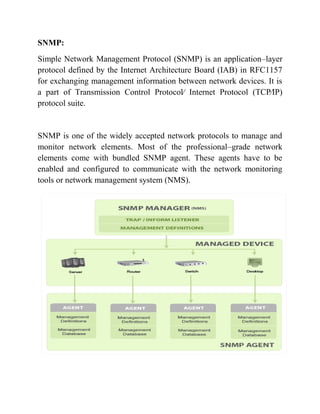
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an application layer protocol used to exchange management information between network devices. SNMP allows a network management system to monitor and control different types of devices on a network such as routers, switches, printers and more. Each network device contains an SNMP agent which collects data from the device and stores it in a Management Information Base (MIB). The SNMP manager can then query the agents to retrieve specific information from their MIBs to monitor network performance and detect issues.