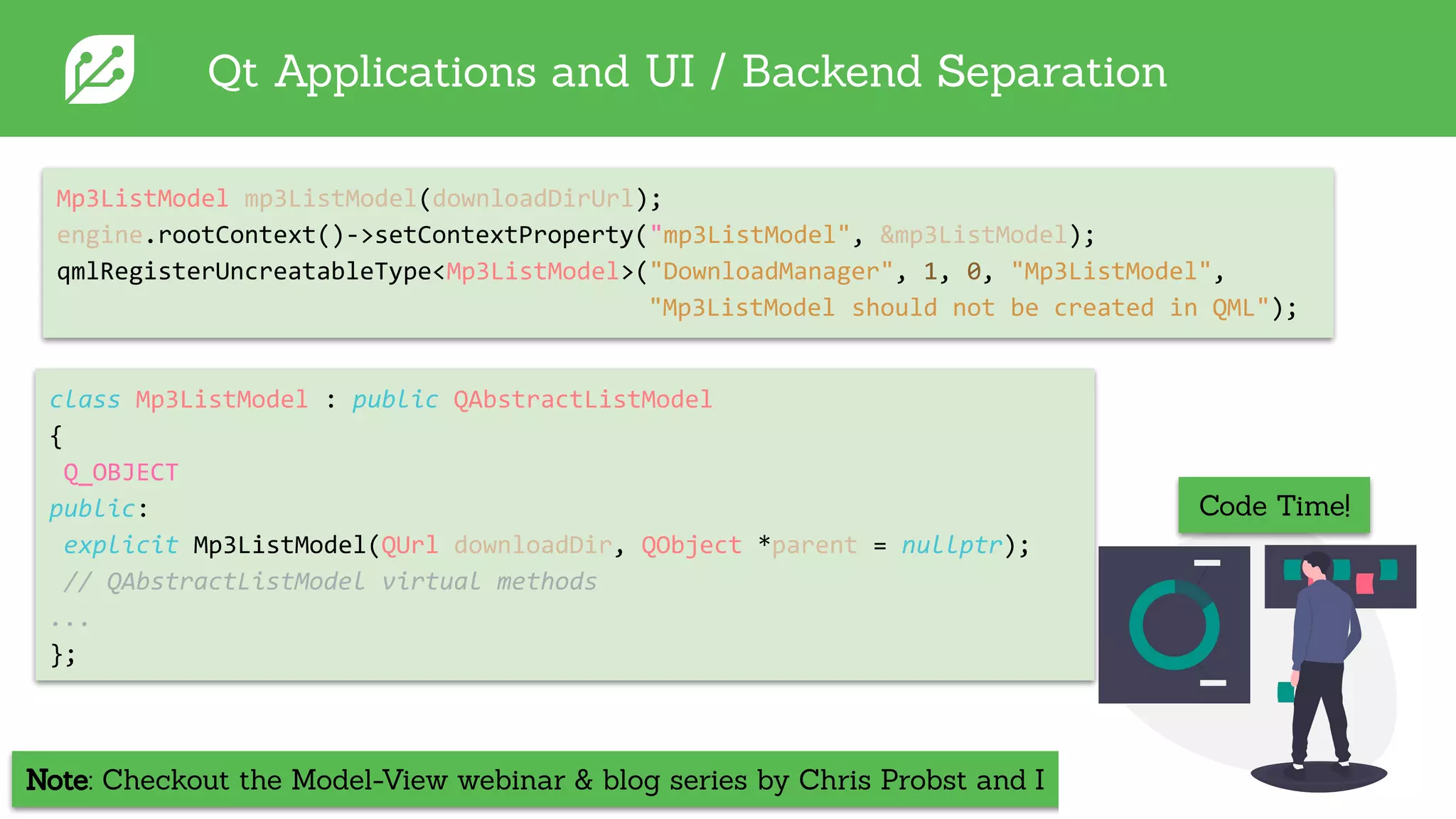
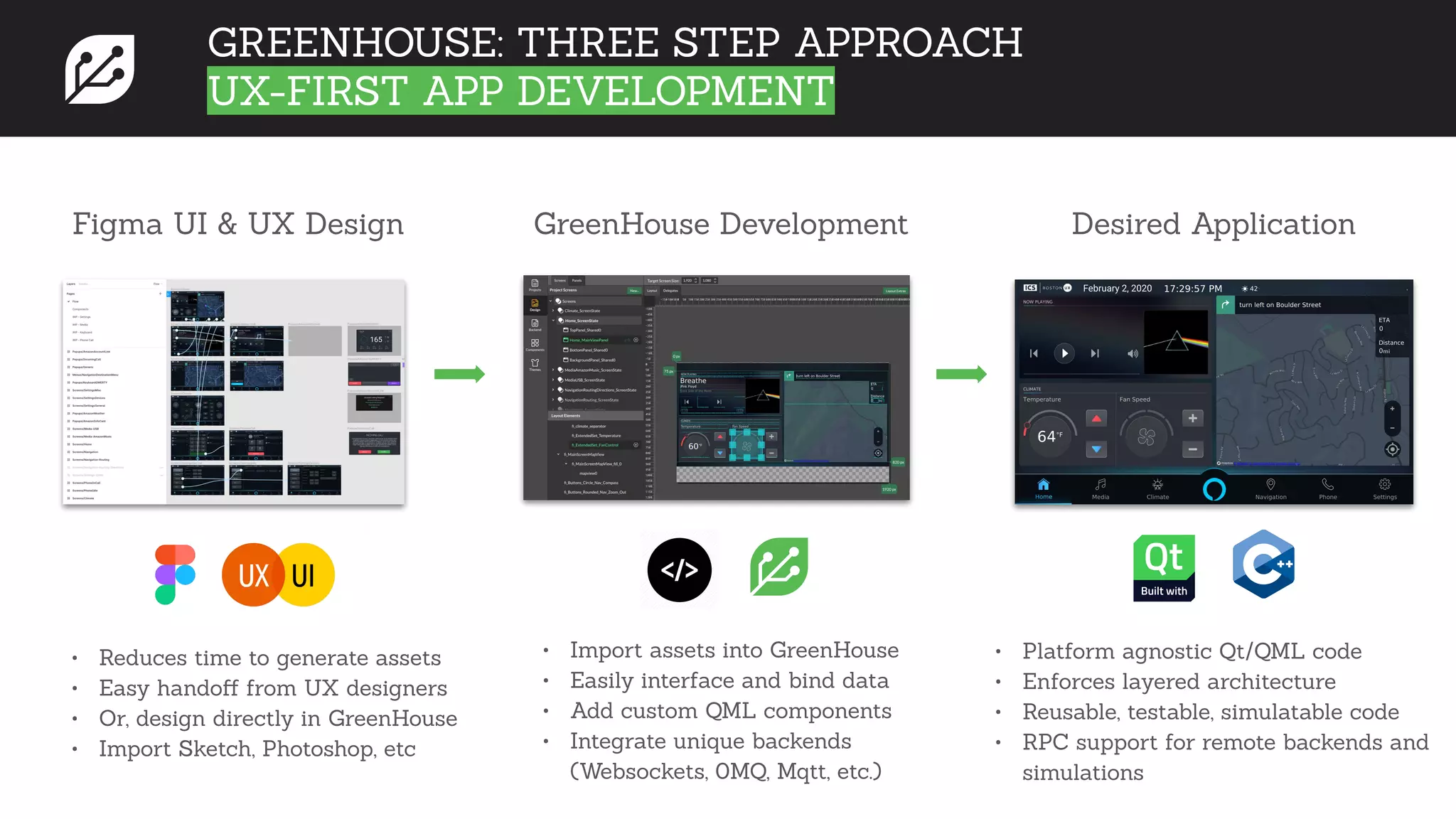
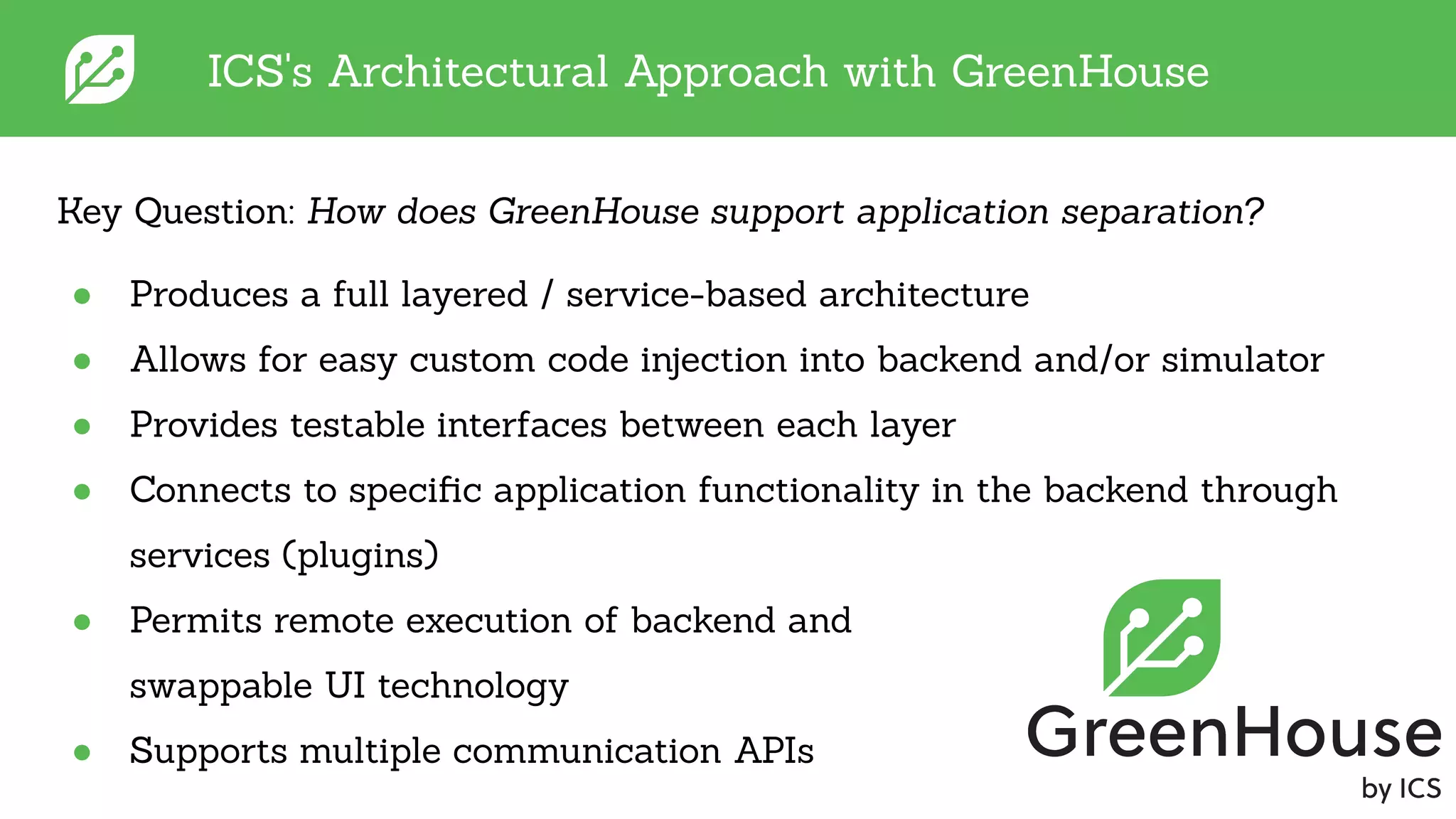
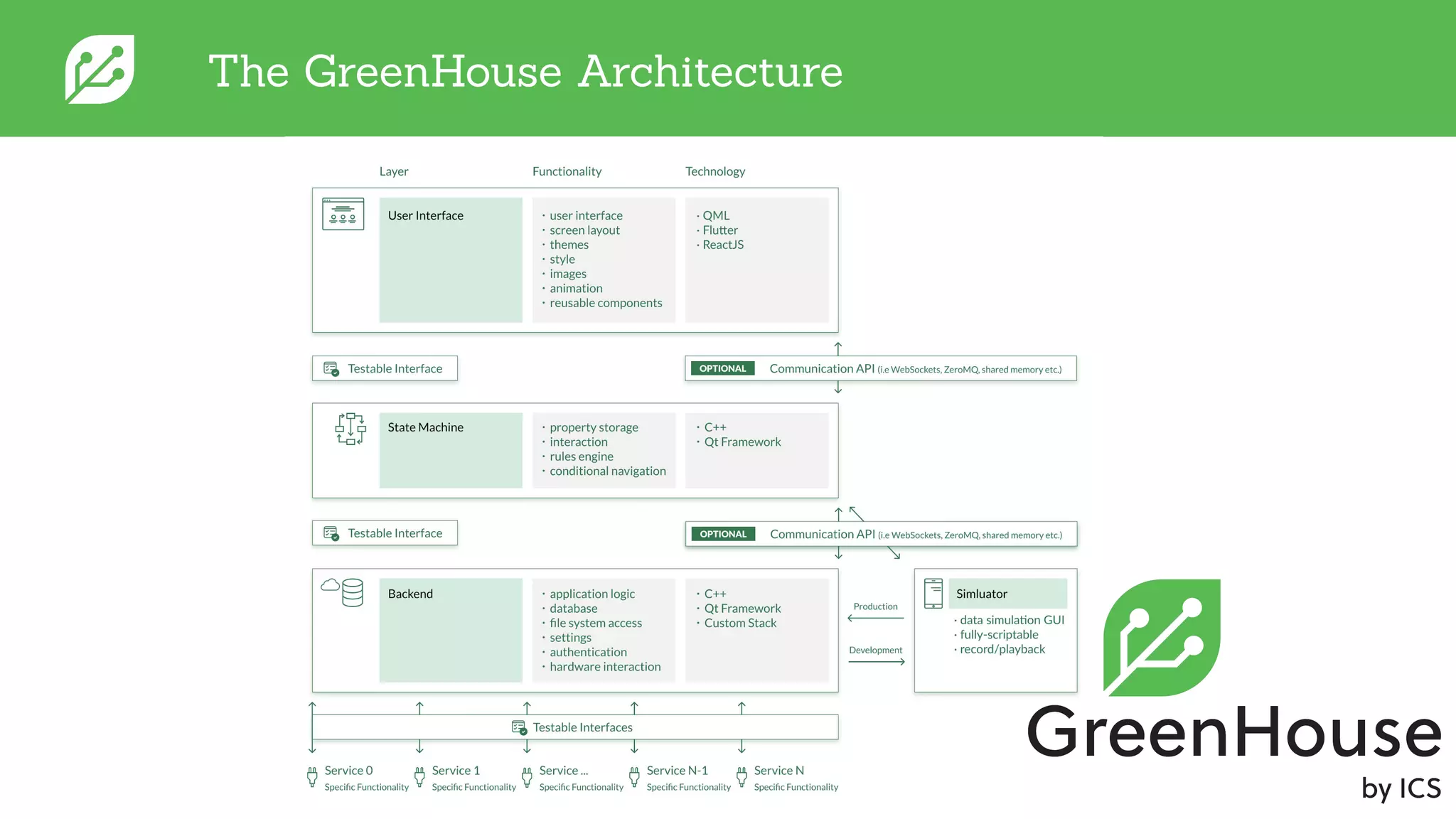
The document discusses software development best practices focusing on the separation of UI from business logic, emphasizing its importance for testability and development efficiency. It introduces Integrated Computer Solutions (ICS) and its architectural approach using Greenhouse, a platform that supports modular application design and facilitates testing and simulation. Key benefits include enhanced parallel development, reduced complexity, and more efficient UX design processes.