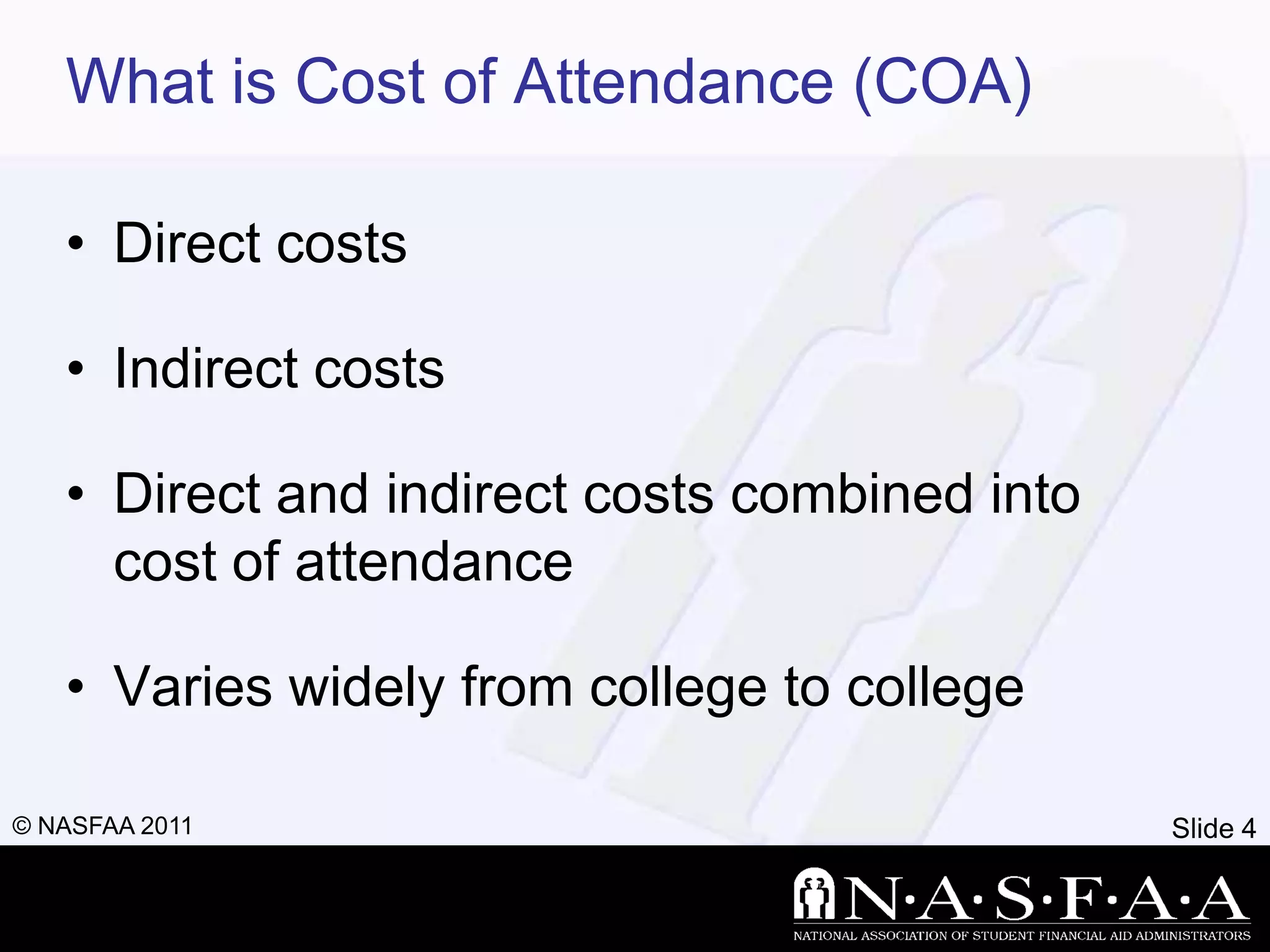
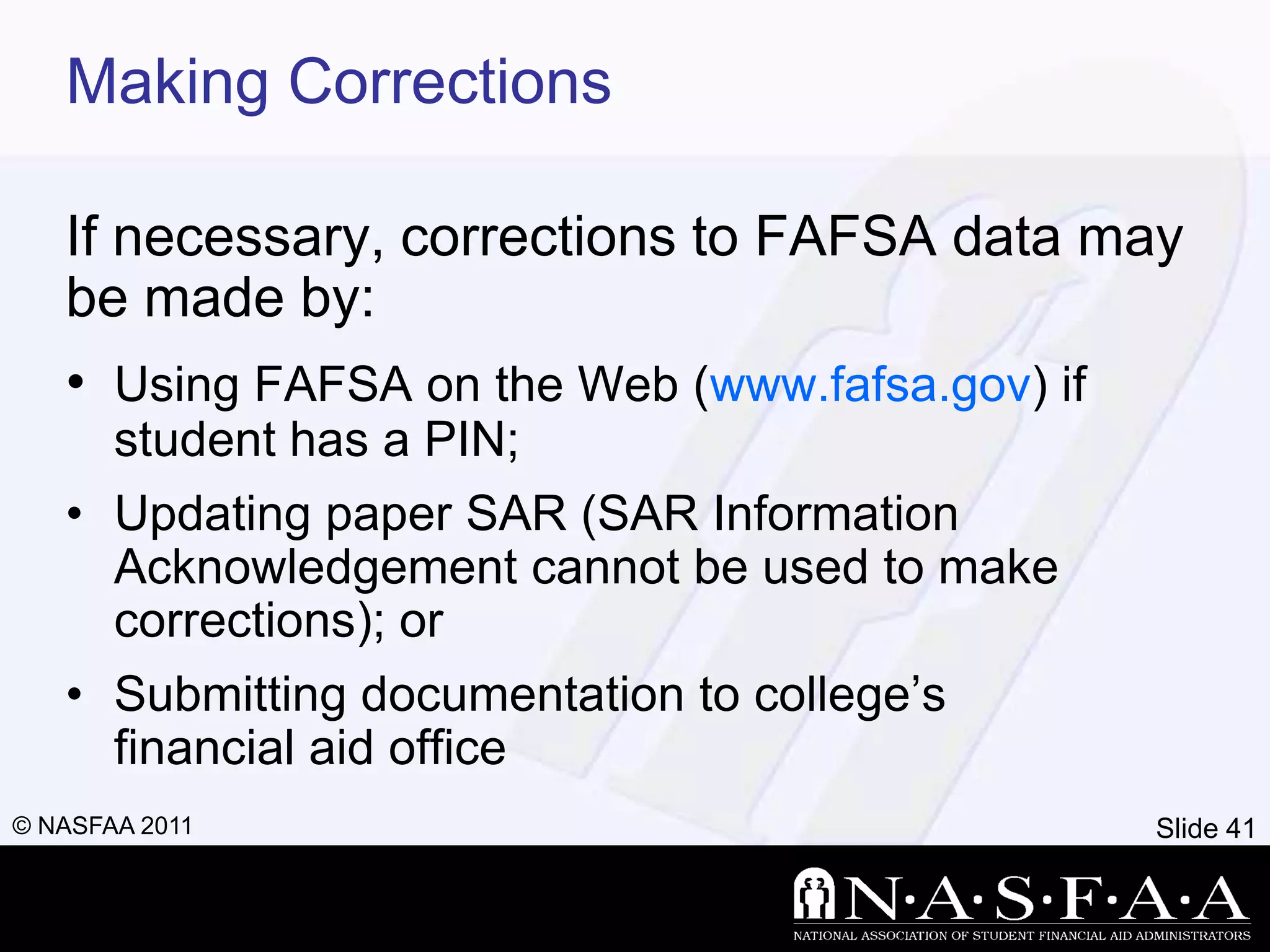
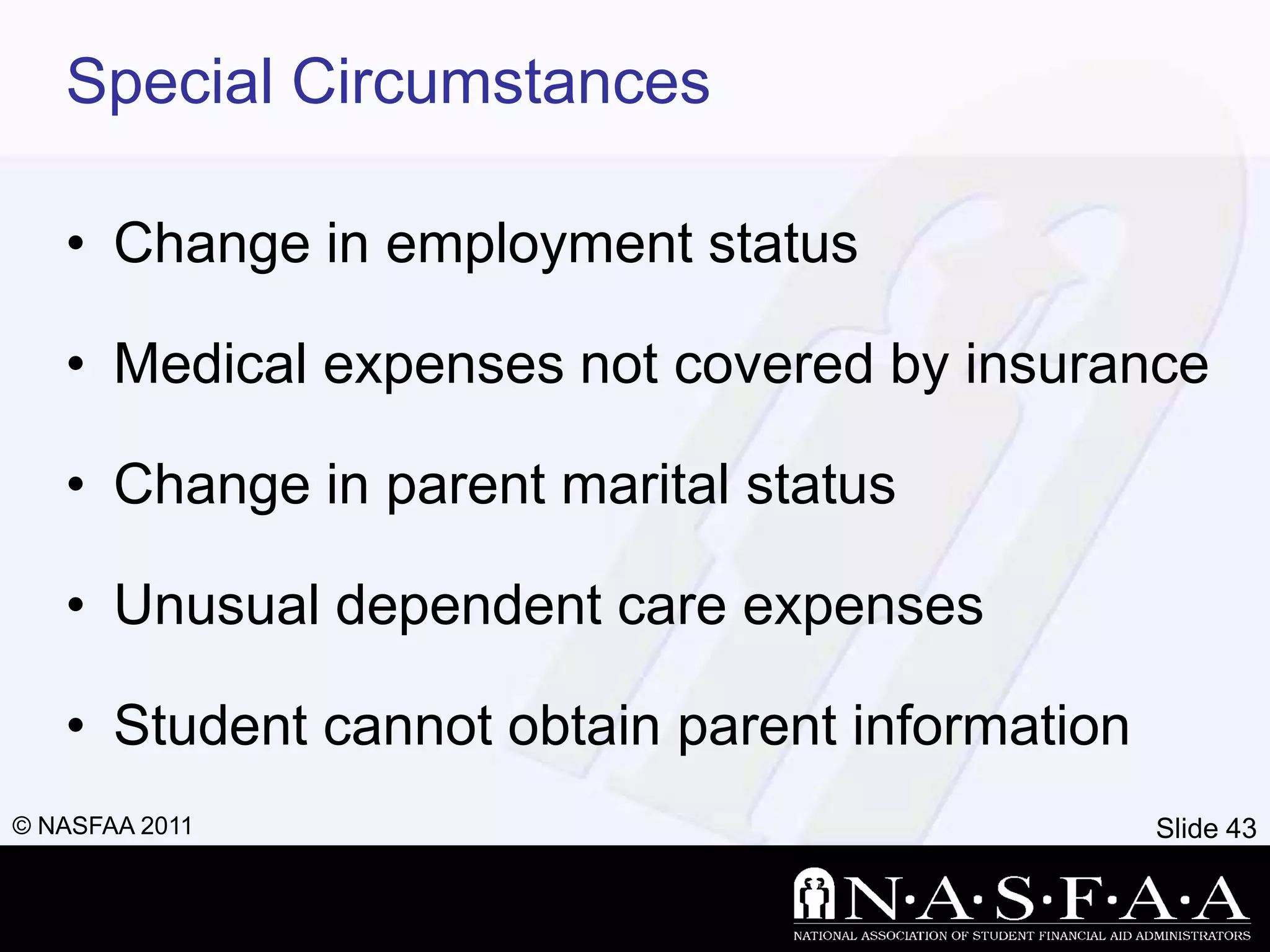
