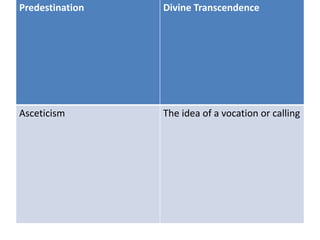
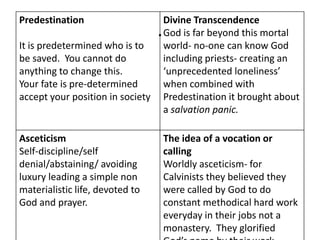
Religion can act as both a conservative and progressive force for social change. While religion often aims to preserve traditional social structures and values, some sociologists argue it has also enabled social change, like Max Weber's view that Calvinism helped bring about modern capitalism. The document discusses different sociological perspectives on how religion maintains the status quo through legitimizing existing power structures, but also provides examples of how religious protest movements in the US, like the Civil Rights Movement, have challenged social inequalities and pushed for progressive reforms.