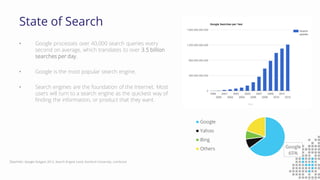
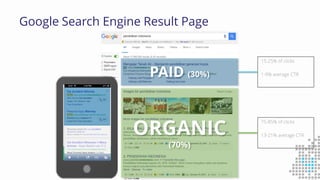
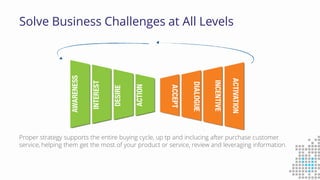
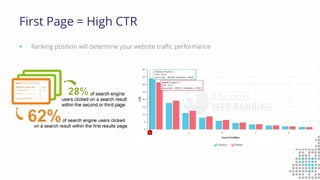
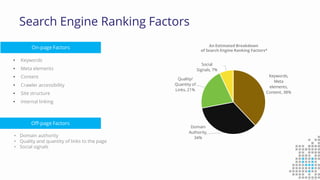
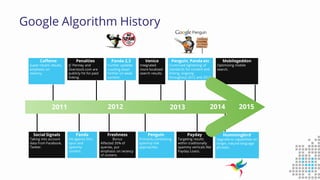
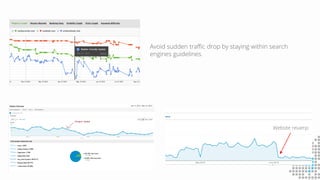
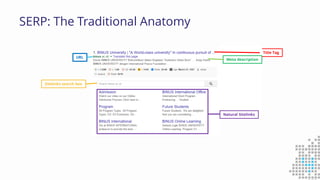
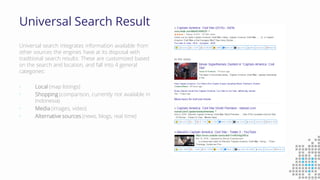
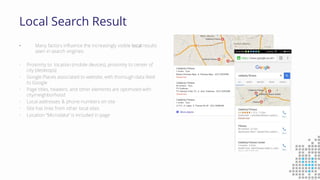
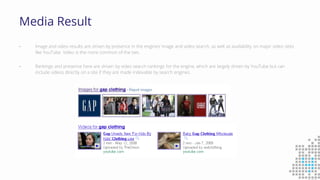
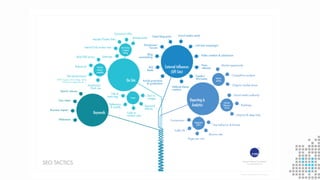
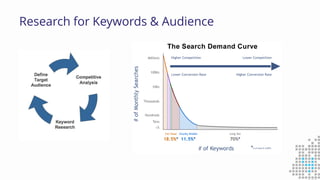
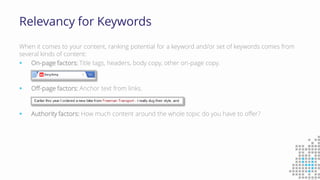
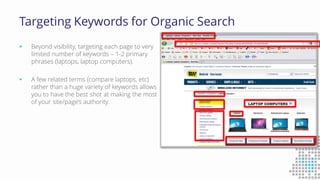
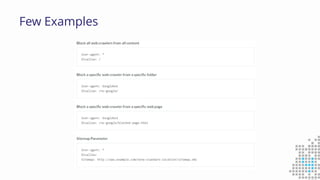
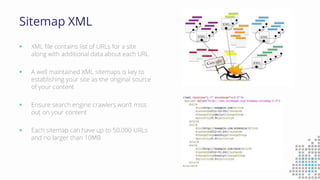
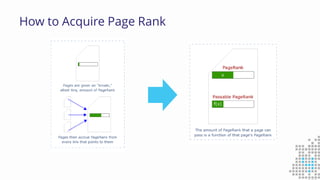
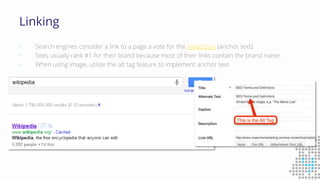
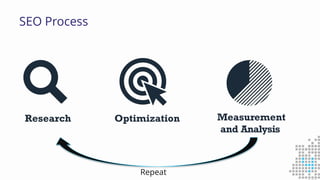
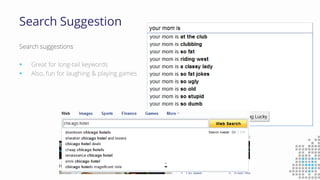
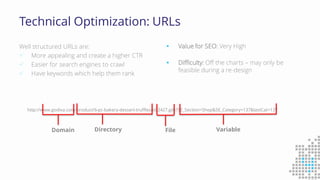
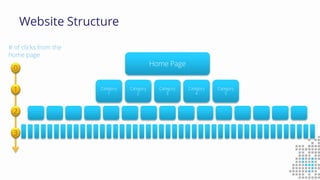
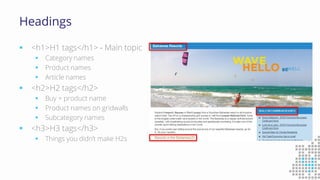
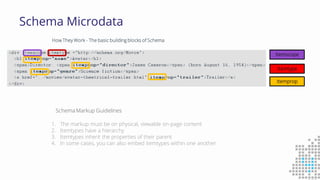
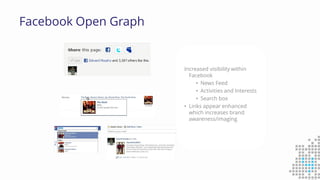
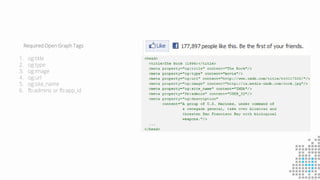
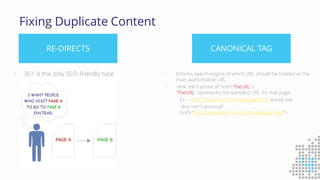
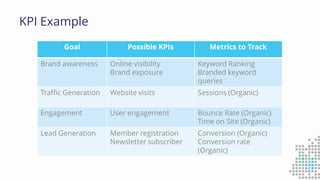
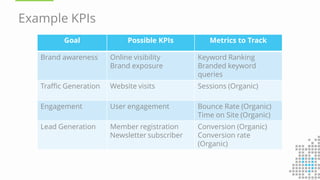
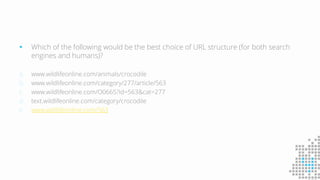
The document discusses the importance of search engine optimization (SEO) and search engine marketing (SEM), highlighting the significant role search engines play in shaping online visibility and traffic. It covers the history of search engines, the evolution of Google's algorithms, and the factors influencing search rankings, including keywords and content quality. Furthermore, it emphasizes the necessity for businesses to develop effective SEO strategies to enhance their website's prominence and customer engagement.