1) The document discusses financial aid, including what it is, how eligibility is determined, and the types and sources available.
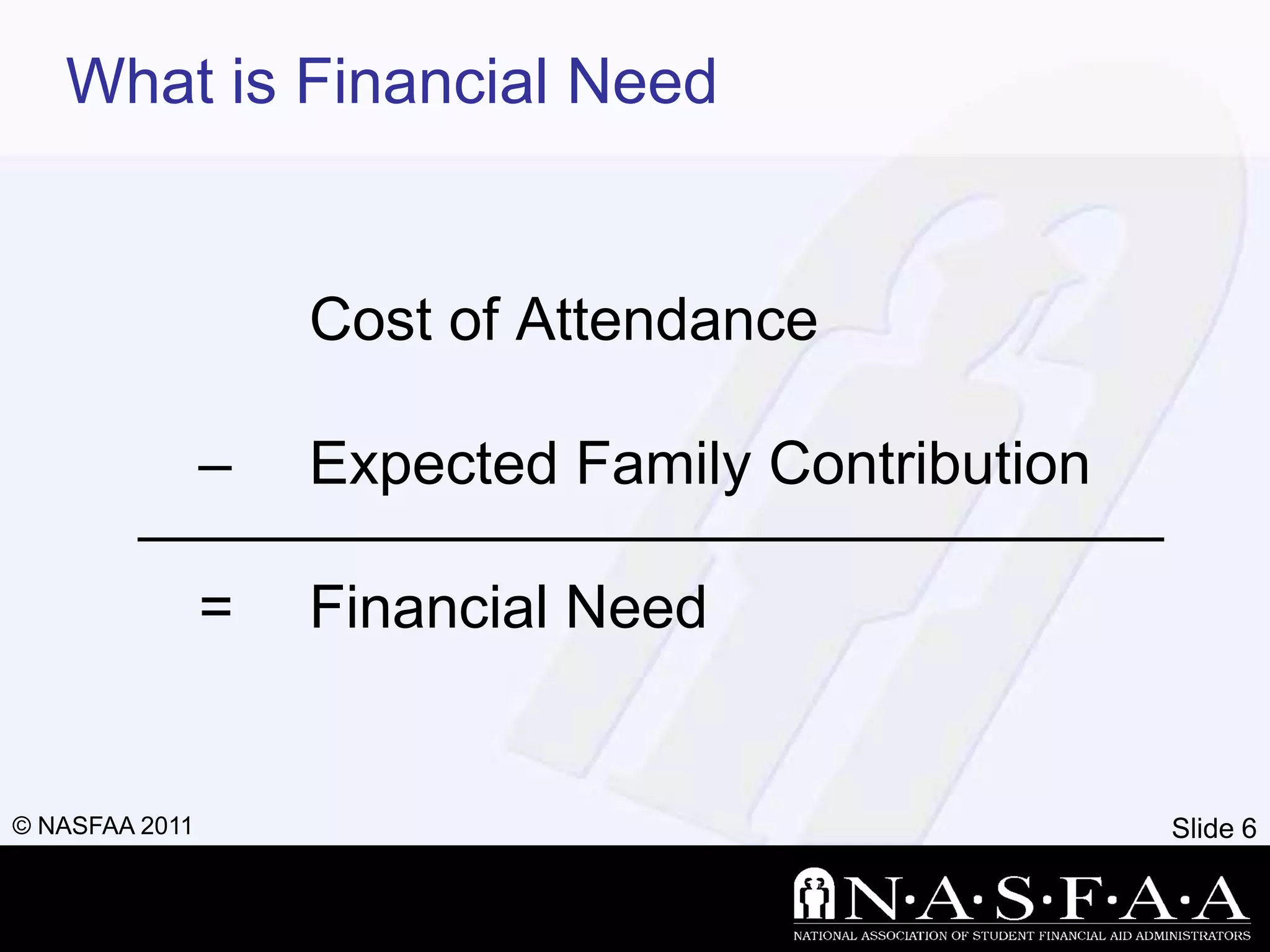
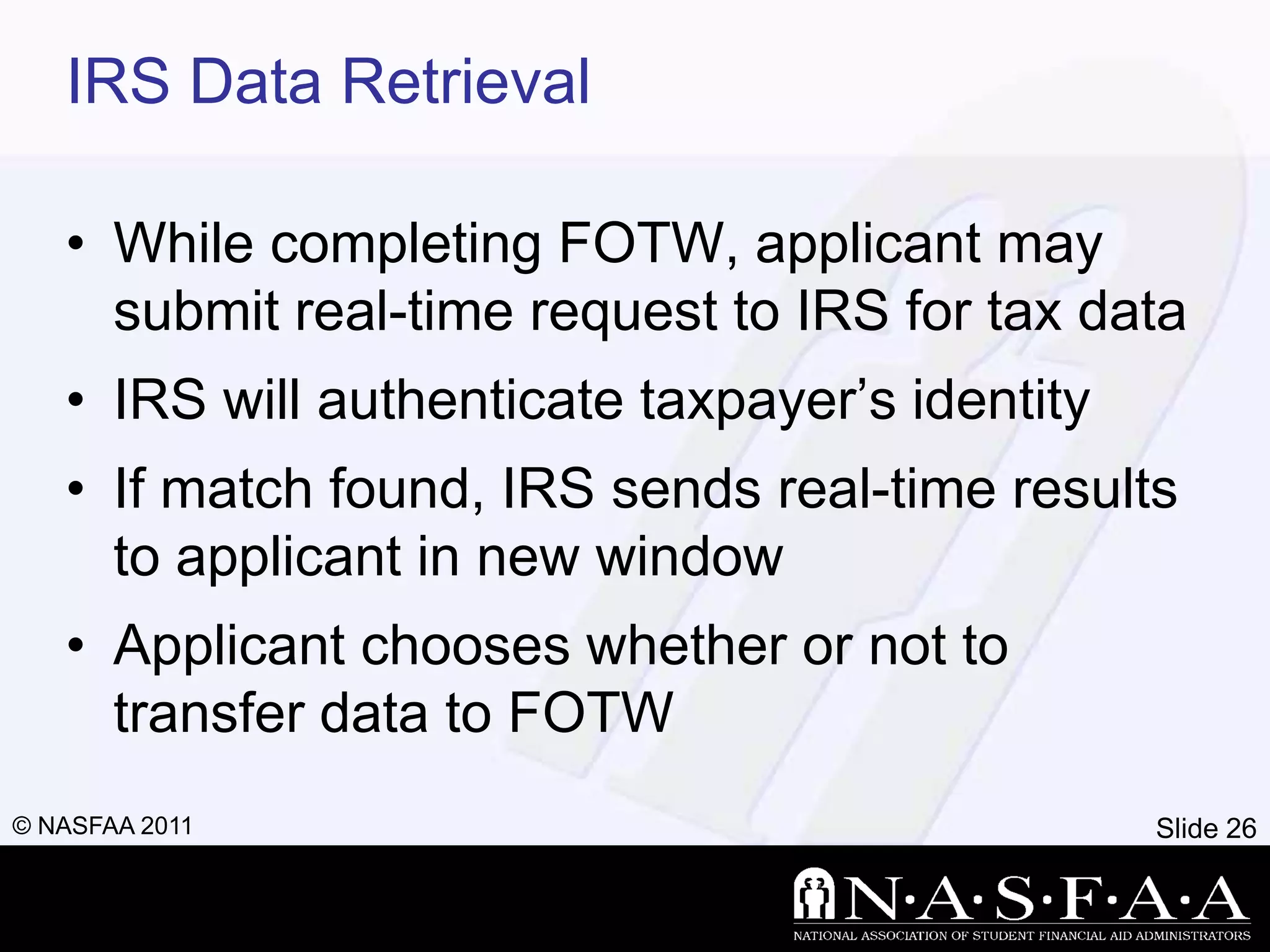
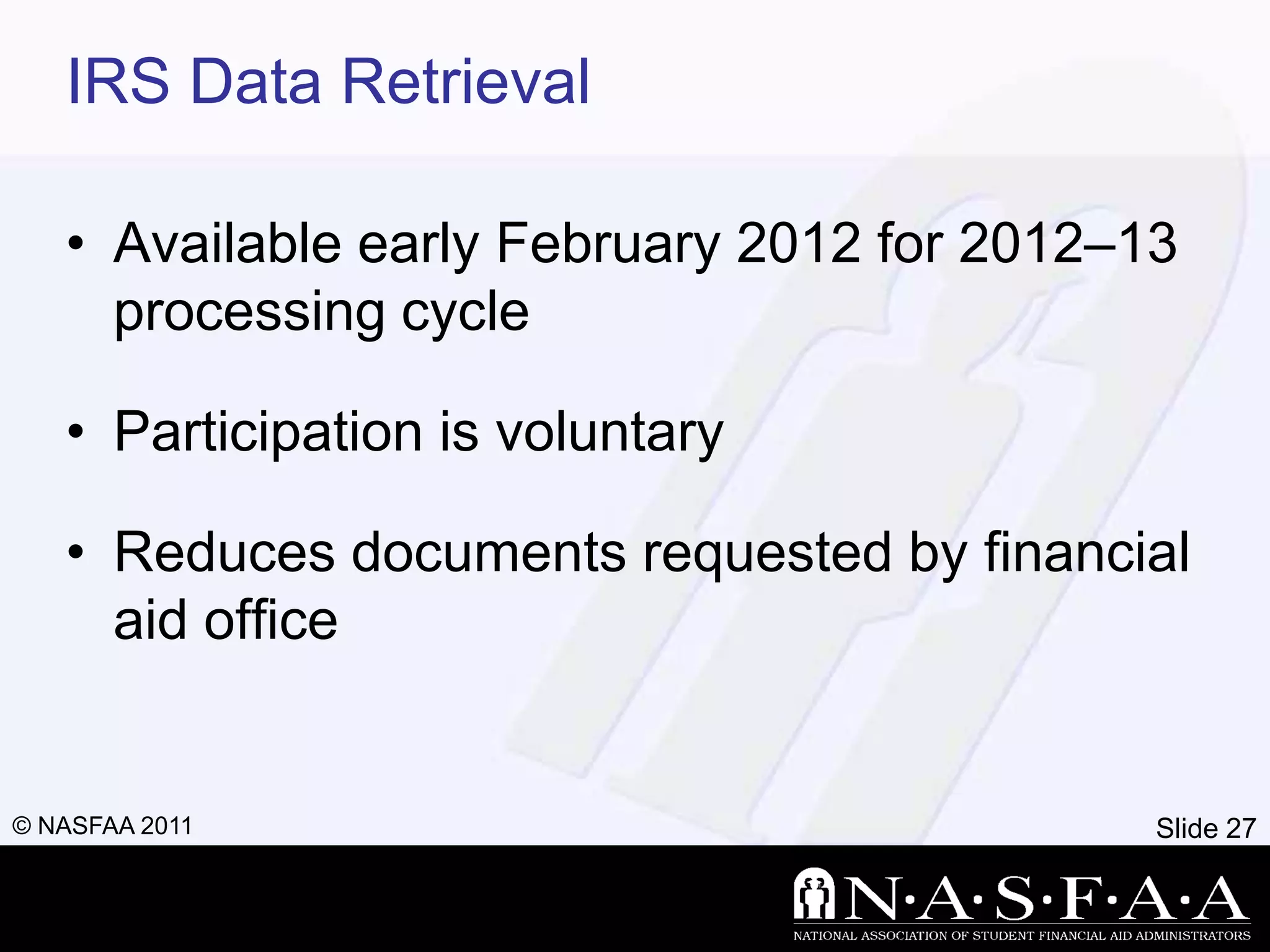
