1) The document discusses driver distraction and its effects on driving performance and crash risk. It focuses on two main types of distraction: visual and cognitive.
2) While visual distraction consistently impairs driving, the evidence on cognitive distraction is mixed. Some studies found impaired performance, while others found no effects or even improvements.
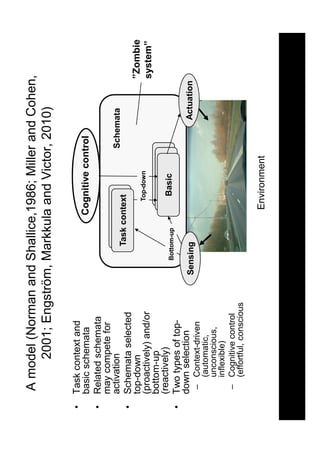
3) The document proposes the "zombie hypothesis" to explain these inconsistent findings. It suggests that cognitive distraction shifts drivers to a more automatic "zombie-like" state, relying more on overlearned routines. This preserves performance in familiar situations but impairs it in novel or difficult situations requiring cognitive control.
4) Several studies provide support for the zombie hypothesis by finding intact performance on routine