Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX
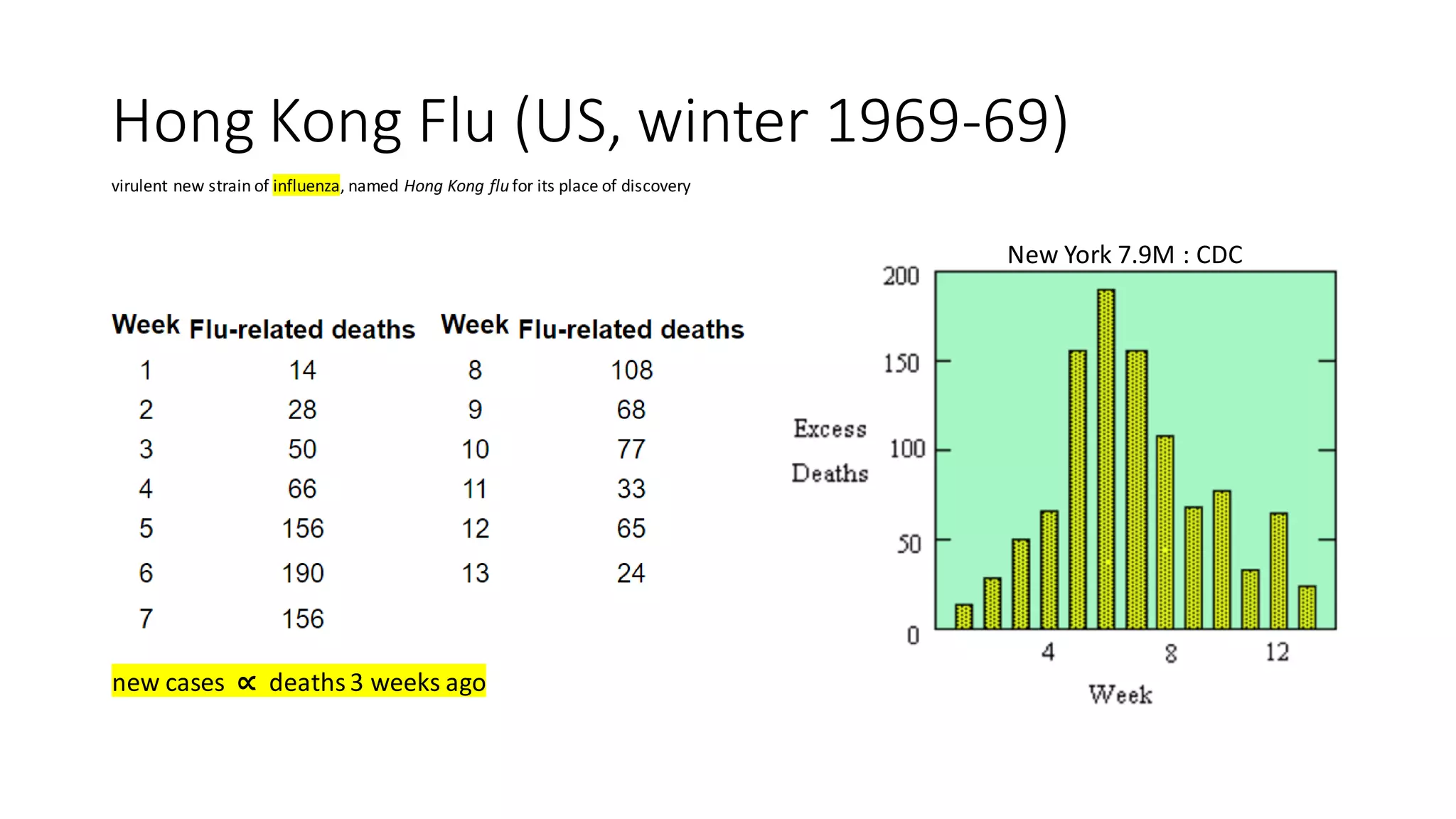


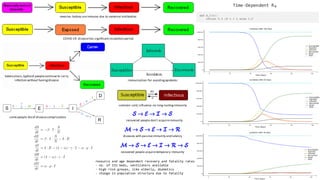


The document discusses the Hong Kong flu outbreak in the US during the winter of 1969-70, detailing its virulence and the mathematical modeling of its spread. It emphasizes the need for herd immunity to halt epidemics, comparing the basic reproductive number (r0) of this flu to historical influenza strains and other diseases. The text also touches on various immunization strategies and the importance of immunity duration in relation to different infections.




