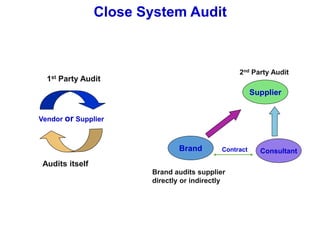
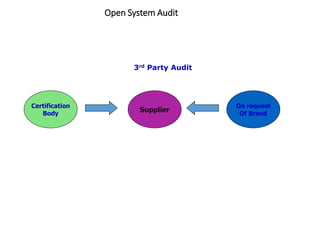
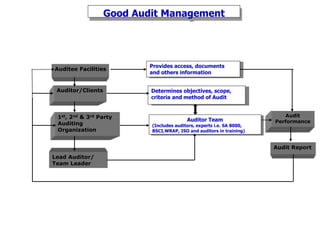
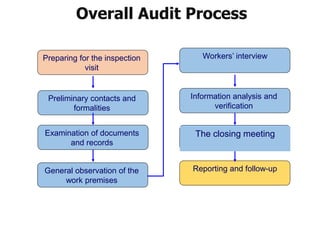
1. The document discusses social compliance audits and codes of conduct audits, outlining key concepts such as the purpose of audits, auditor roles and responsibilities, and audit types and strategies.
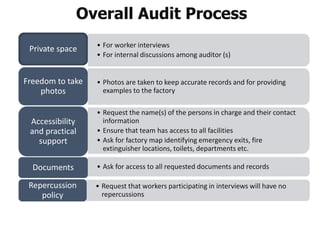
2. It explains that social compliance audits systematically and independently assess facilities against standards to determine if requirements are being met.
3. Effective audits are planned, independent, have management cooperation, and have a compliance orientation to evaluate implementation of standards.