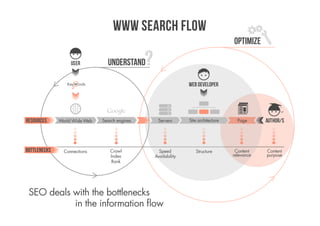
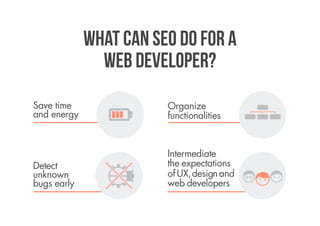
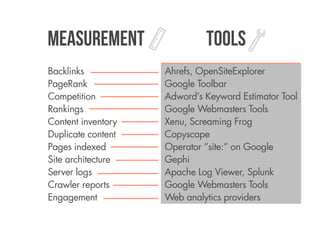
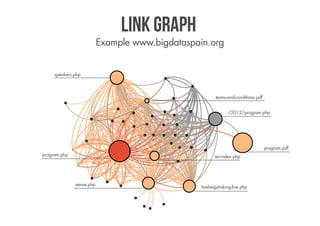
SEO is everything that helps a website generate more revenues from search engines. It deals with bottlenecks in the information flow between users, search engines, websites, and servers. An experienced SEO will audit a website by crawling it, filtering the results, visualizing the link network, and analyzing variables like backlinks, content inventory, site architecture, and engagement. Developers can carry out SEO by focusing on findable, accessible, clear, controllable, valuable, and measurable content.