The document introduces several key concepts about angles:
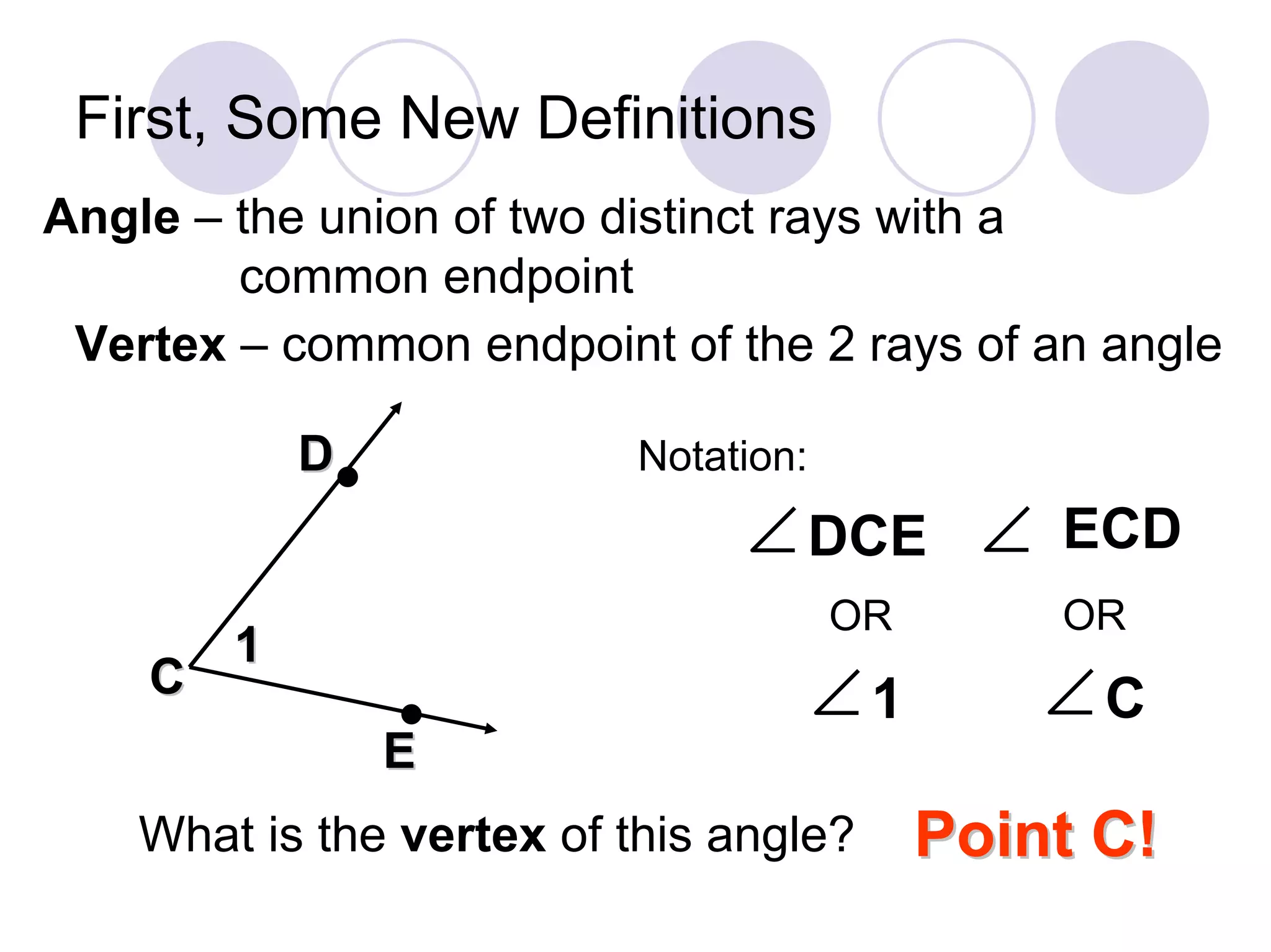
1) It defines an angle as the union of two rays with a common endpoint called the vertex.
