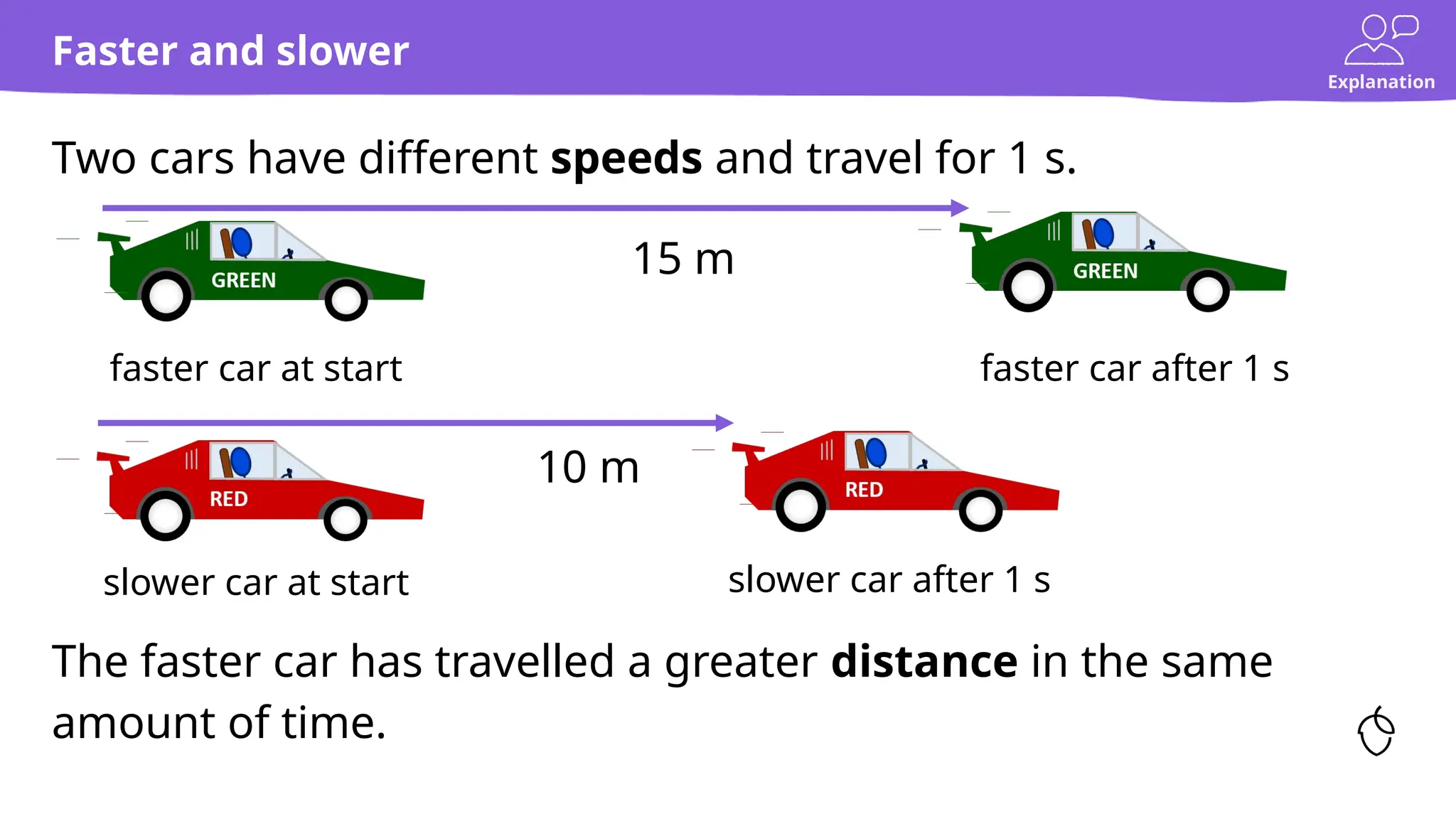
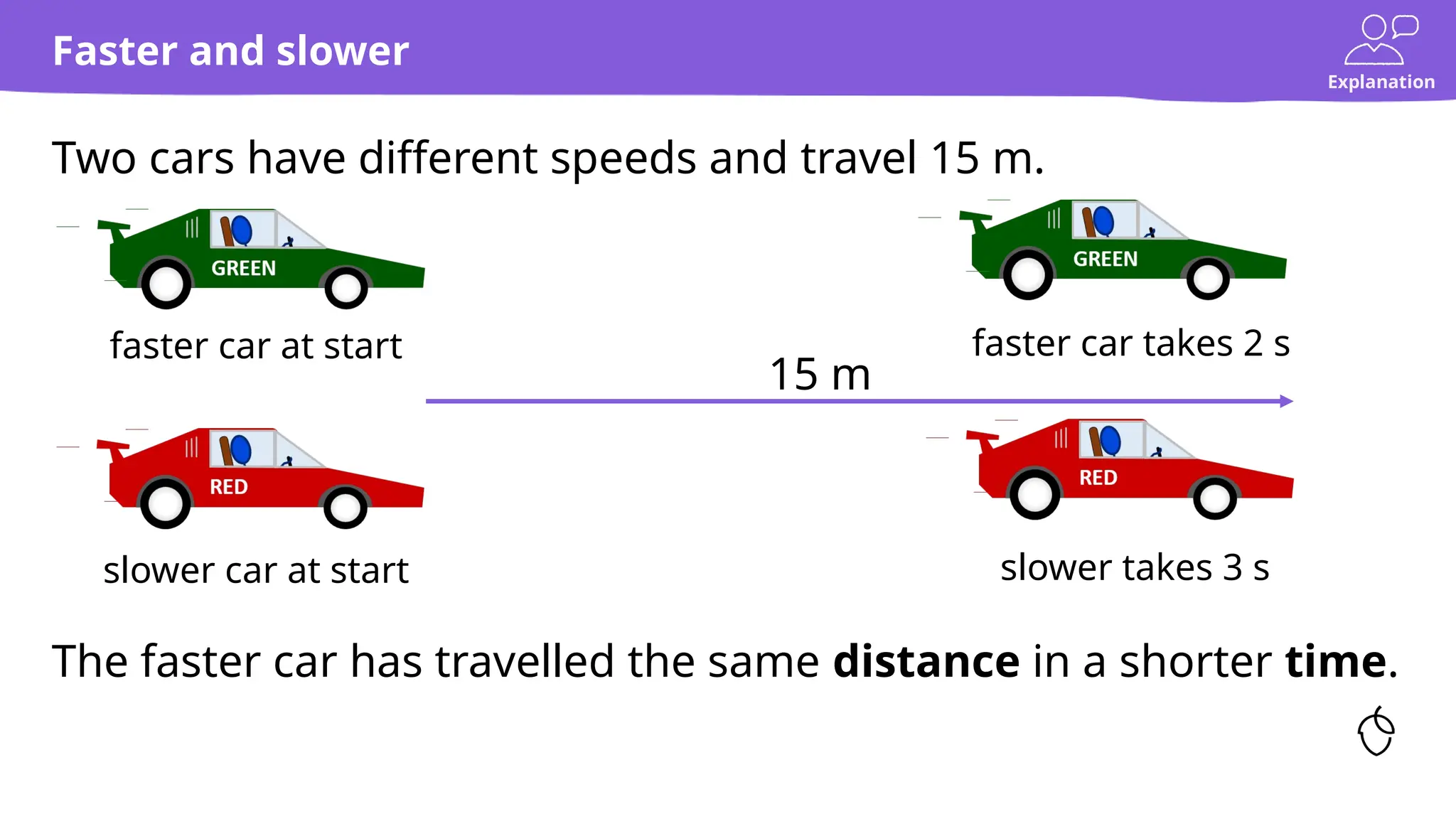
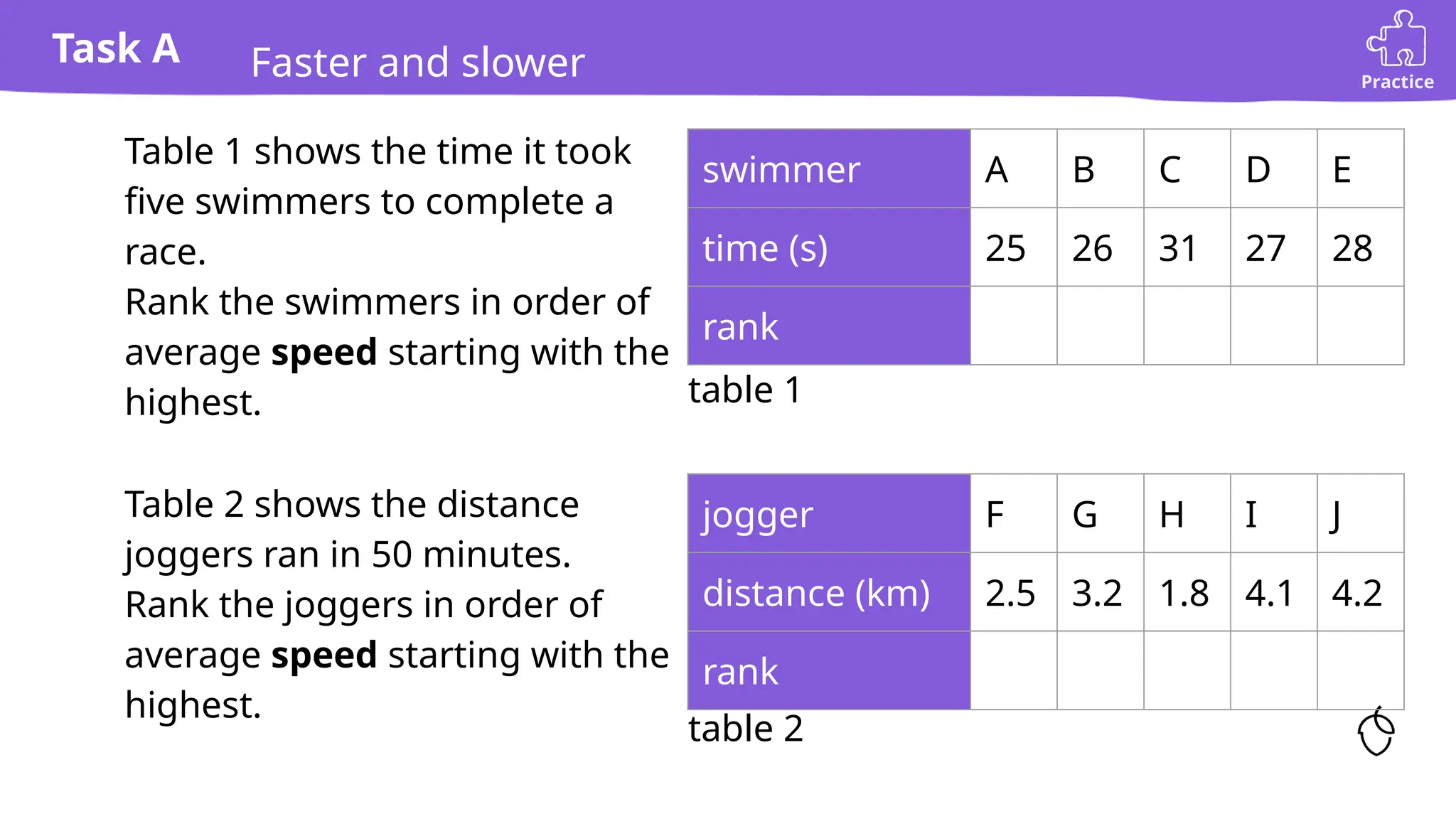
