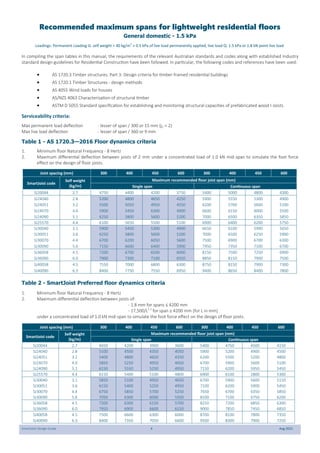
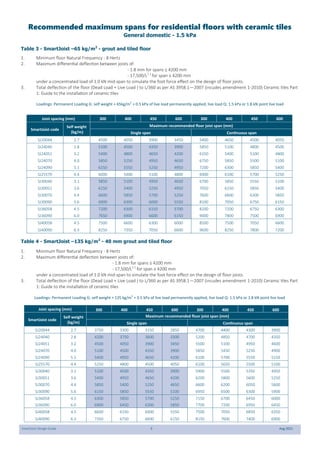
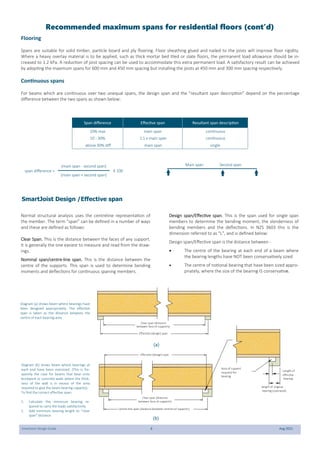
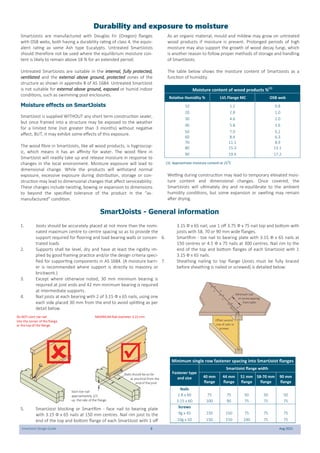
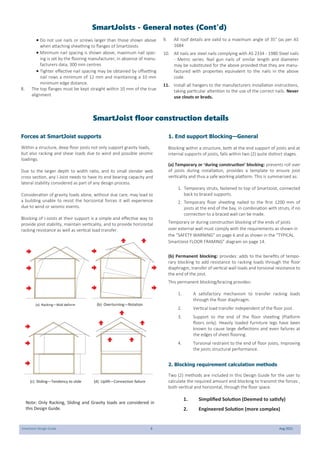
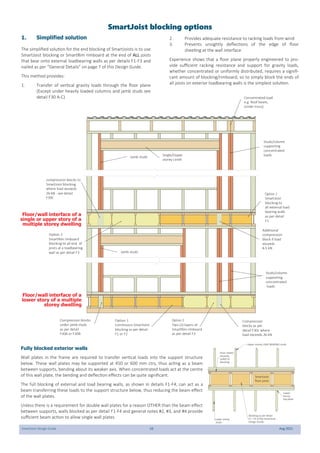
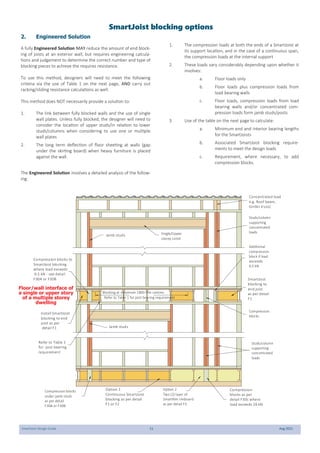
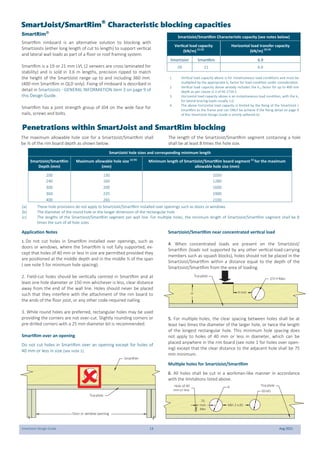
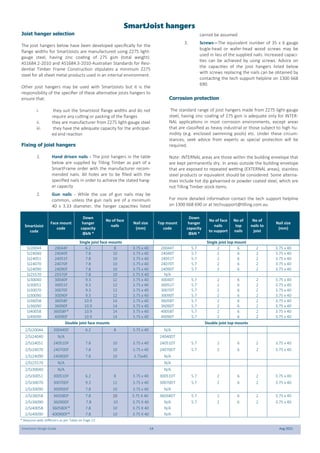
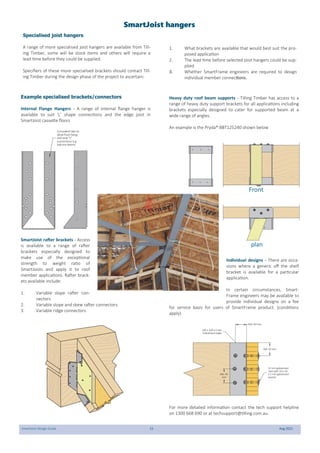
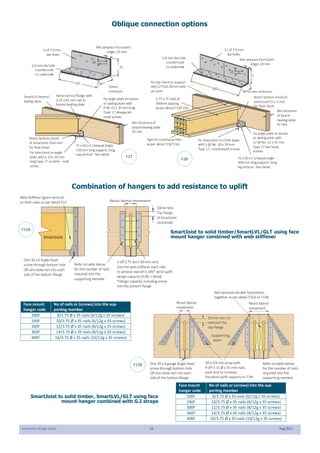