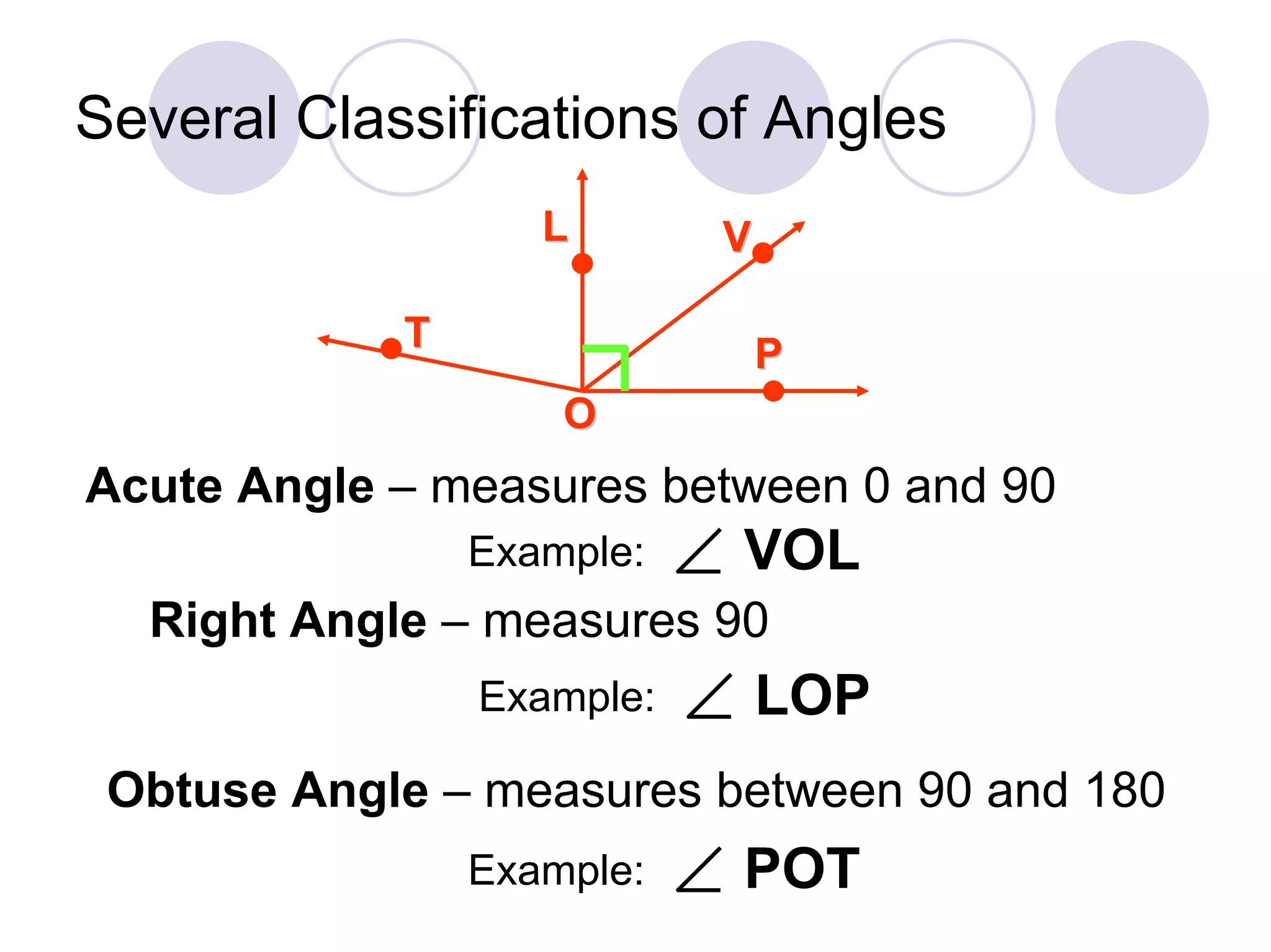
2) It classifies angles as acute, right, or obtuse based on their measure.
