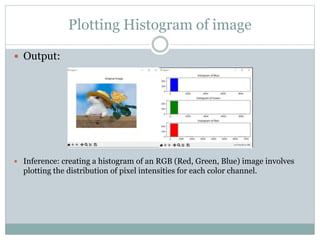
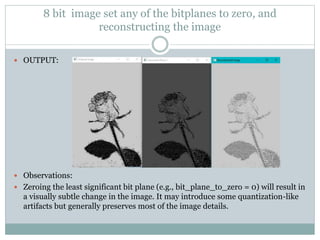
Gamma transformation is used to adjust image brightness and contrast by decreasing overall brightness and reducing darker area contrast with higher gamma values. Creating a histogram for an RGB image involves plotting the pixel intensity distribution for each color channel. Neighborhood operations like simple average and weighted average filtering can blur an image, while median and gaussian filters reduce noise and preserve edges. High-boost filtering and unsharp masking enhance edges and details while preserving image structure. Altering bitplanes by zeroing them out impacts image intensity levels and contrast, with more significant effects from the most versus least significant bitplane. Zooming via pixel replication can cause pixelation, loss of detail, and artifacts due to enlarged pixels.