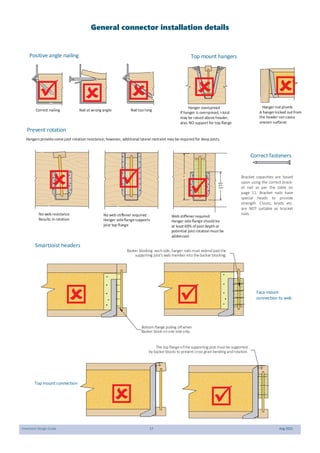
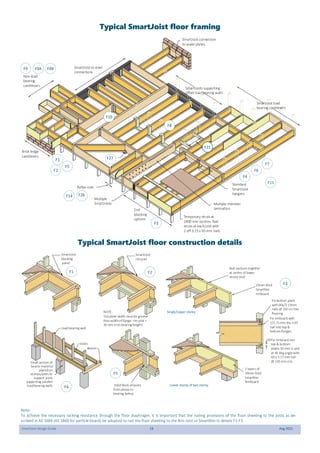
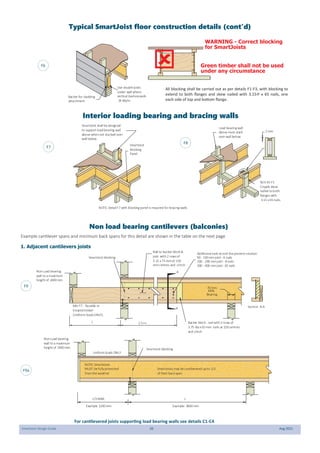
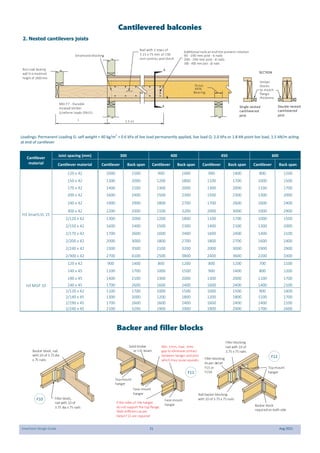
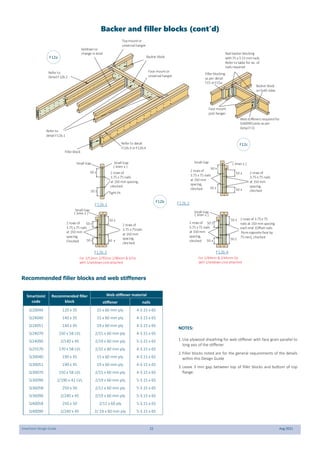
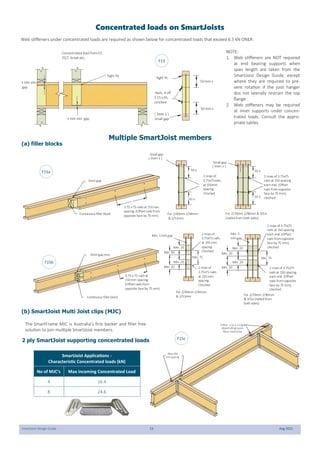
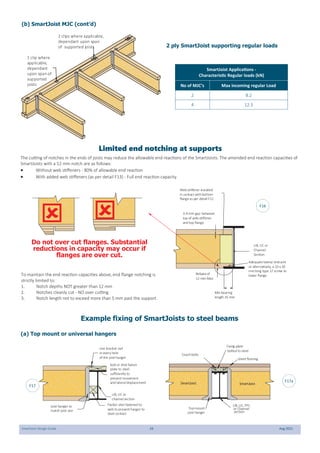
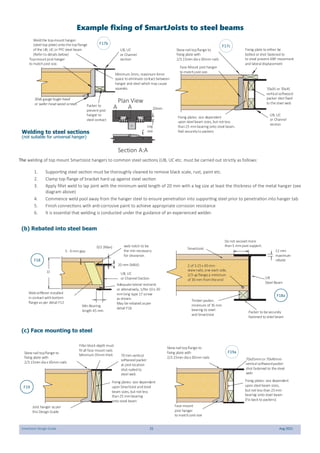
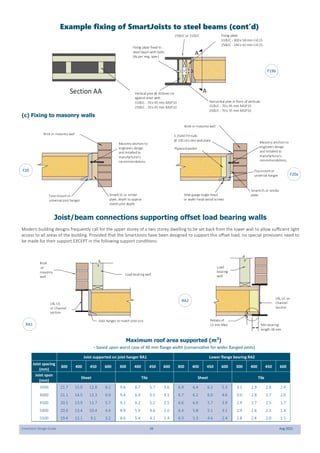
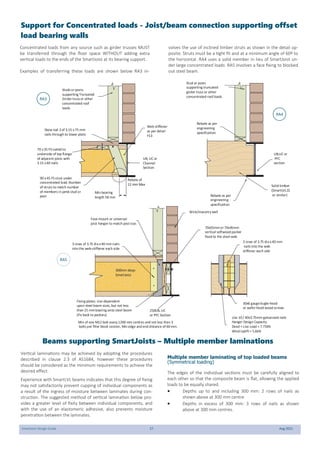
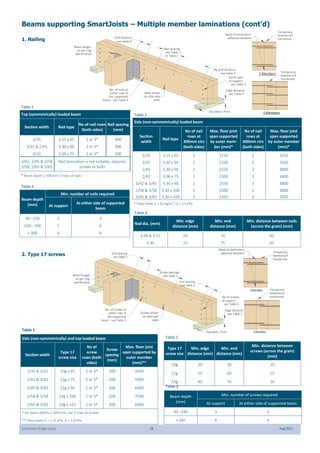
