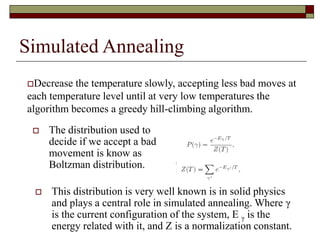
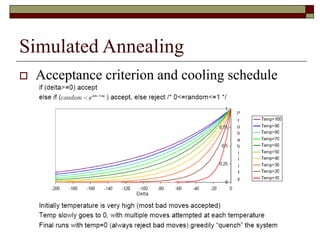
Simulated annealing is a local search algorithm that can find good approximations to global optimization problems. It is inspired by the physical process of annealing in solids. The algorithm starts with a random solution and uses the Metropolis algorithm to probabilistically accept moves to neighboring solutions based on a cooling schedule, allowing it to escape local optima. It has been applied successfully to problems like the traveling salesman problem, graph partitioning, and VLSI design placement and routing. The cost function and cooling schedule are important factors that affect its performance.