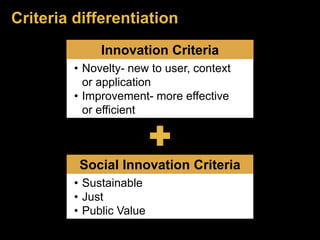
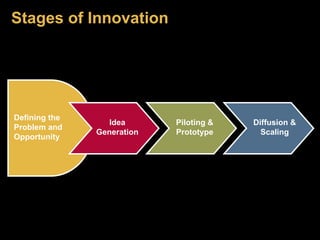
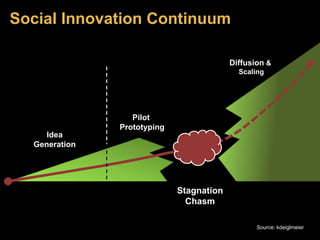
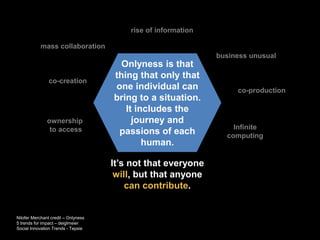
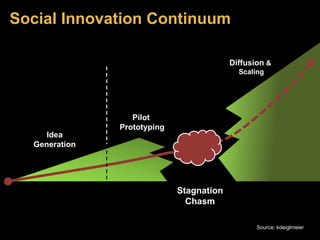
The document discusses social innovation, defining it as novel solutions to social problems that prioritize societal value over private gain. It outlines the stages of innovation, including idea generation, piloting, prototyping, and diffusion, and emphasizes the importance of collaboration across sectors for effective social innovations. Additionally, it explores trends in the field, including microfinance and fair trade, and highlights the need for research and partnerships to overcome challenges in implementing social innovations.






![SI Drive definition
Social Innovation is a new combination
of social practices in certain areas of
action or social contexts with the goal of
better satisfying or answering social
needs and problems than is possible on
the basis of existing practices.
SI drive: Theoretical Approaches to Social Innovation – A Critical Literature Review [p. 2] September 2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/krisdeiglmeiersidrivefinal-141125085742-conversion-gate01/85/SI-LIVE-Opening-Session-Kris-Deiglmeier-CEO-of-Tides-8-320.jpg)