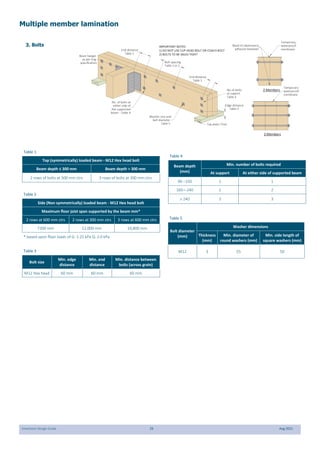
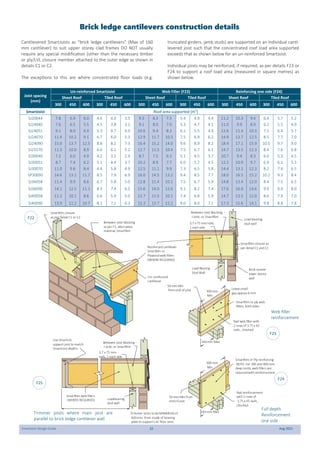
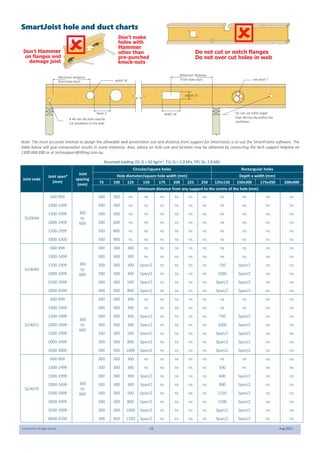
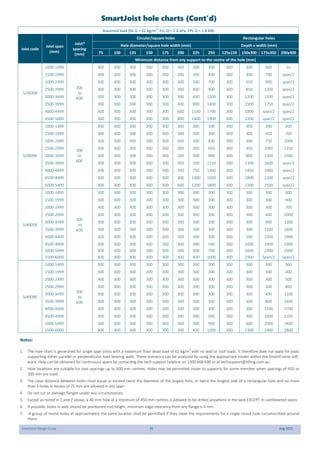
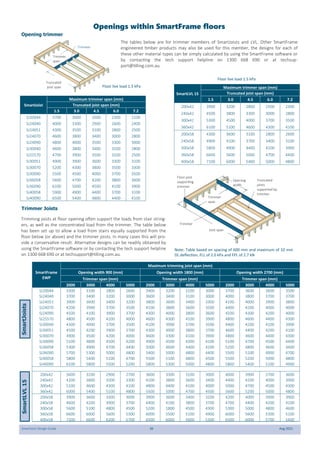
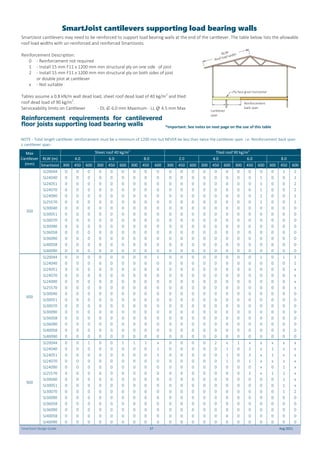
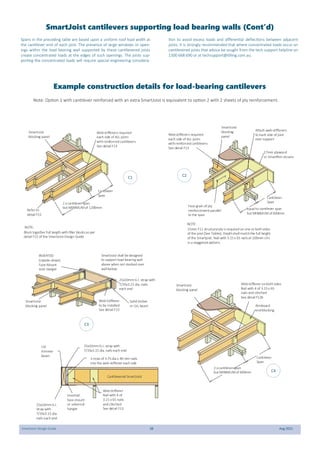
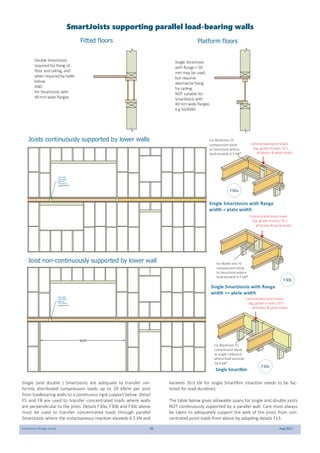
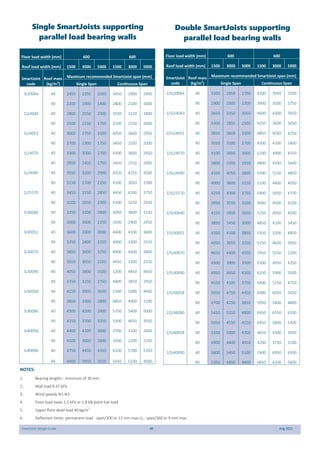
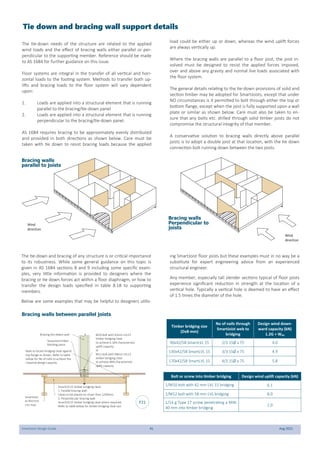
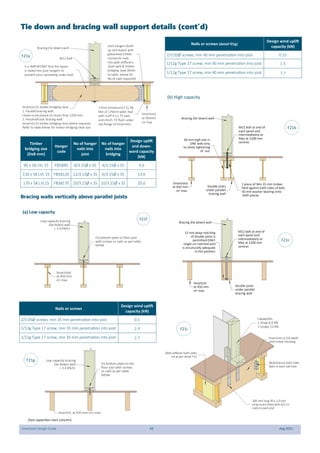