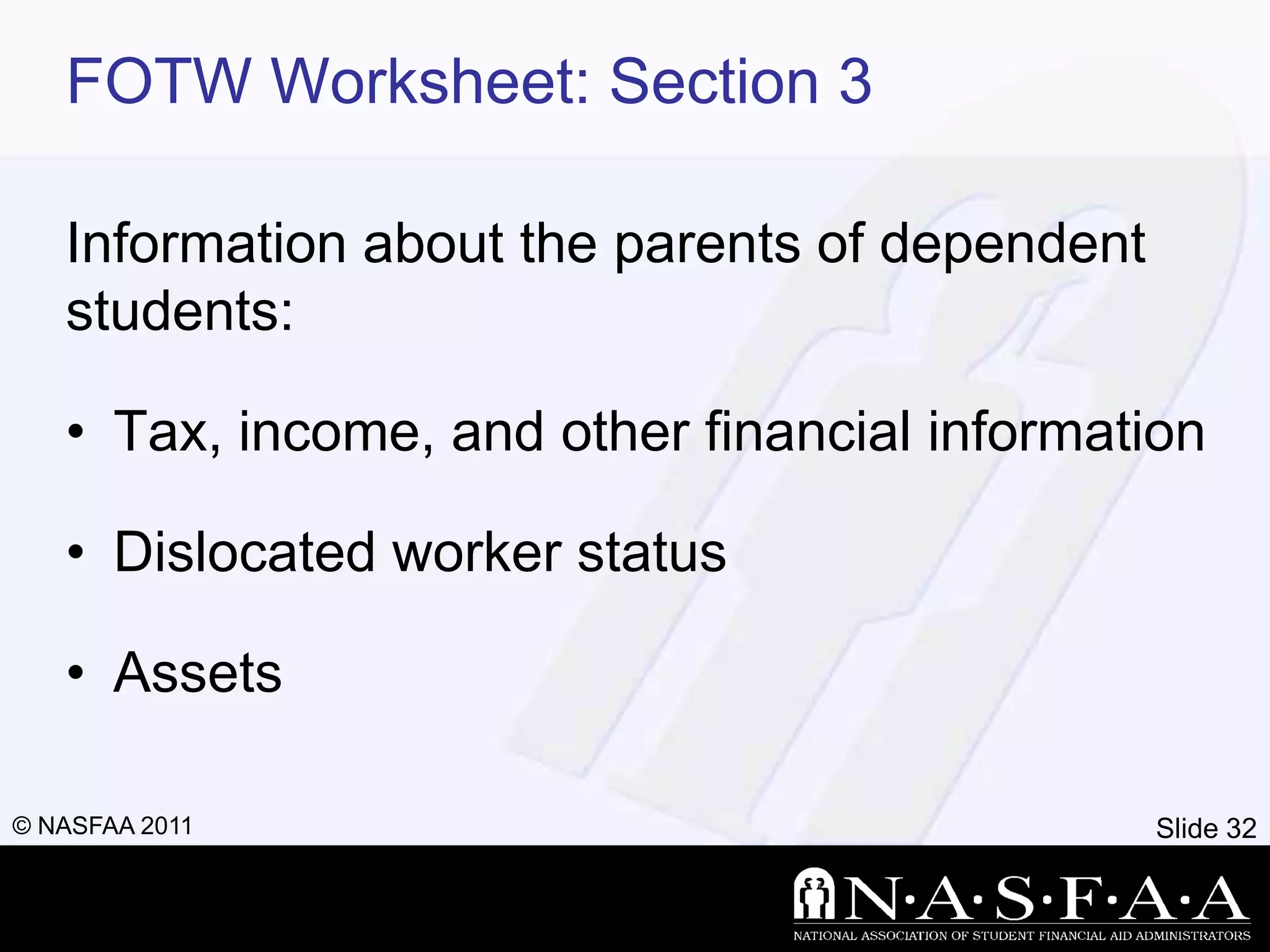
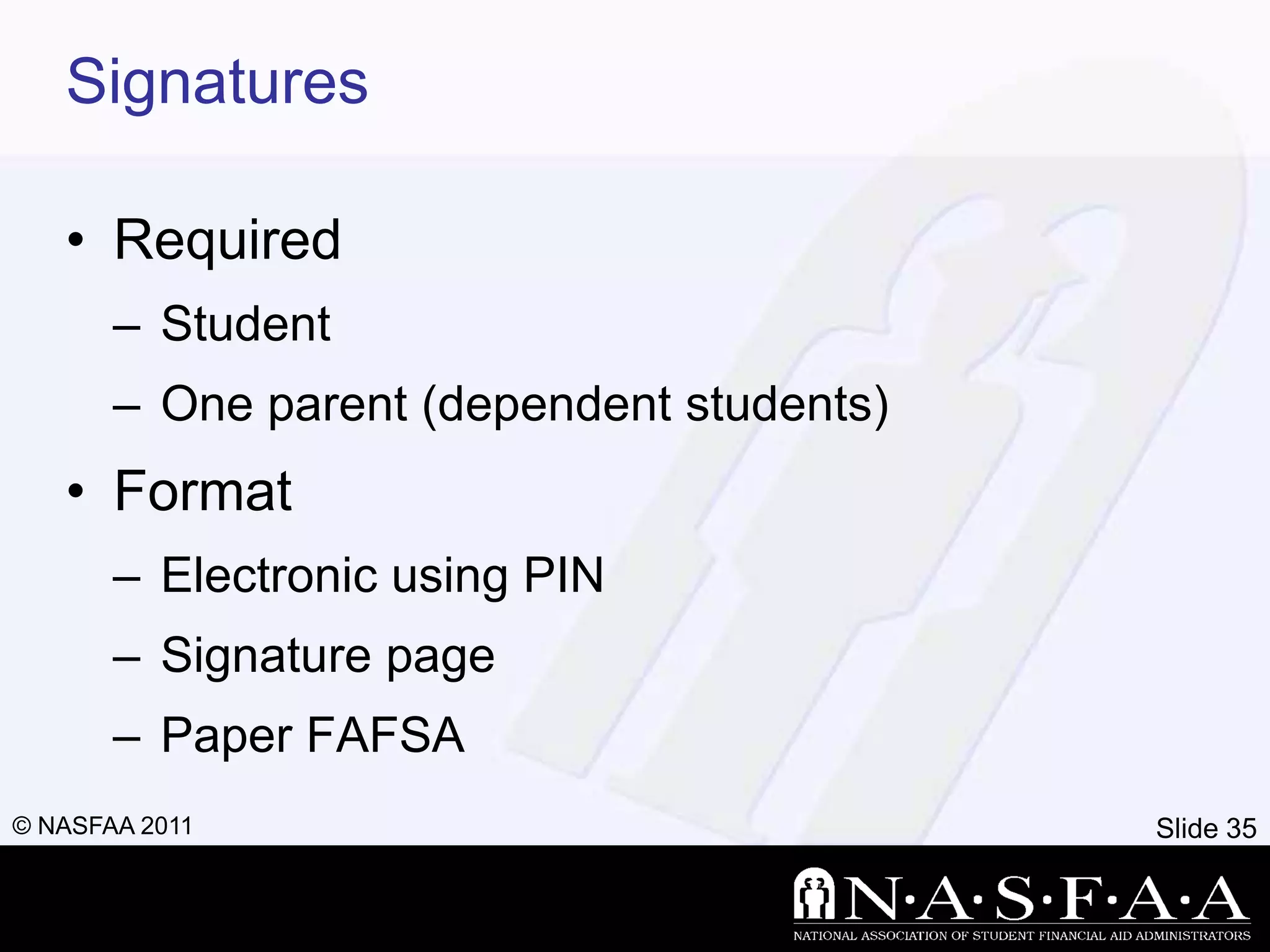
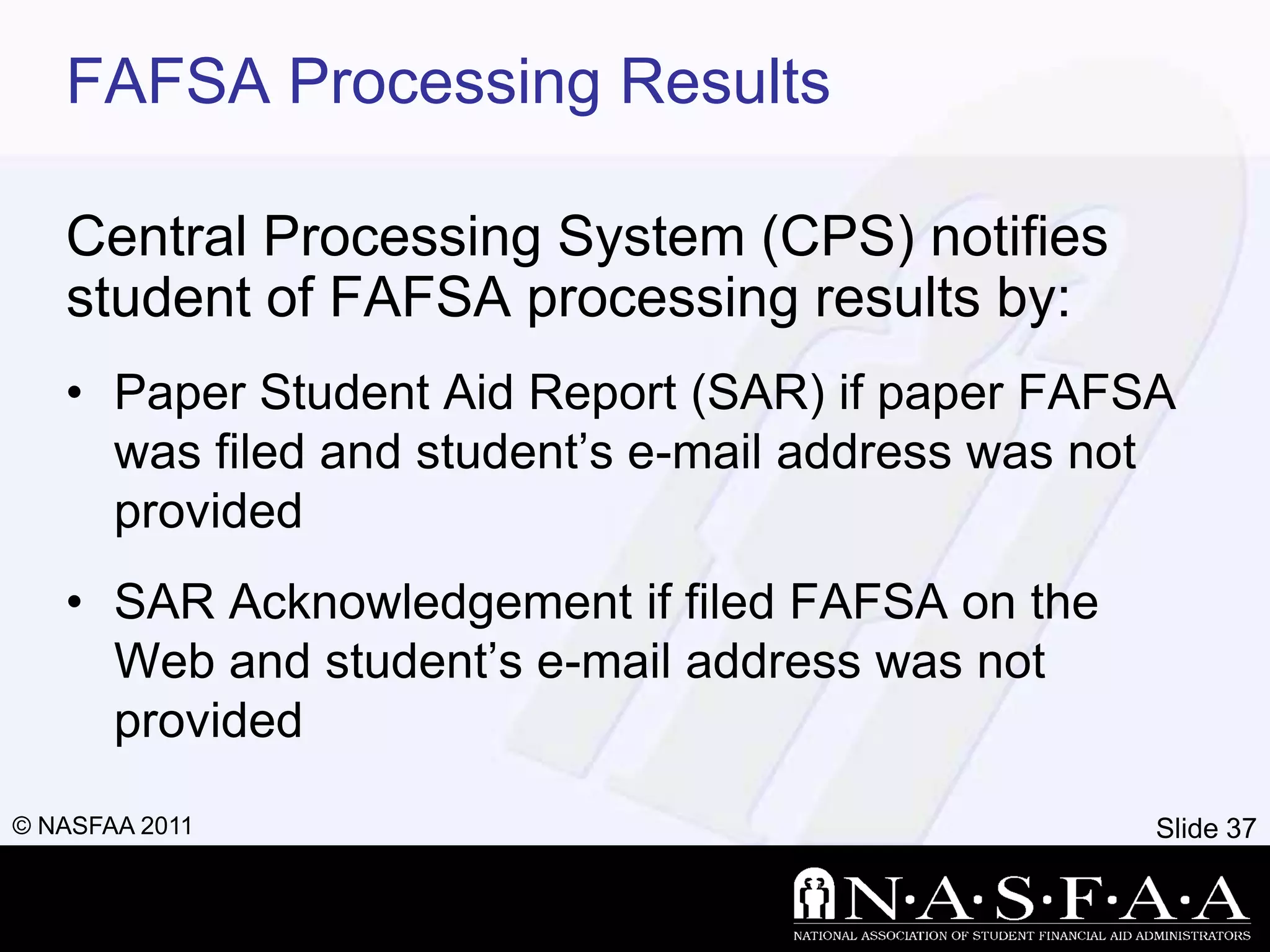
