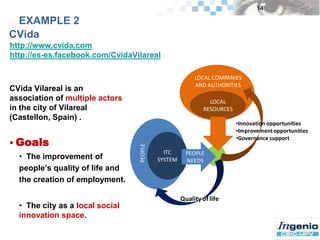
The document explores the concept and measurement of social innovation (SI), emphasizing its significance in addressing contemporary social challenges and enhancing quality of life. It discusses the intertwining nature of SI with technological and economic innovations and presents frameworks for understanding and measuring SI. Additionally, it highlights various social innovation initiatives and calls for further research to refine measurement methodologies and theoretical frameworks.