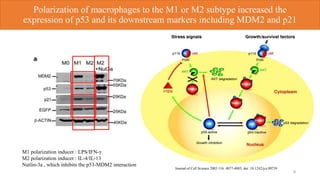
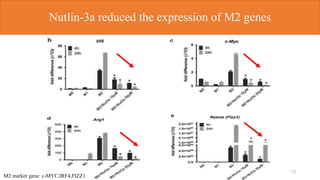
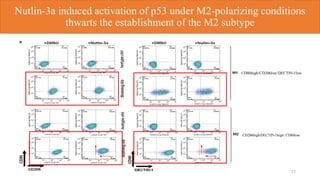
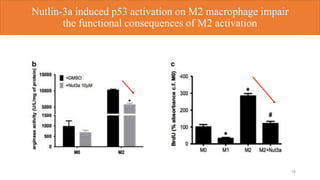
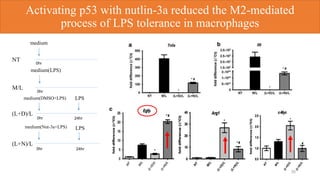
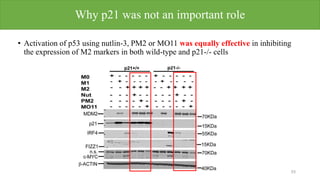
1) p53 activation through nutlin-3a treatment suppressed M2 macrophage polarization by downregulating M2 marker genes like c-MYC, IRF4 and FIZZ1.
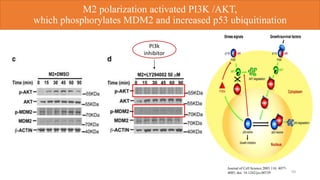
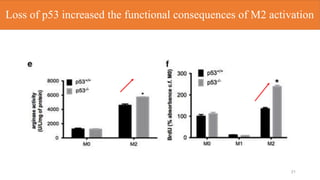
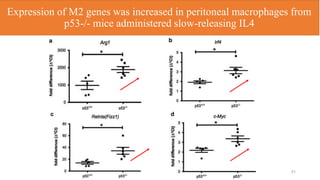
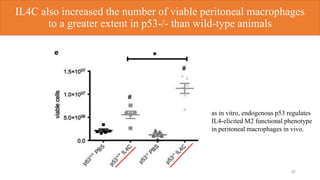
2) Loss of p53 increased M2 macrophage polarization both in vitro and in vivo by increasing the expression of M2 marker genes.
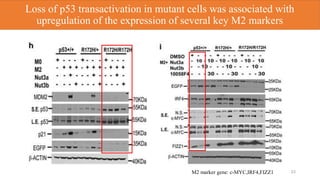
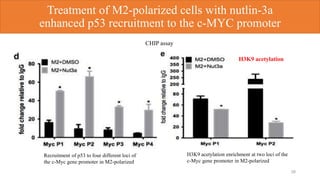
3) p53 was found to suppress M2 macrophage polarization by directly binding to the promoter region of c-MYC gene, reducing its expression and influencing the expression of downstream M2 genes.