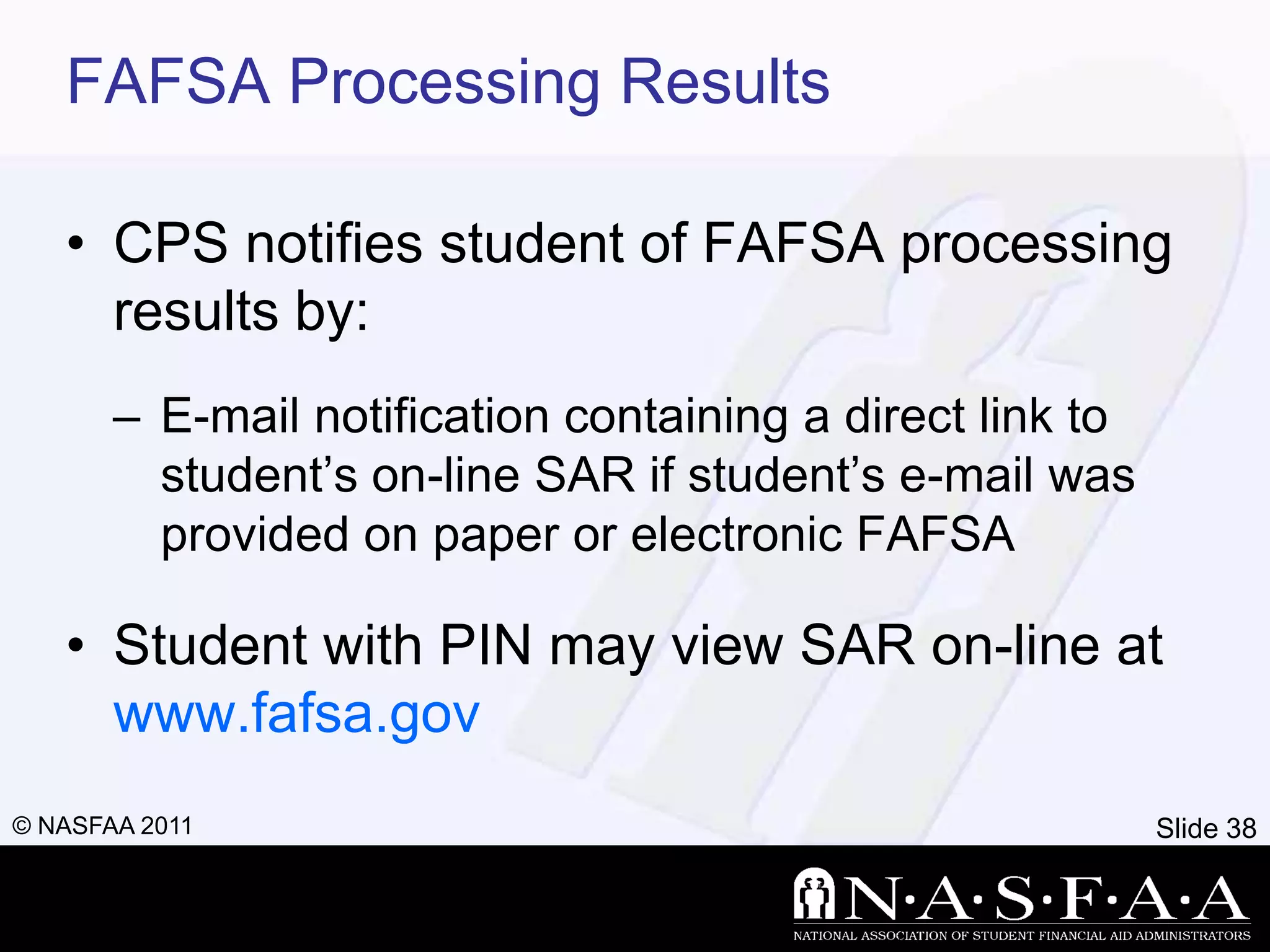
2) It emphasizes completing the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) to apply for federal and state aid. Key information from tax returns is used to calculate an expected family contribution.
3) The major sources of financial aid are discussed as federal and state governments, private organizations, employers, and colleges. Grants, loans, scholarships, and employment are described as the primary categories and types.