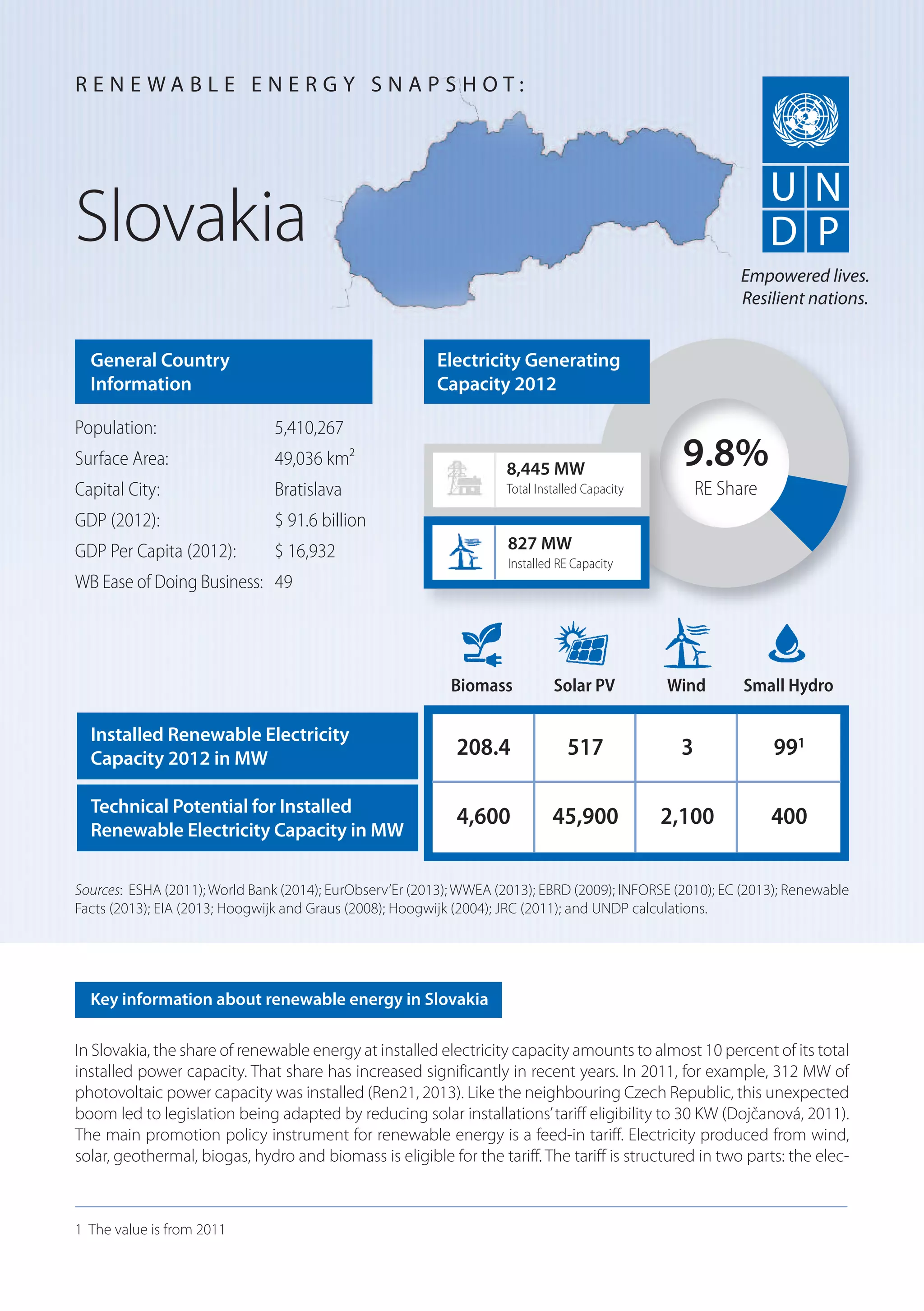
In Slovakia, renewable energy accounts for almost 10% of total installed electricity capacity. Solar PV capacity increased significantly in recent years, reaching 312 MW installed in 2011, until legislation reduced tariff eligibility for solar installations to 30 kW. The main policy support for renewable energy is a feed-in tariff program that pays a premium price for electricity generated from wind, solar, geothermal, biomass, hydro, and biomass. The tariff is structured in two parts and applies for 15 years except for installations under 1 MW which receive the tariff for their lifetime.