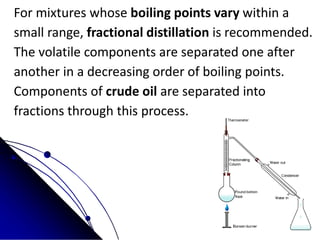
The document outlines various separation techniques for mixtures, including filtration, sieving, flotation, sedimentation, decantation, chromatography, extraction, distillation, and evaporation. Each method is described in terms of its process, applications, and examples, emphasizing differences in density, particle size, and boiling points. The document aims to convey the principles of these techniques and their relevance to purifying substances, particularly water.