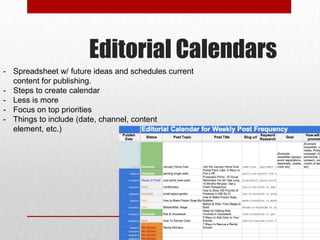
This document discusses processes for content strategy and management. It defines key roles like web editors, content creators, and subject matter experts. Individuals must understand their roles. Content strategy responsibilities can be assigned to a business unit or specific individuals. Content is created, maintained, and evaluated on an ongoing basis. Governance ensures alignment with business goals. Processes are documented in a logical workflow. Clear communication keeps stakeholders informed and involved.