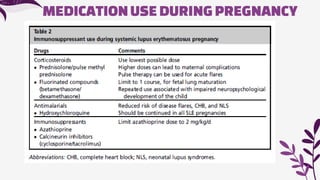
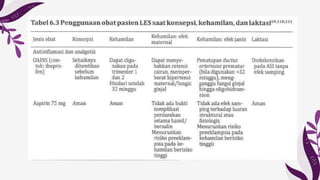
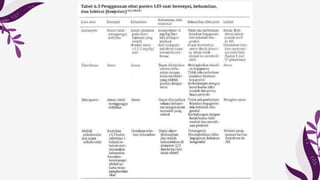
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) predominantly affects young women, so pregnancy is a common occurrence; however, it requires comprehensive planning to ensure a safe pregnancy. SLE can increase the risks of disease flares during pregnancy, preterm birth, miscarriages, and hypertensive diseases of pregnancy. Recognition of SLE disease activity during pregnancy can be difficult due to overlapping physiological changes. Increased disease activity, high prednisone use, hypertension, and other risk factors can contribute to preterm birth and preeclampsia. The presence of antiphospholipid antibodies in SLE patients increases the risks of pregnancy loss, intrauterine growth retardation, and preterm births. Medications must be carefully managed during