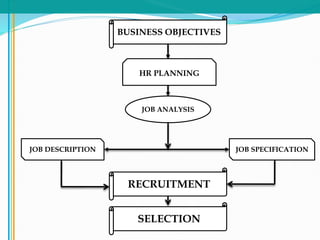
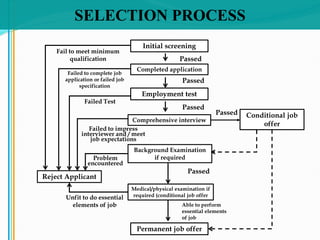
The document discusses the selection process for hiring employees. It defines selection as the process of making "hire" or "no hire" decisions for job applicants based on their qualifications. The objective of selection is to choose the most suitable candidate.
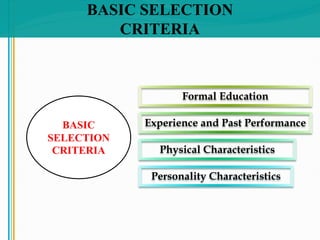
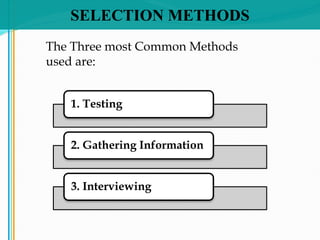
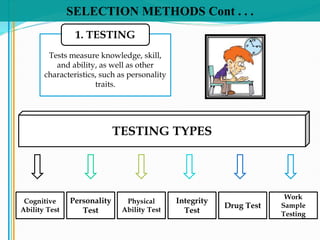
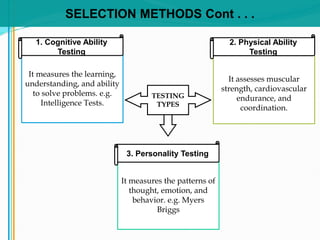
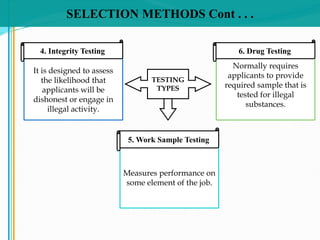
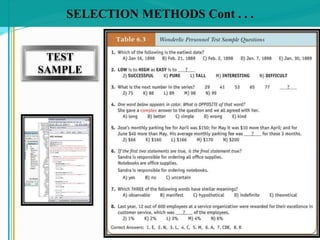
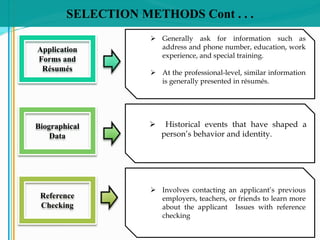
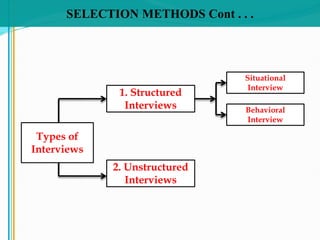
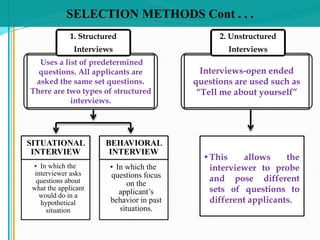
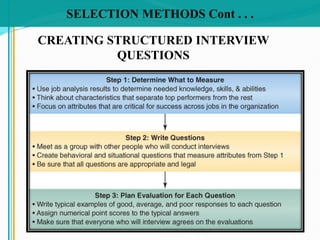
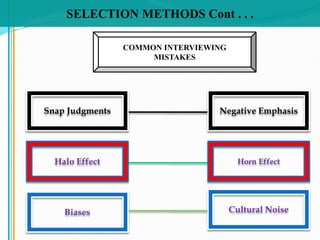
Some key aspects of the selection process covered include establishing selection criteria like education, experience, and personality; common selection methods like testing, gathering application information, and interviewing job candidates; and potential biases that can occur during interviews like snap judgments, halo effects, and cultural noise. Testing methods evaluate traits like cognitive ability, integrity, personality, and physical fitness for the job. Information is also gathered from application forms, resumes, references, and background checks.