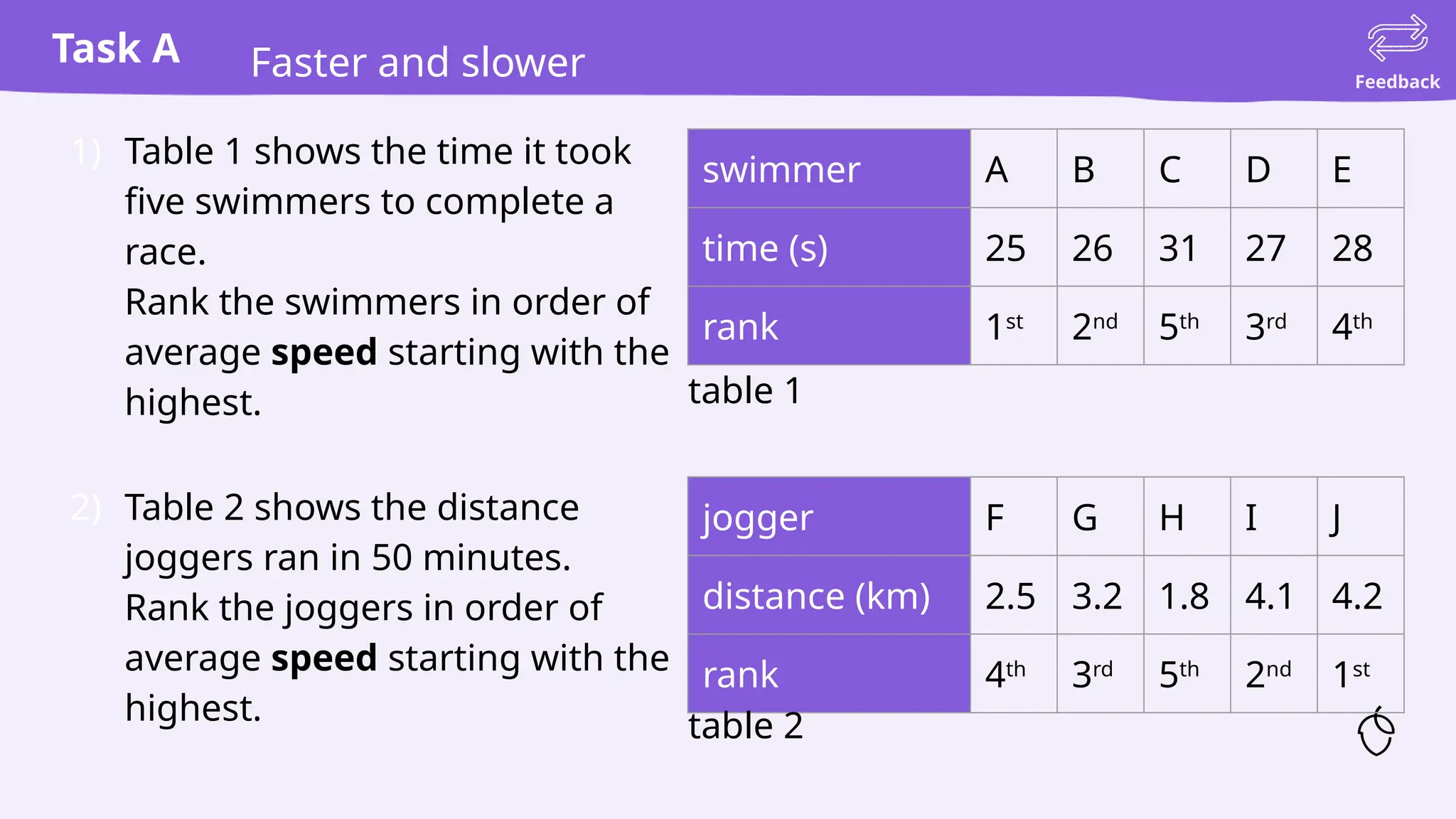
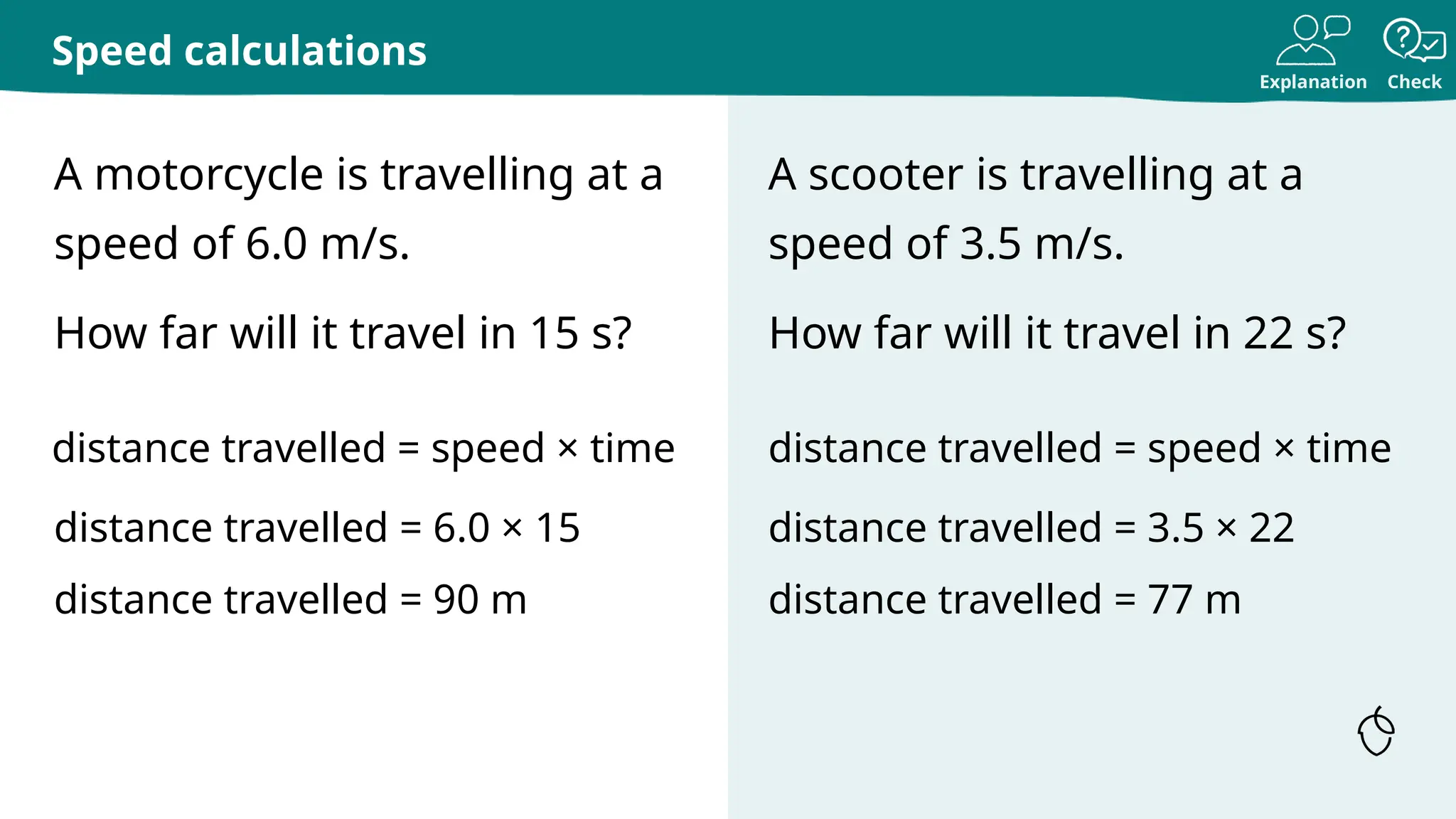
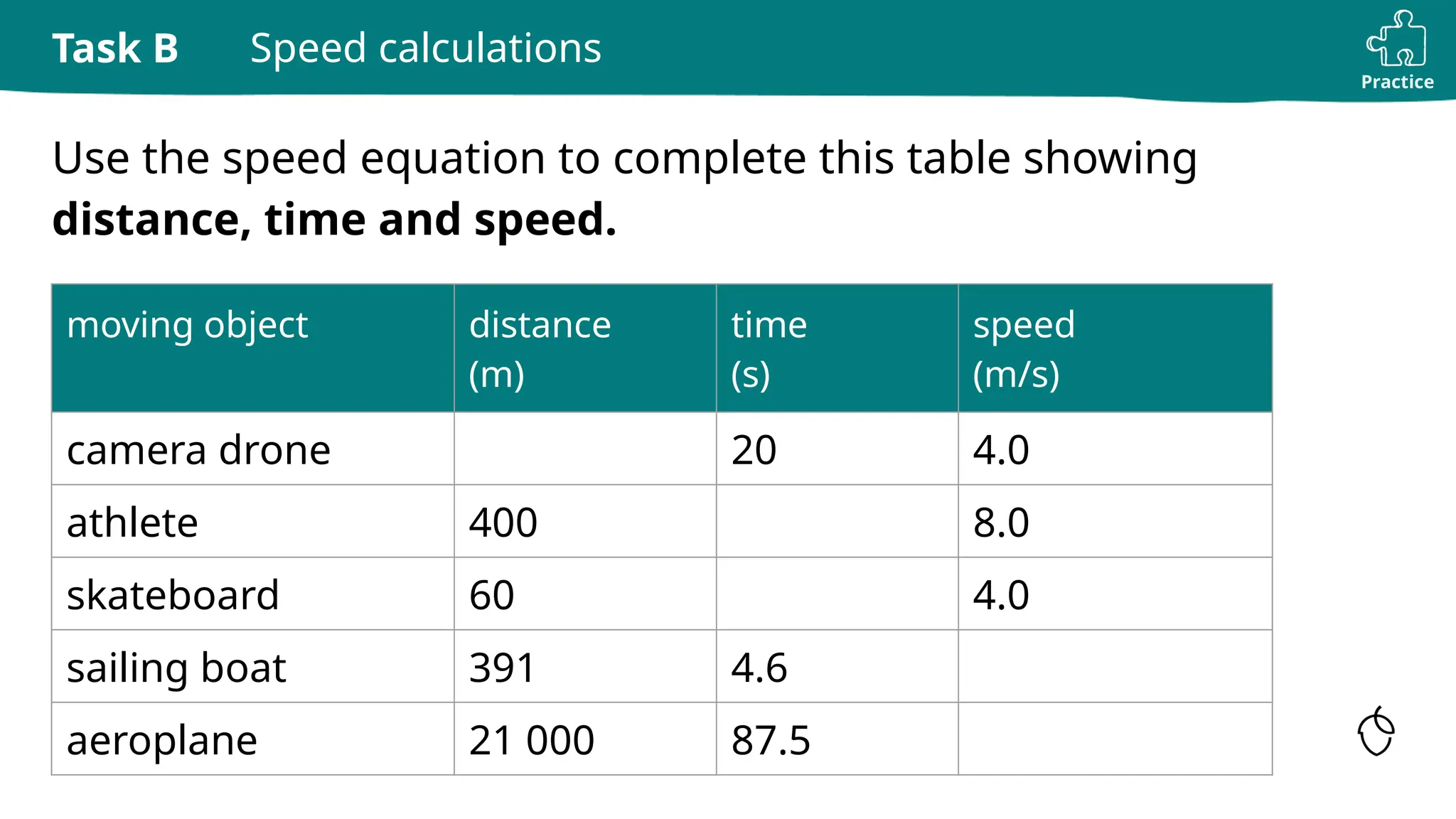
