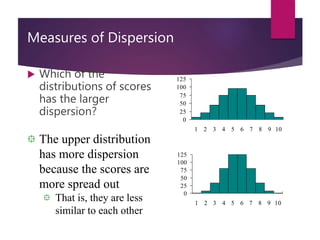
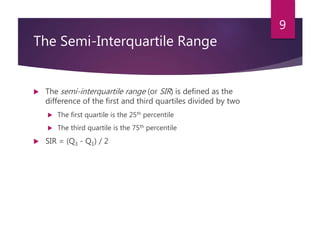
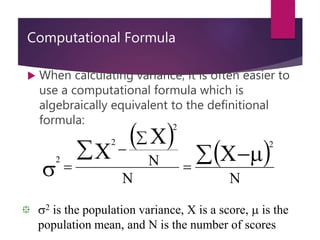
This document defines and explains various measures of dispersion used in statistics, including range, semi-interquartile range (SIR), variance, standard deviation, skew, and kurtosis. It provides formulas for calculating each measure and discusses how to interpret the results, such as how skew values indicate the direction and degree of asymmetry and how kurtosis compares the spread of a distribution to a normal distribution. The purpose of measuring dispersion is to understand the variability and shape of distributions for purposes like determining reliability and facilitating other statistical analyses.