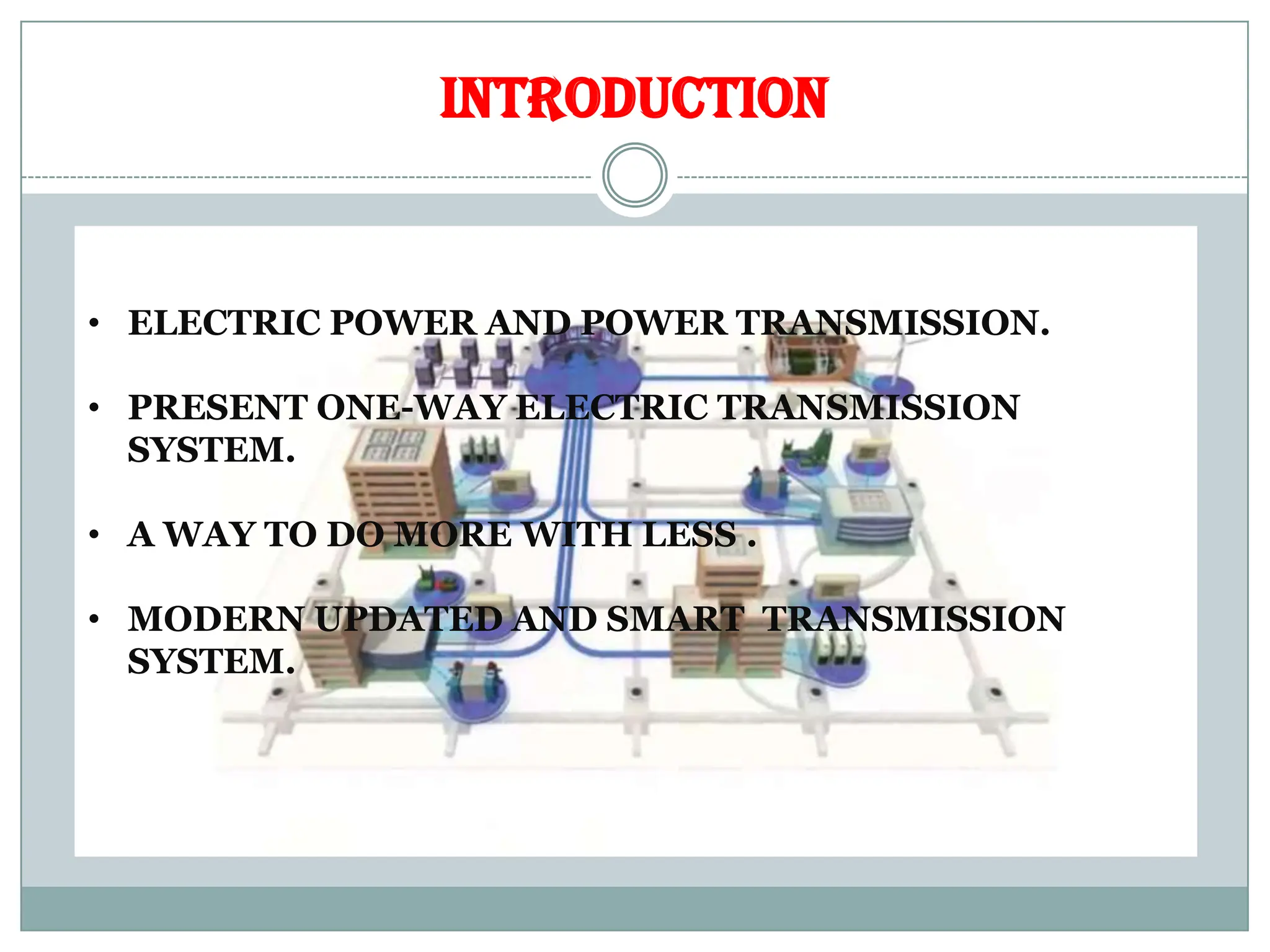
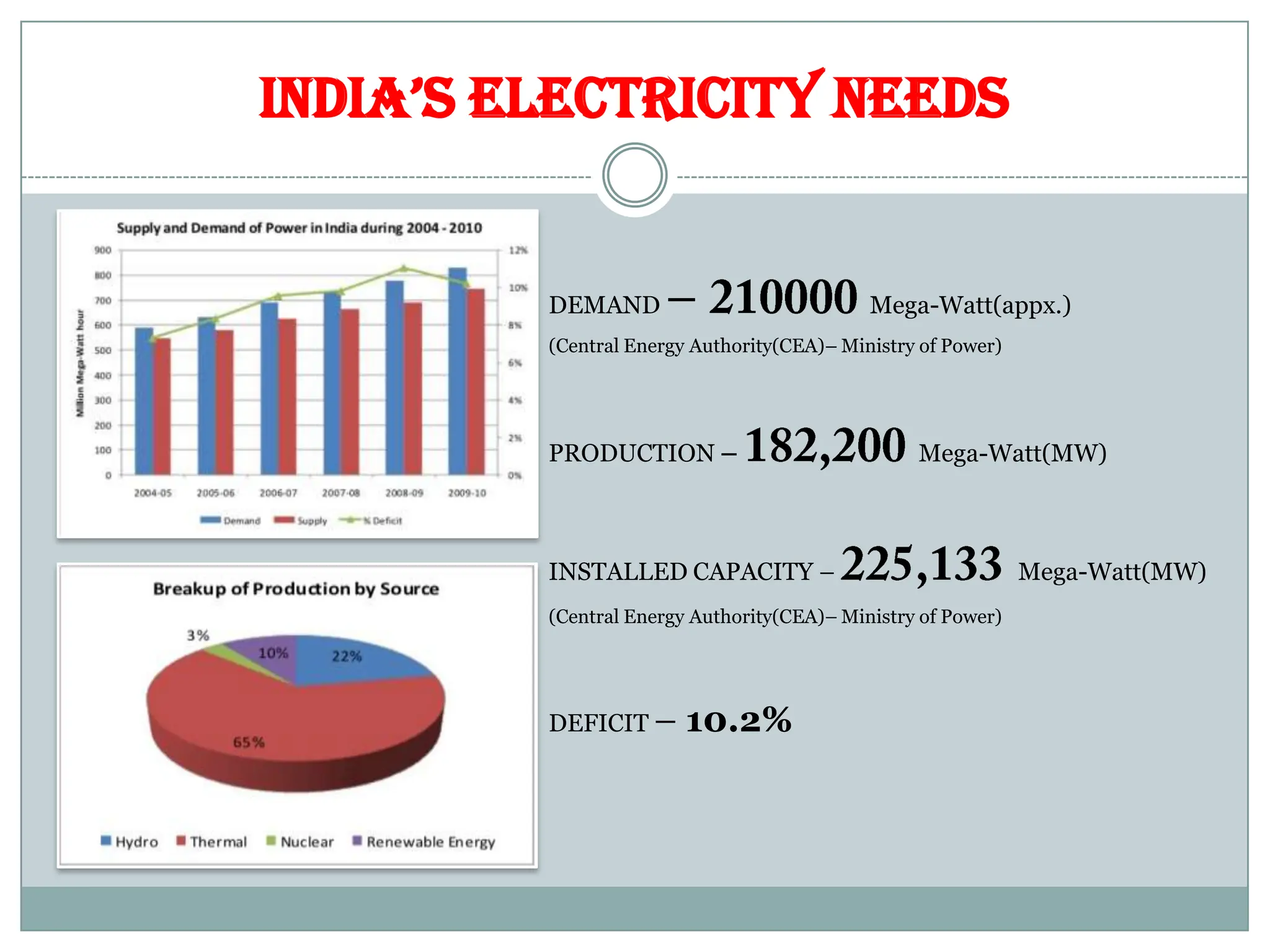
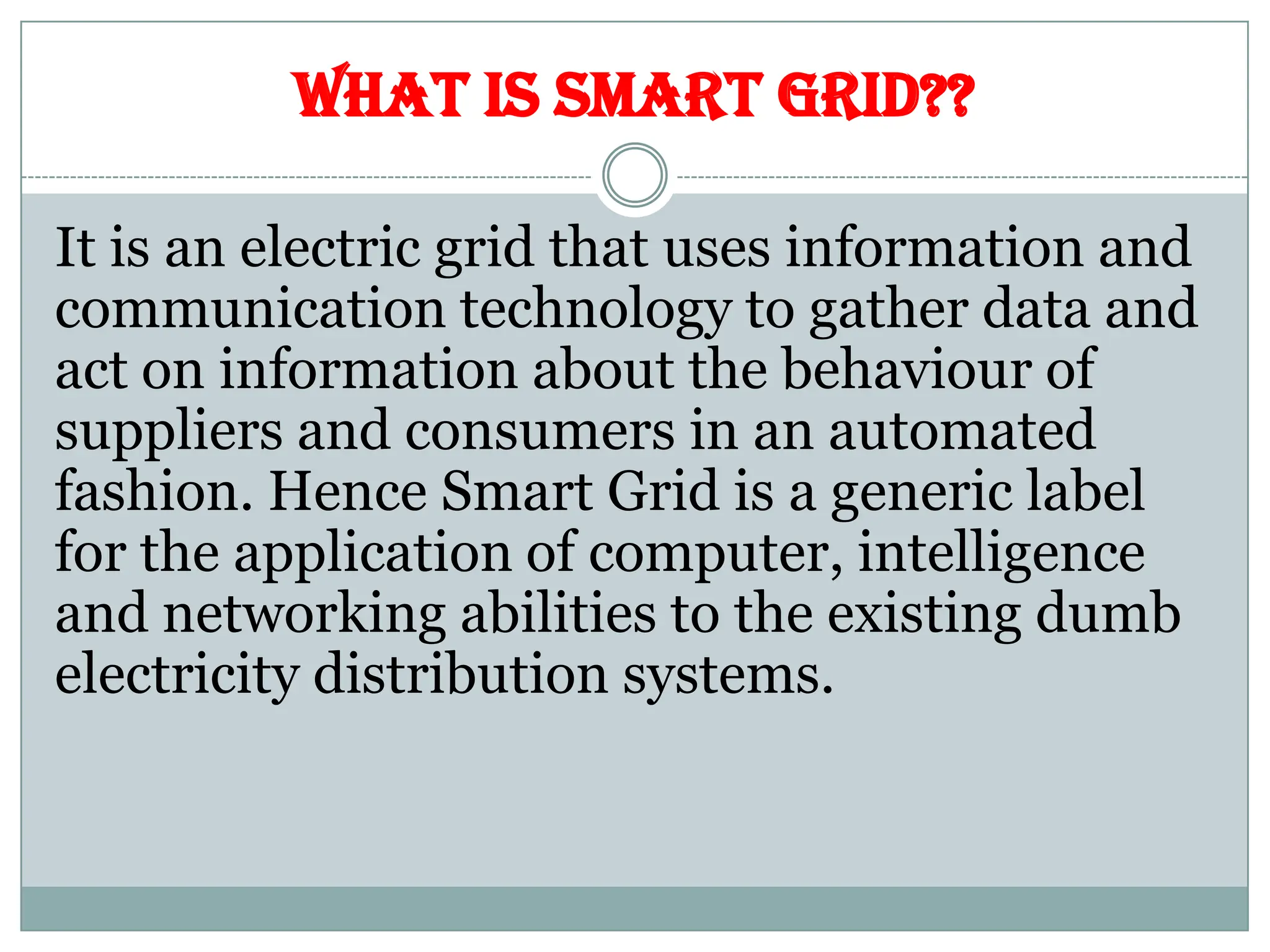