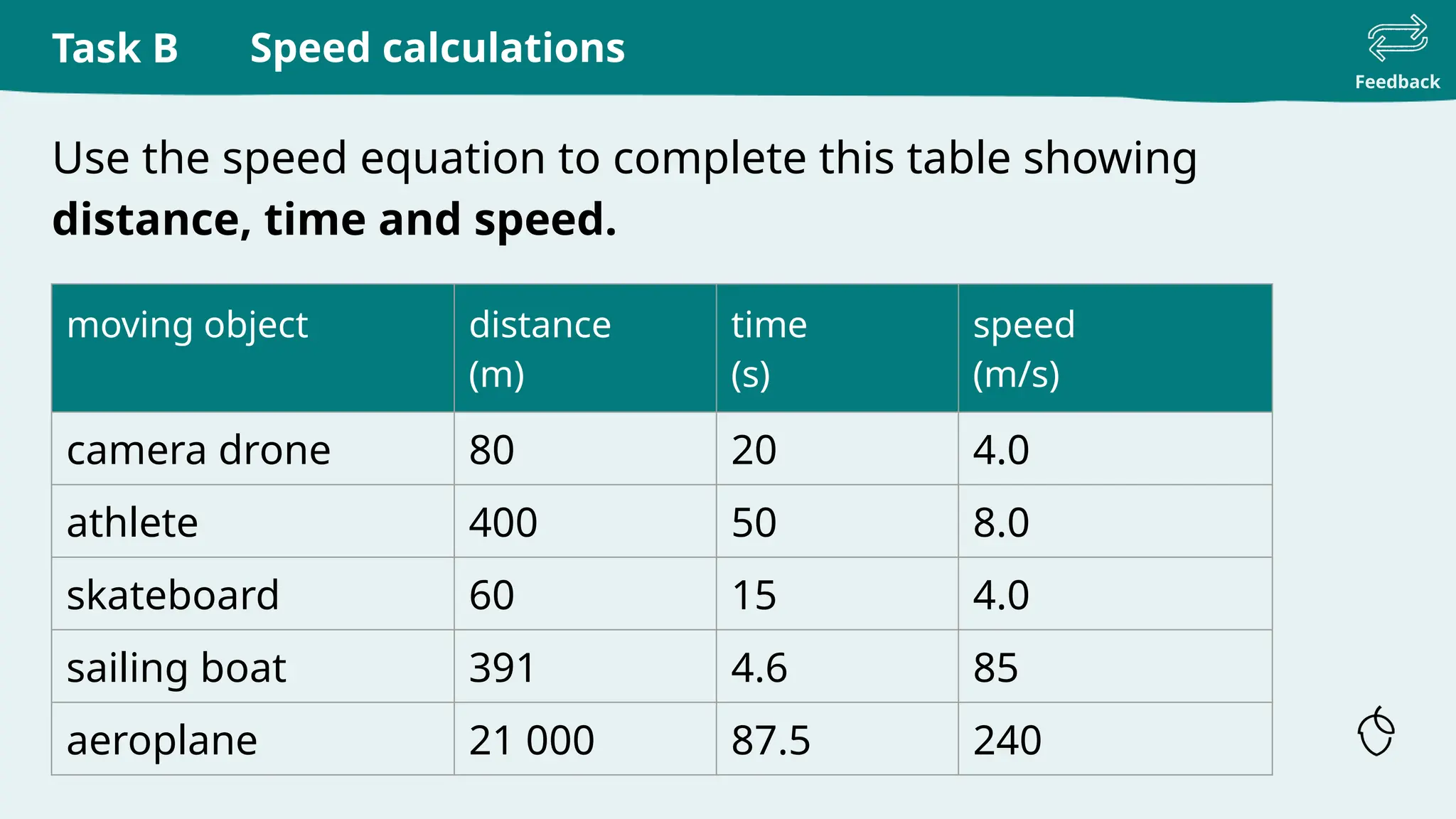
The document provides a comprehensive guide on calculating speed, emphasizing the relationship between distance, time, and speed, with standard units being meters per second (m/s) and miles per hour (mph). It includes explanations, examples, and practice tasks for measuring speed, using various units and understanding the mathematical concepts behind speed calculations. The summary highlights that greater speeds result in shorter travel times for fixed distances and covers both theoretical and practical applications of speed measurement.