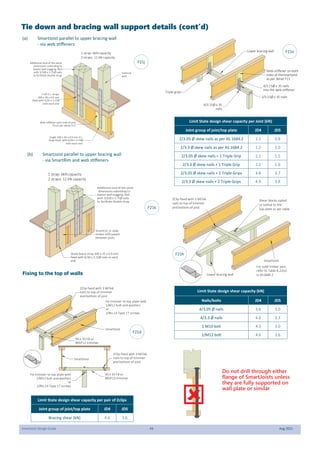
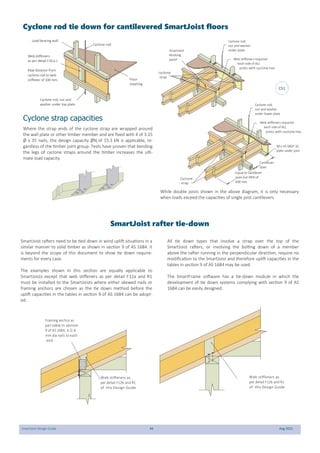
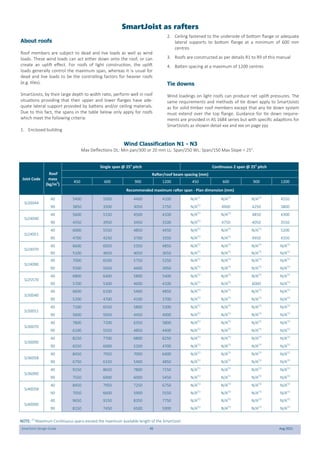
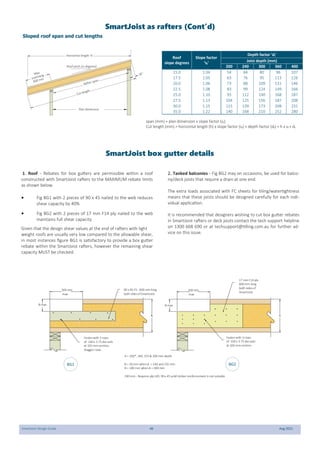
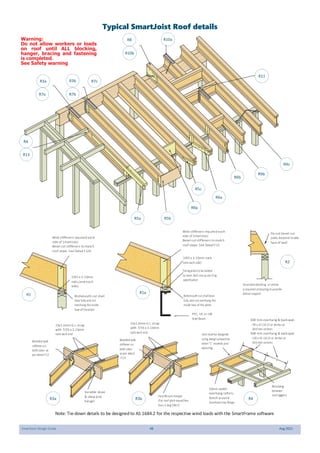
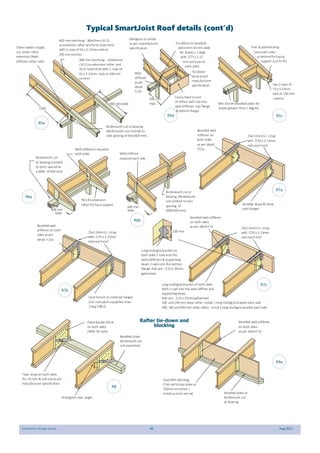
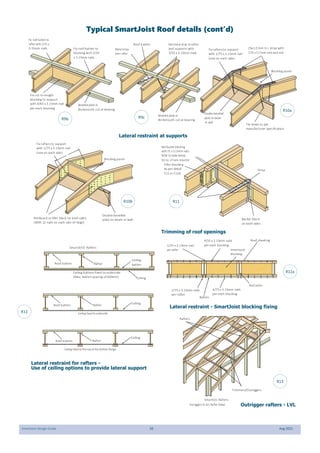
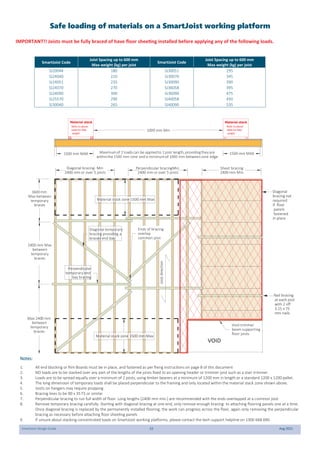
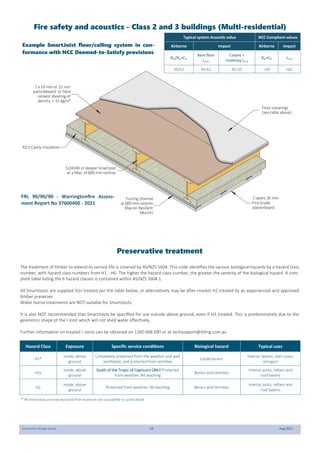
This document provides design guidelines and specifications for SmartJoist engineered wood floor joists. It includes tables with maximum recommended joist spans for different wood depths and spacing under various loading conditions. It also provides details on joist installation, blocking, penetrations, connections, and floor construction. The guidelines are intended to help designers and builders properly select and install SmartJoists to meet building code requirements for strength, stiffness, and floor performance.