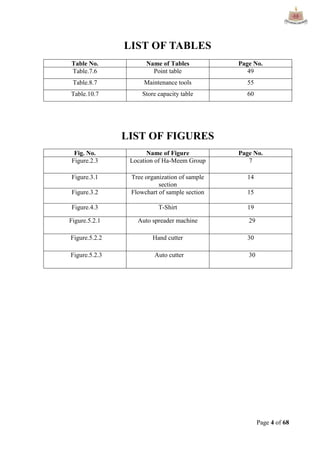
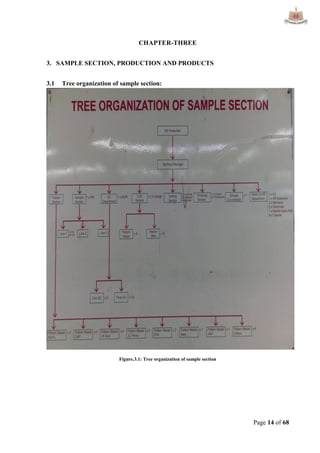
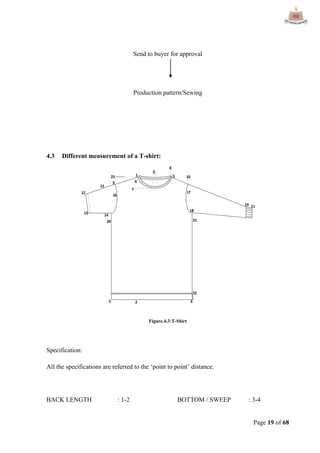
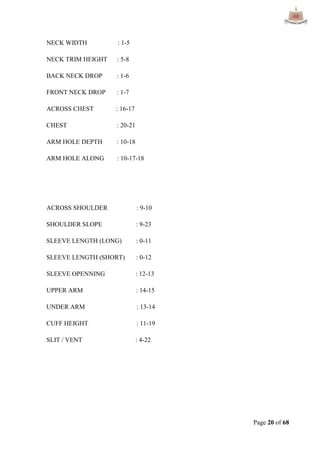
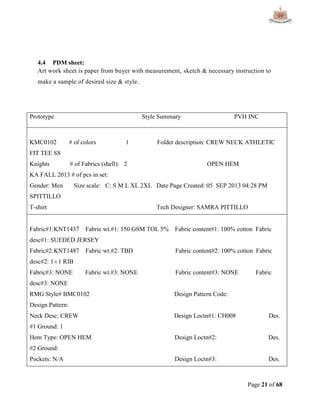
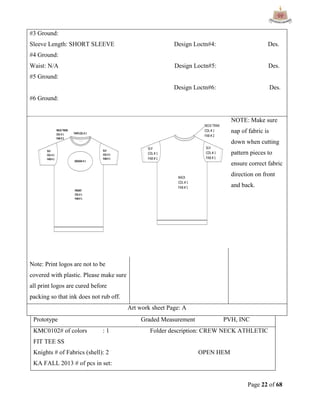
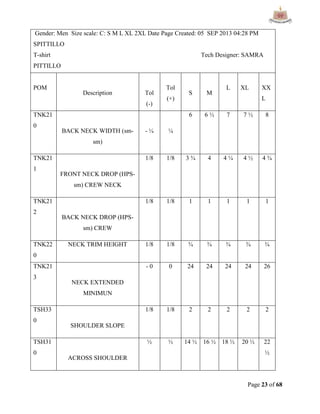
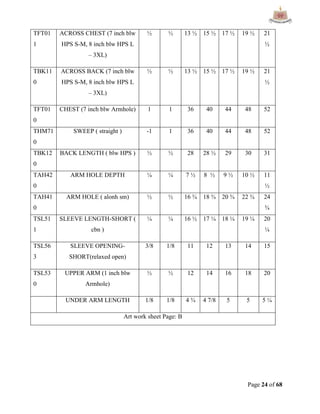
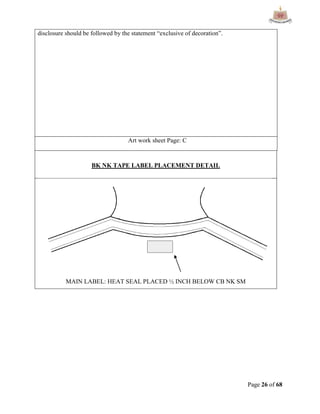
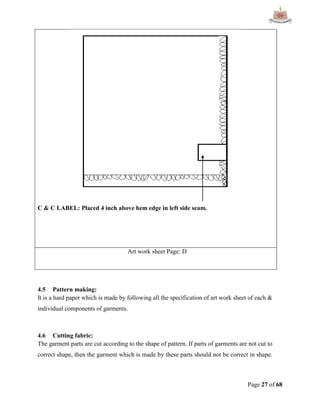
This document provides an overview of Ha-Meem Group, a Bangladeshi apparel manufacturer. It discusses the company's history, facilities, production capacity, quality standards, certifications and major buyers. It also describes the organizational structure and key responsibilities of different departments like sample section, production, merchandising, quality assurance, maintenance, utilities and store/inventory. Finally, it covers topics like cost analysis, marketing strategy and concludes with future goals of the company.