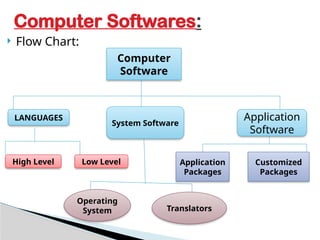
The document provides an overview of software, defining it as a sequence of instructions for computers to perform specific tasks and categorizing it into system software and application software. It explains the differences between low-level and high-level programming languages, along with the roles of translators that convert source programs into machine-readable object programs. Additionally, it distinguishes between general application software and customized packages tailored to specific organizational needs.