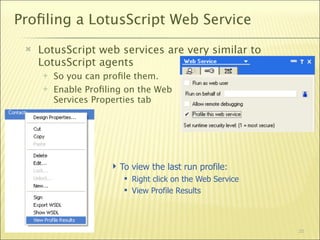
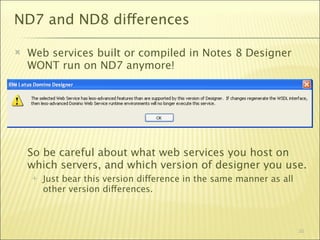
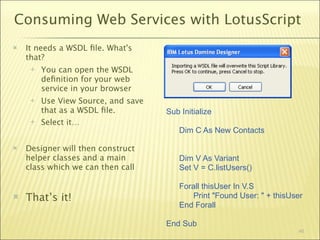
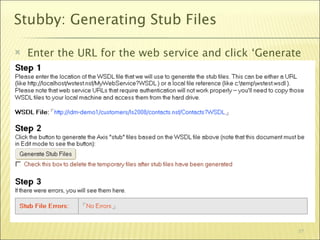
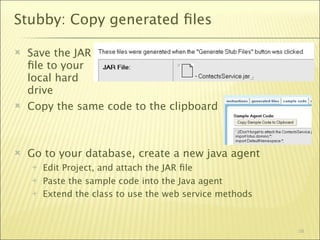
The document outlines a web services bootcamp conducted by Bill Buchan, focusing on using Lotus Domino for web services development and consumption. It covers an overview of web services, methodologies for creating services with Lotusscript in Domino versions 7 and 8, and how to consume these services using different approaches. The presentation includes demonstrations, examples, and best practices for designing, testing, and handling web services, as well as considerations for security, version compatibility, and error management.