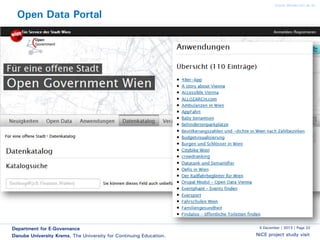
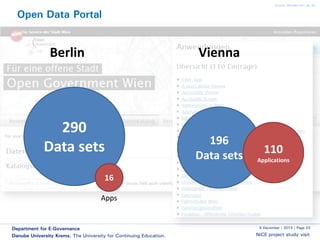
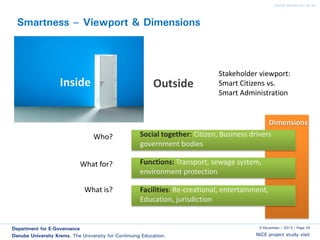
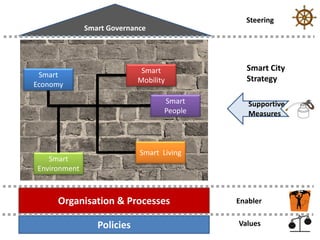
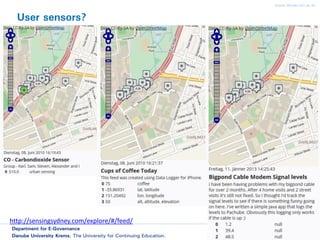
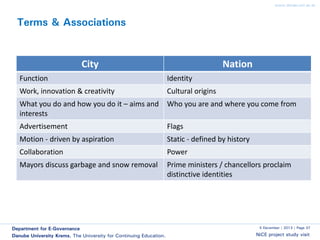
The document discusses smart cities and smart ICT. It describes the Center for E-Governance at Danube University Krems and their research projects related to government processes, stakeholders, and ICT. Their projects include work with the City of Vienna on open government and open data, and with the Austrian Chancellery on e-democracy, open government data standards, and the workplace of the future.