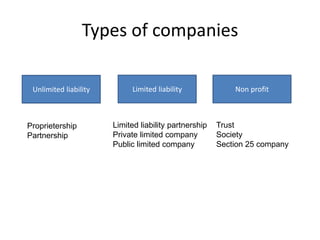
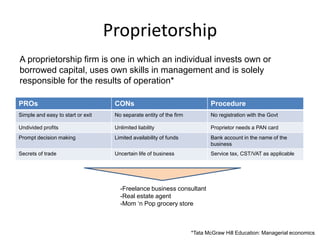
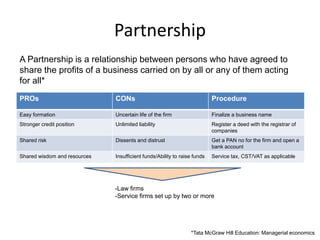
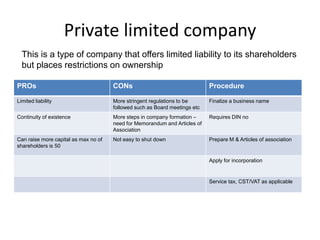
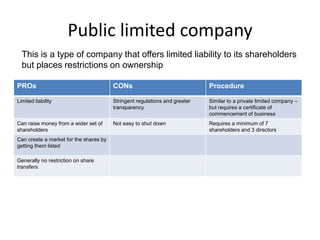
The document presents an overview of various forms of enterprises that can be established in India, including their pros and cons. It discusses different business structures such as proprietorships, partnerships, limited liability partnerships, private limited companies, and public limited companies. Additionally, it includes a case study of three engineering students contemplating the formation of a startup, highlighting the factors to consider in choosing the right enterprise type.