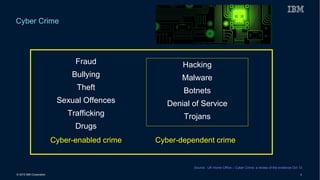
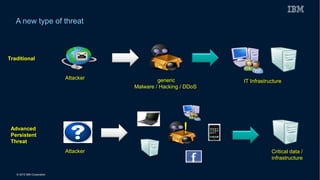
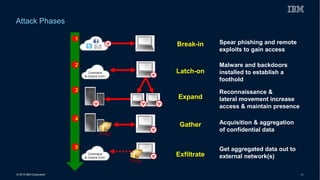
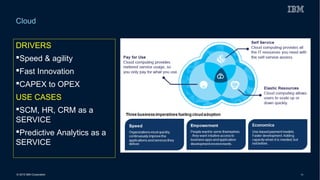
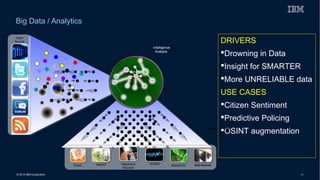
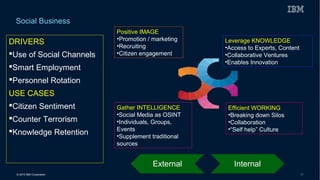
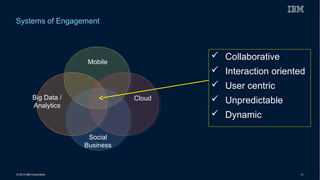
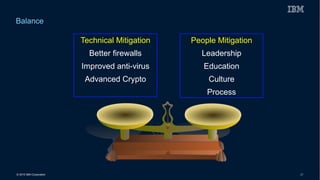
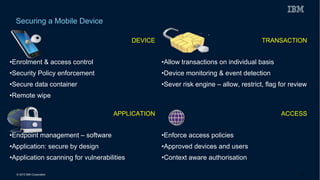
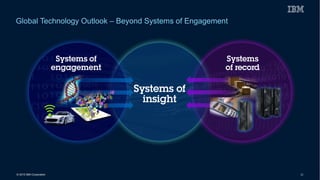
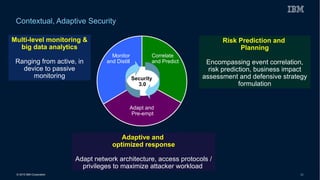
This document discusses securing systems of engagement against cyber threats. It begins with an overview of cyber security definitions, common attack methods and challenges. New technologies like cloud, mobile, big data and social media create new opportunities for cyber crimes but also require smarter security approaches. Risk management principles of monitoring threats, understanding systems, assessing impact and designing containment are recommended over perfect defenses. Securing mobile devices involves enrollment/access control, security policies, secure data containers and remote wipe. A secure social business requires leadership setting the right culture, clear processes, education and testing of applications. The future of security is predicted to involve contextual, adaptive approaches with multi-level monitoring, big data analytics, and adaptive, optimized responses.