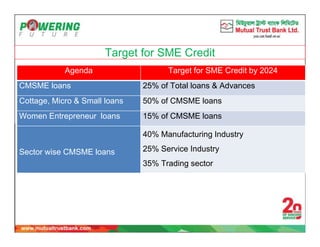
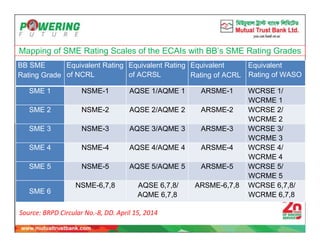
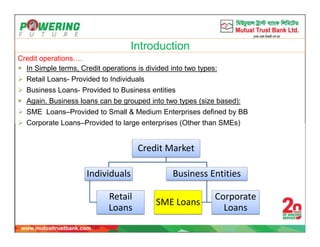
The document discusses small and medium enterprise (SME) financing policies and programs in Bangladesh. It provides an overview of SME credit operations and definitions. The Bangladesh Bank (BB) has introduced several programmes to expand SMEs, including priority lending to small entrepreneurs and women entrepreneurs. BB monitors SME credit disbursement and recovery. Regulations for SME financing include requiring cash flow analysis, personal guarantees, exposure limits, and security requirements that vary based on loan size. The implementation of strategies aims to improve access to finance, technology, markets and training to develop Bangladesh's SME sector.


























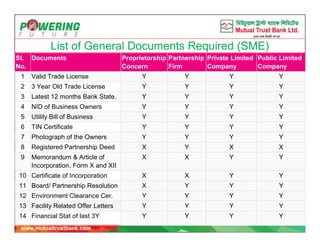
![Definition of CMSME (as per National Industrial Policy, 2016)
Industry/
Enterprise
Industry/
Enterprise
Type
Fixed Assets
(Excluding Land
& Building)
[Million]
Employees Annual
Turnover
[ Million]
Loan
Limit
[Million]
Product
Cottage - Less than 1.00 15 Max - 1.50 Property Loan
Purpose: To purchase/
construct/renovate
house/Flat/commercial
space
Term loan
Purpose: For expansion
of business,
procurement of
machinery and other
fixed assets, seasonal
requirement, any valid
business requirement
Cash Credit
Purpose : For Working
capital requirement
Micro
Manufacturing 1.00 - 7.50 16-30 or less - 10.00
Service Less than 1.00 15 Max - 2.50
Small
Manufacturing 7.50-150.00 31-120 - 200.00
Service 1.00-20.00 16-50 - 50.00
Medium
Manufacturing 150.00 - 500.00
121-300
(Garments
1,000 Max) - 750.00
Service 20.00-300.00 51-120 - 500.00
Business/
Trading
Sector
Micro
Enterprise Less than 1.00 15 Max
20.00
max 5.00
Small
Enterprise 1.00-20.00 16-50
20.00
Min -
200.00
Max 50.00](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smefinancing-200429141311/85/SME-Financing-28-320.jpg)