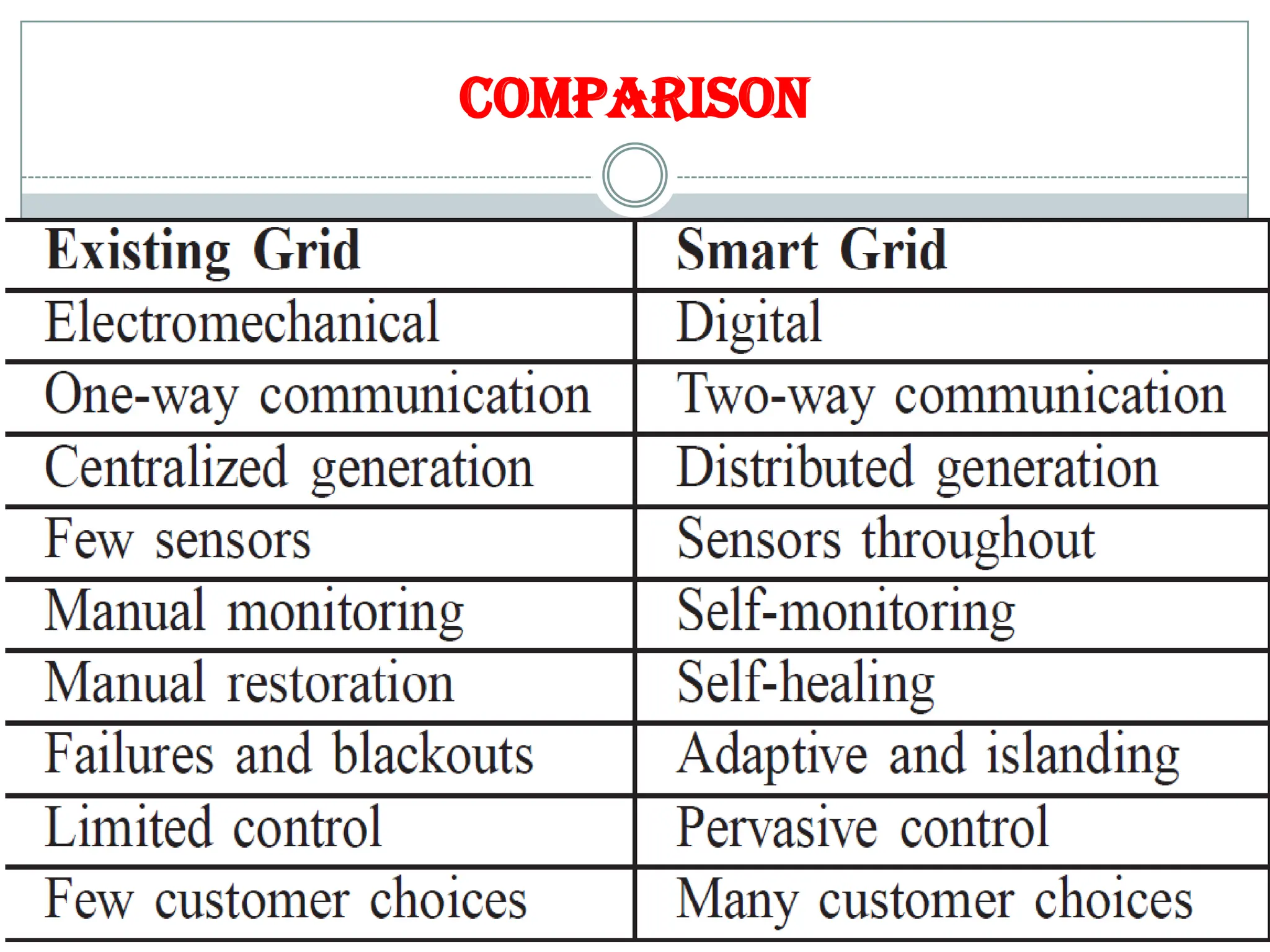
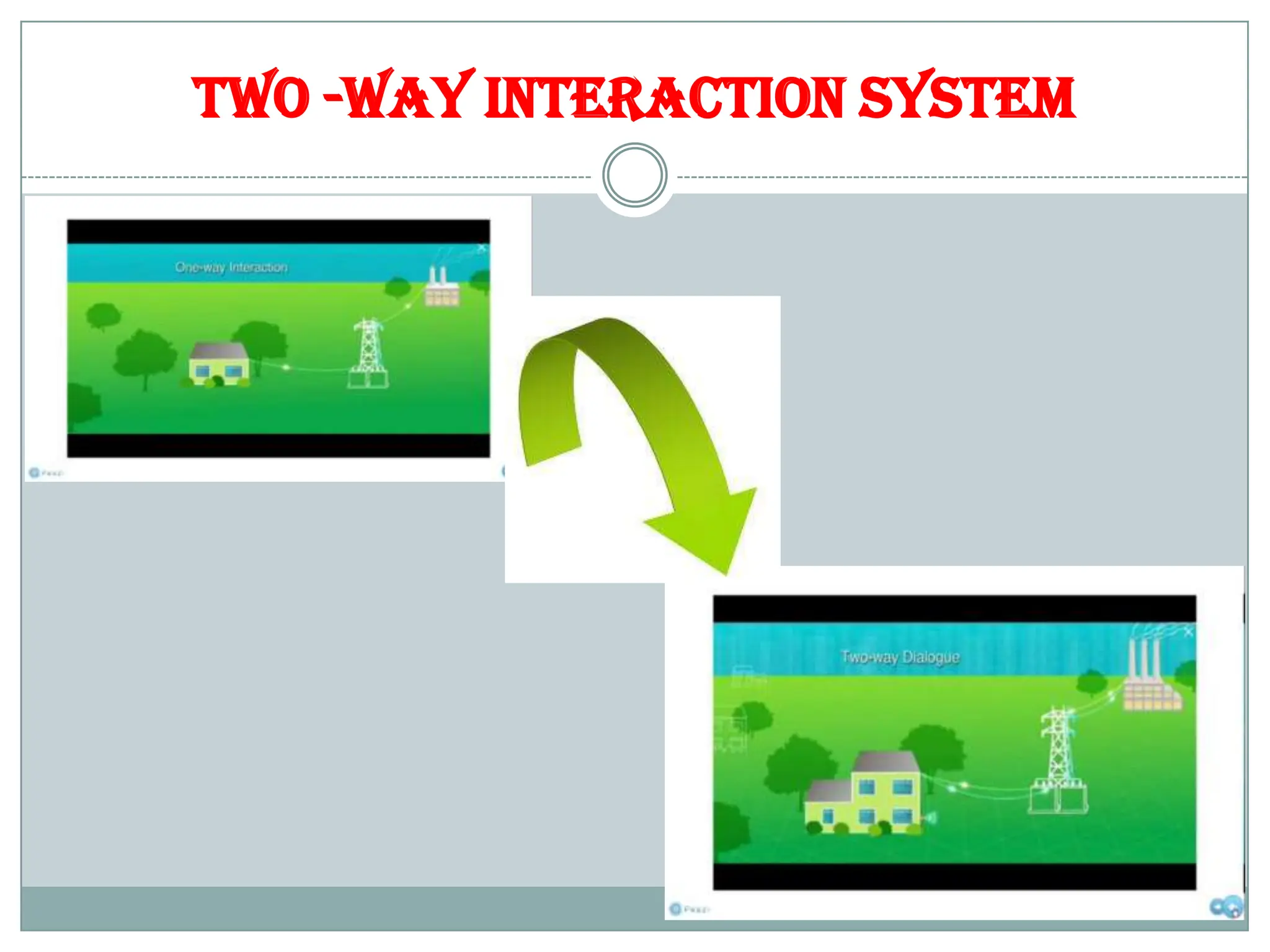
