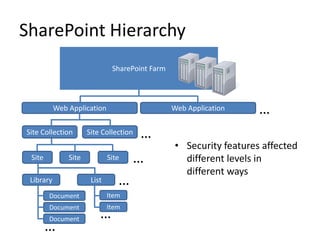
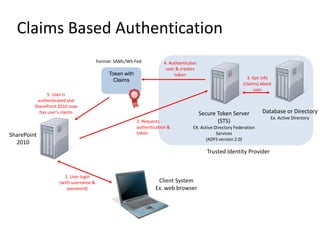
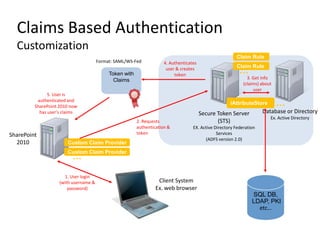
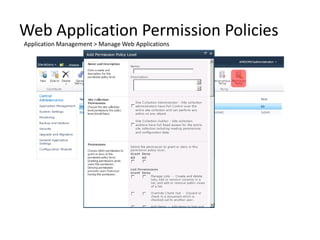
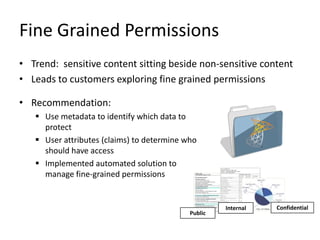
- SharePoint security features are built into many aspects of deployment and configuration, requiring planning.
- Managed service accounts with least privileges should be used for SQL, setup, and the farm account.
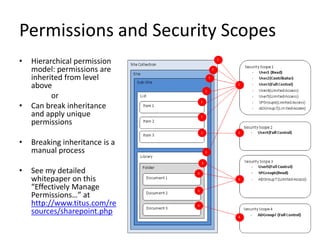
- Authentication can be classic or claims-based, configured at the web application level.
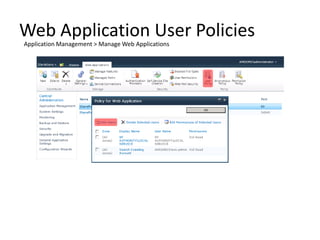
- Web application policies control permissions, permission policies, user policies, and blocked file types across a web app.
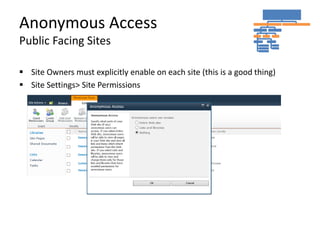
- Anonymous access must be explicitly enabled for public-facing sites and brings risks if not configured correctly.