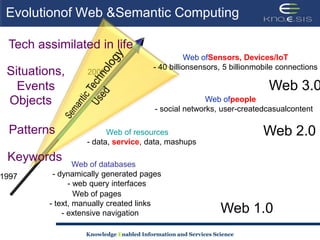
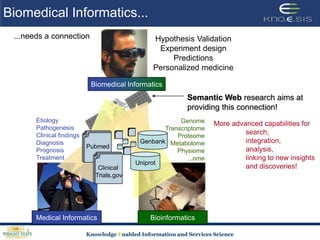
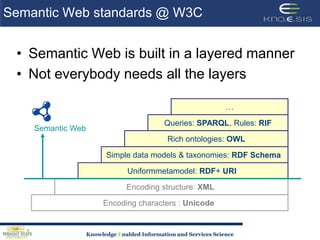
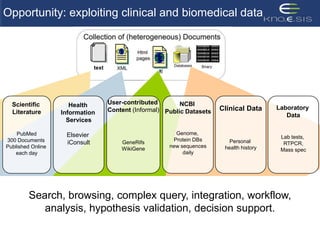
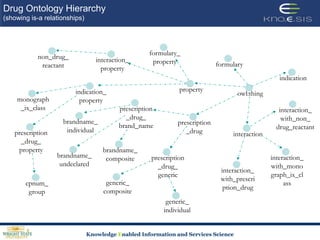
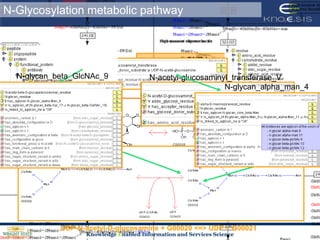
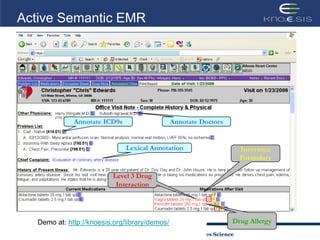
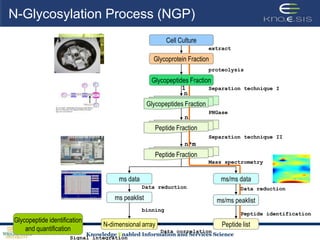
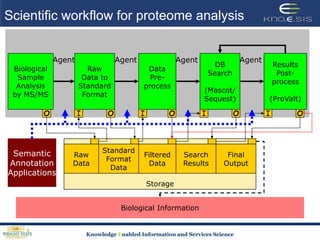
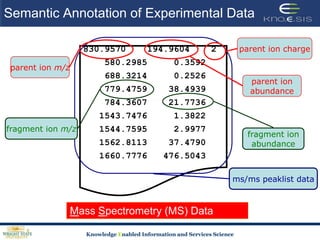
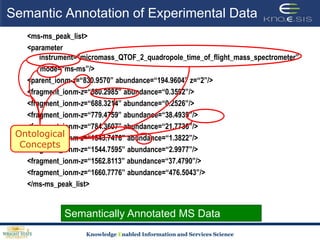
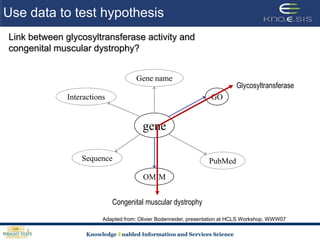
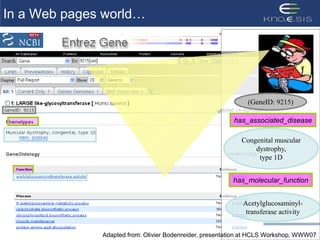
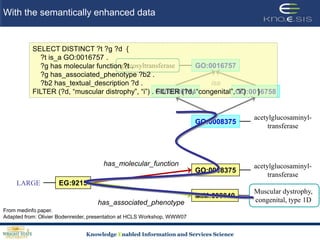
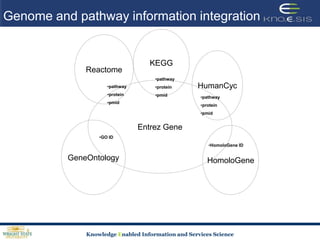
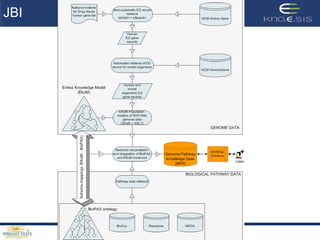
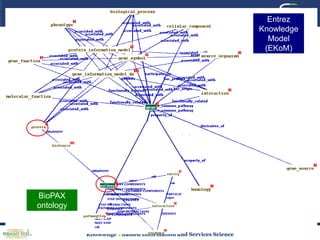
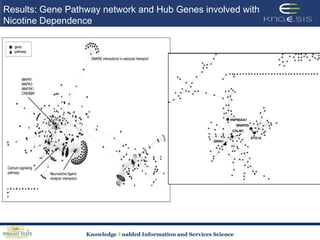
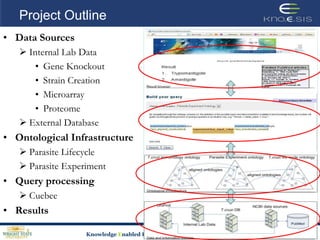
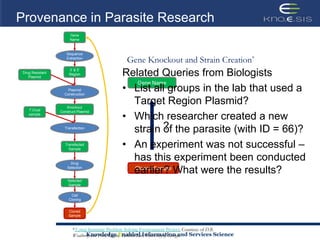
