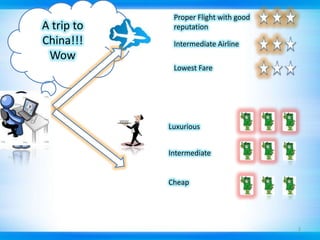
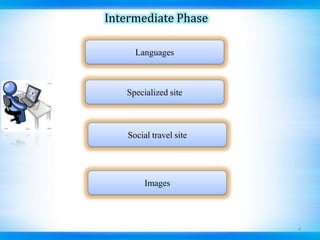
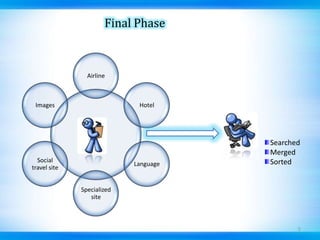
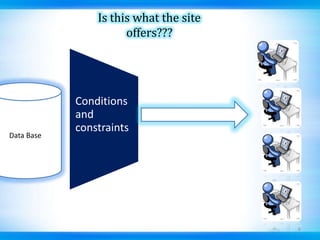
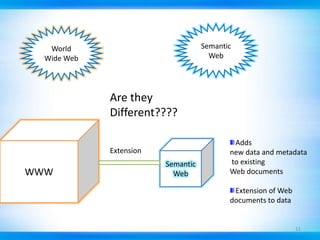
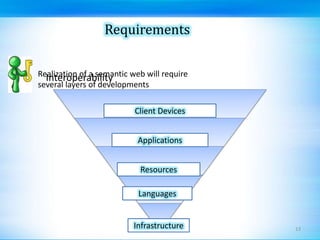
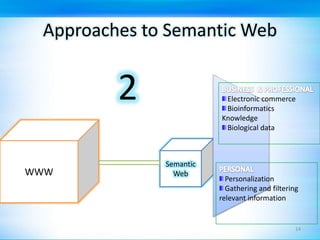
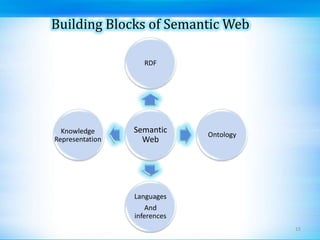
This document discusses defect tracking and correction in software development. It defines a defect as any non-conformity to specifications. The defect discovery process involves identifying defects and notifying the development team. The developer then acknowledges, fixes, and verifies the defect. Defects go through a tracking lifecycle of being raised, reported, fixed, and closed. Defects are found through static, dynamic, and operational techniques and categorized by functionality, severity, and priority. The document outlines the contents of a defect report and explains the purpose of defect recording and reporting in the defect management process.