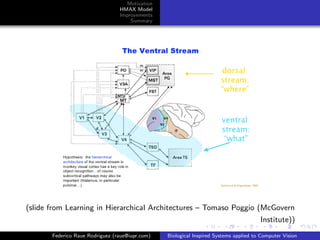
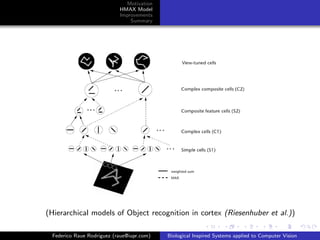
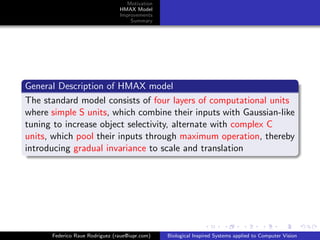
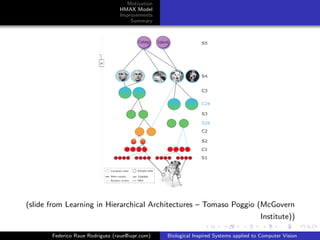
The document discusses improvements that can be made to the HMAX model of object recognition inspired by the human visual system. It proposes adding sparsity through lateral inhibition, exploring new pooling mechanisms, and using salient inputs like optical flow. The goal is to make the model more biologically plausible while reducing computational costs.





















![Motivation
Sparsity
HMAX Model
Pooling Mechanism
Improvements
Input
Summary
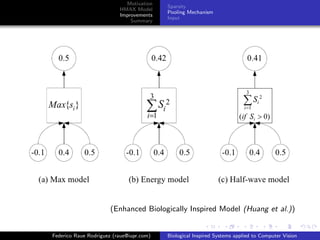
1 Find the maximal response and its neighbors
2 Weak responses are removed due to inhibition effect
3 New pooling Mechanism
a sum the energy of all responses remained by using different
weights for S1 units
1
C= [wi S 2 (xi , yi )]
NI 0
xi ,yi ∈I0
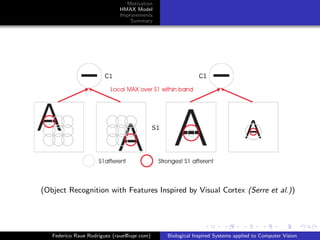
(Human age estimation using bio-inspired features (Guo et al.))
b the STD operation is performed on the maximum map using a
cell grid of size Ns x Ns
Ns ×Ns
1 ¯ 2
std = Fi − F
Ns × Ns
i=1
(Enhanced Biologically Inspired Model (Huang et al.))
Federico Raue Rodriguez (raue@iupr.com) Biological Inspired Systems applied to Computer Vision](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slideshare-120702042307-phpapp02/85/Biological-inspired-system-applied-to-Computer-Vision-31-320.jpg)
![Motivation
Sparsity
HMAX Model
Pooling Mechanism
Improvements
Input
Summary
1
C= [wi S 2 (xi , yi )]
NI 0
xi ,yi ∈I0
Federico Raue Rodriguez (raue@iupr.com) Biological Inspired Systems applied to Computer Vision](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slideshare-120702042307-phpapp02/85/Biological-inspired-system-applied-to-Computer-Vision-32-320.jpg)




![Motivation
Sparsity
HMAX Model
Pooling Mechanism
Improvements
Input
Summary
S1 Units
Gray-value video sequence at all position
Three different types of S1
a Space-time gradient-based: Space and time gradients
It It
| | | |
Ix + 1 Iy + 1
b Optical flow based S1 units: Optical flow of the input using
Lucas & Kanade’s alg.
1
b(θ, θp ) = { [1 + cos(θ − θp )]}q × exp(−|v − vp |)
2
4 directions and two speeds
c Space-time oriented S1 units:
Add a temporal dimension to their receptive fields
3rd derivatives fo Gaussians
8 space-time filters tuned to 4 directions and 2 speeds
Size of receptive fields was 9(pixels)x9(pixels)x9(frames)
Federico Raue Rodriguez (raue@iupr.com) Biological Inspired Systems applied to Computer Vision](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slideshare-120702042307-phpapp02/85/Biological-inspired-system-applied-to-Computer-Vision-37-320.jpg)