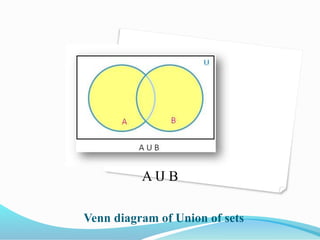
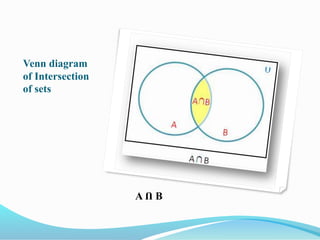
This document defines and provides examples of different types of sets. It discusses the empty set, finite and infinite sets, equal sets, subsets, power sets, and the universal set. Properties of set operations like union and intersection are also covered. Visual representations of sets using Venn diagrams are described.