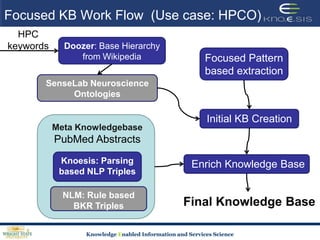
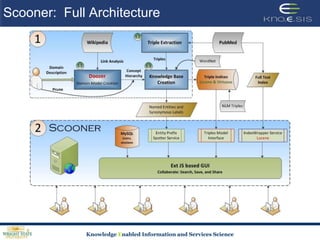
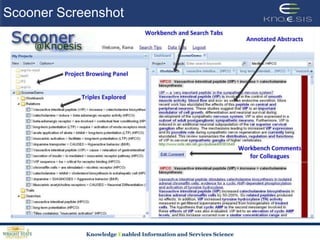
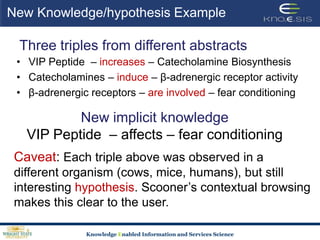
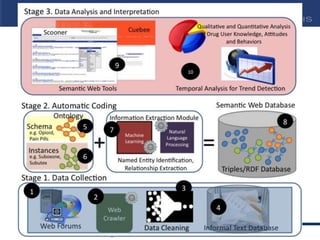
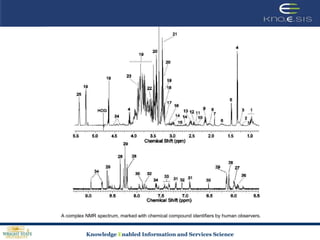
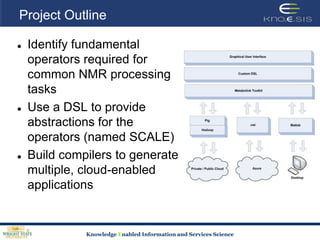
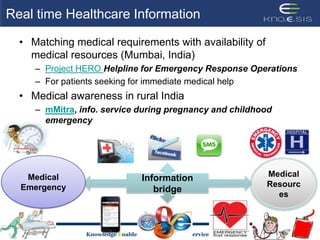
This document discusses using semantic web technologies for translational research in life sciences. It provides an overview of semantic web standards and outlines several projects demonstrating applications in healthcare and biomedical research. These include developing an active semantic electronic medical record, semantically annotating experimental glycomics data, and integrating diverse biomedical data sources using ontologies to enable complex querying and knowledge discovery.