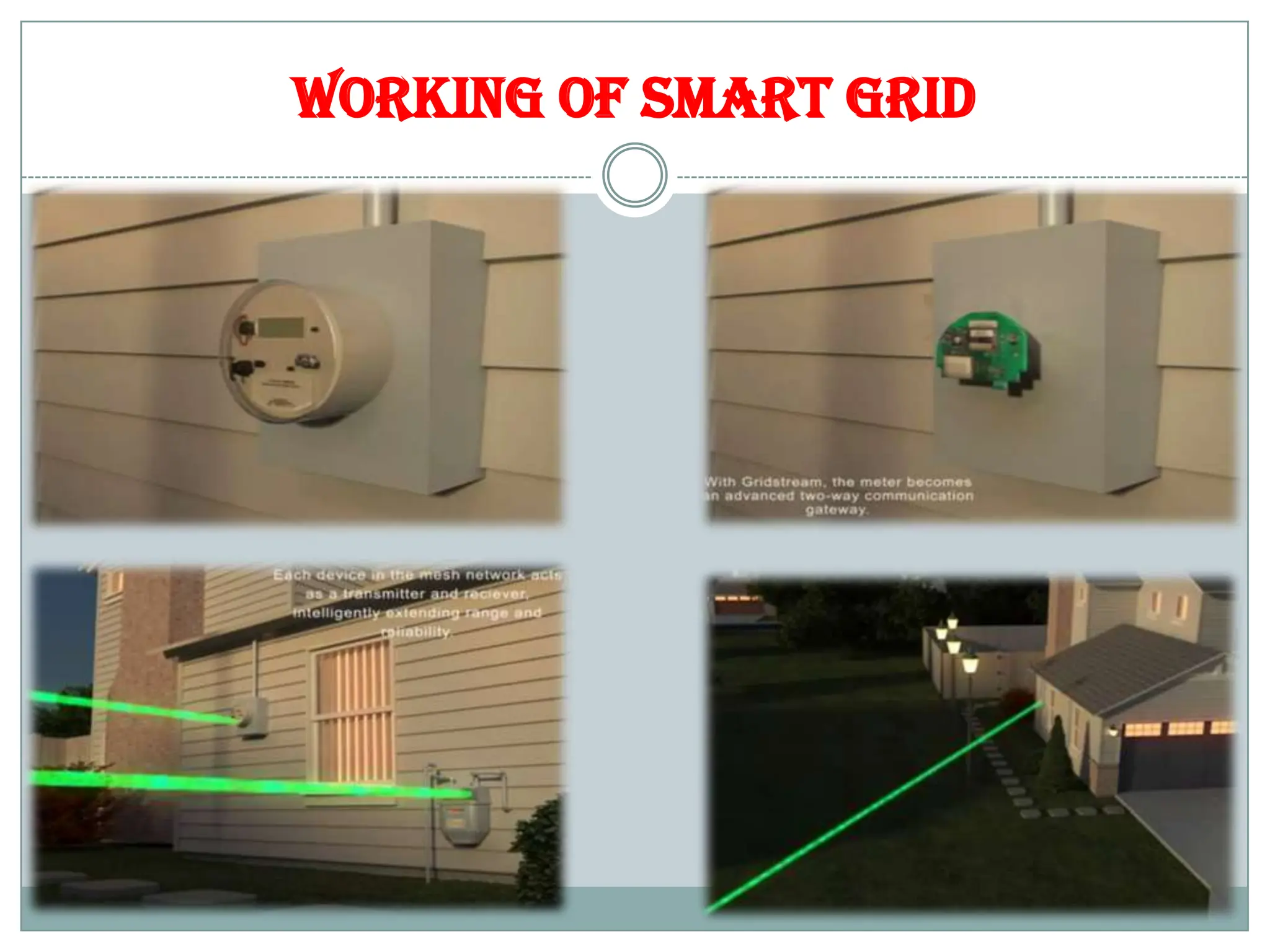
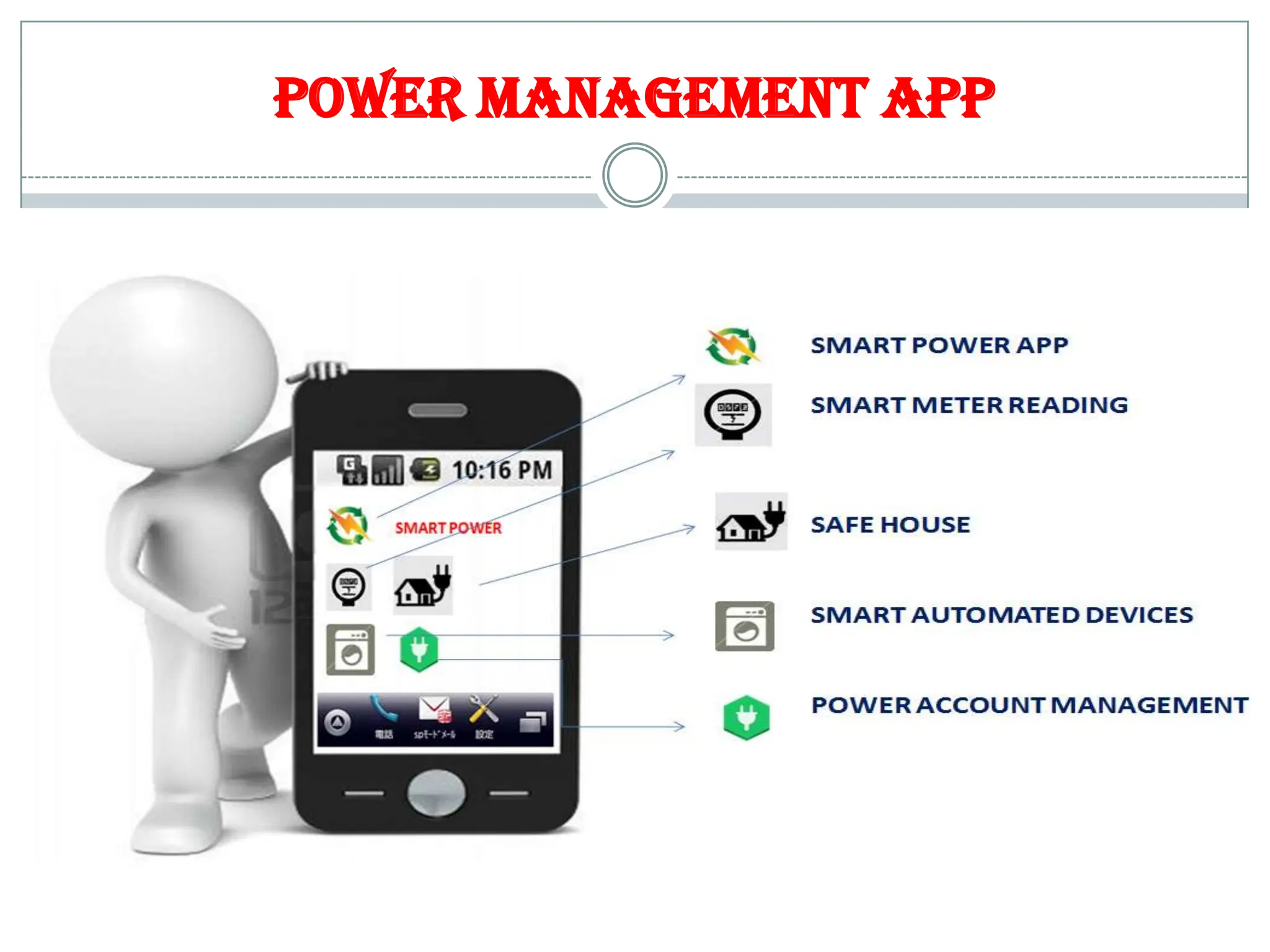
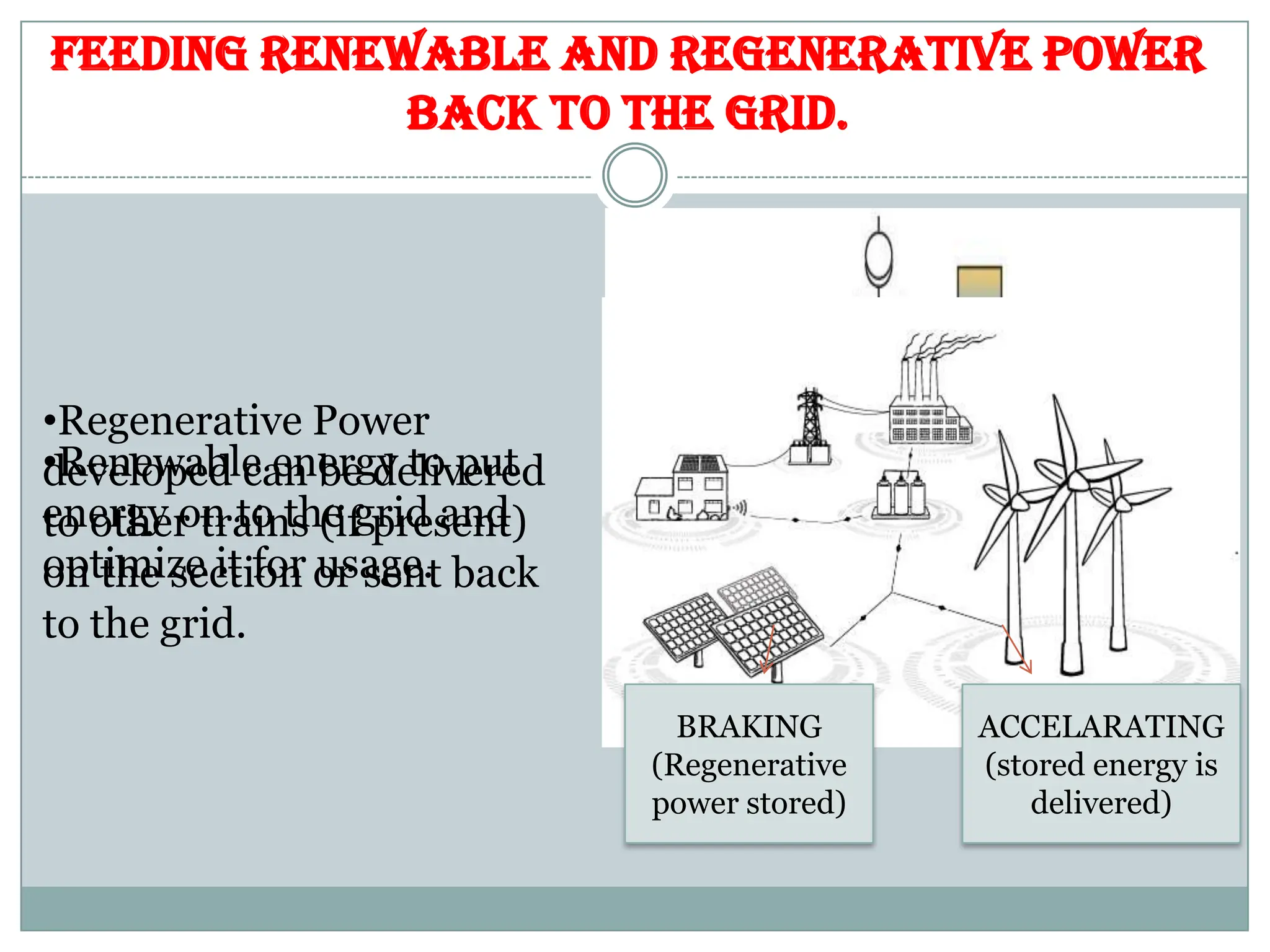
The document outlines the concept of smart grid technology, which transforms traditional one-way electricity transmission systems into interactive networks utilizing information and communication technology for improved efficiency and management. It discusses the components of smart grids, such as smart meters and distributed generation, and emphasizes their benefits, including reduced carbon footprints and automated controls. The agenda highlights advancements in electrical infrastructure and the potential for new technologies in household and power management.