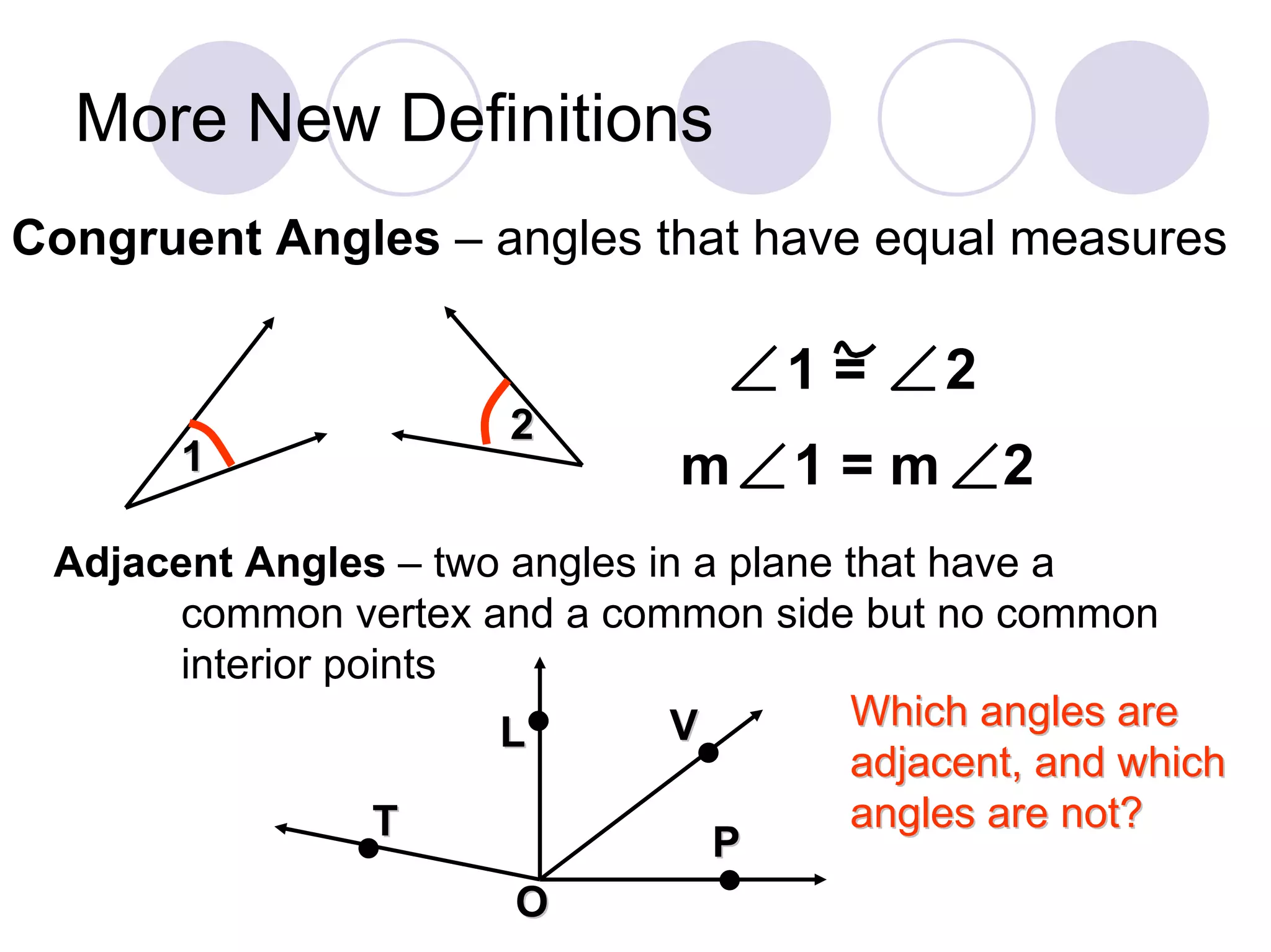
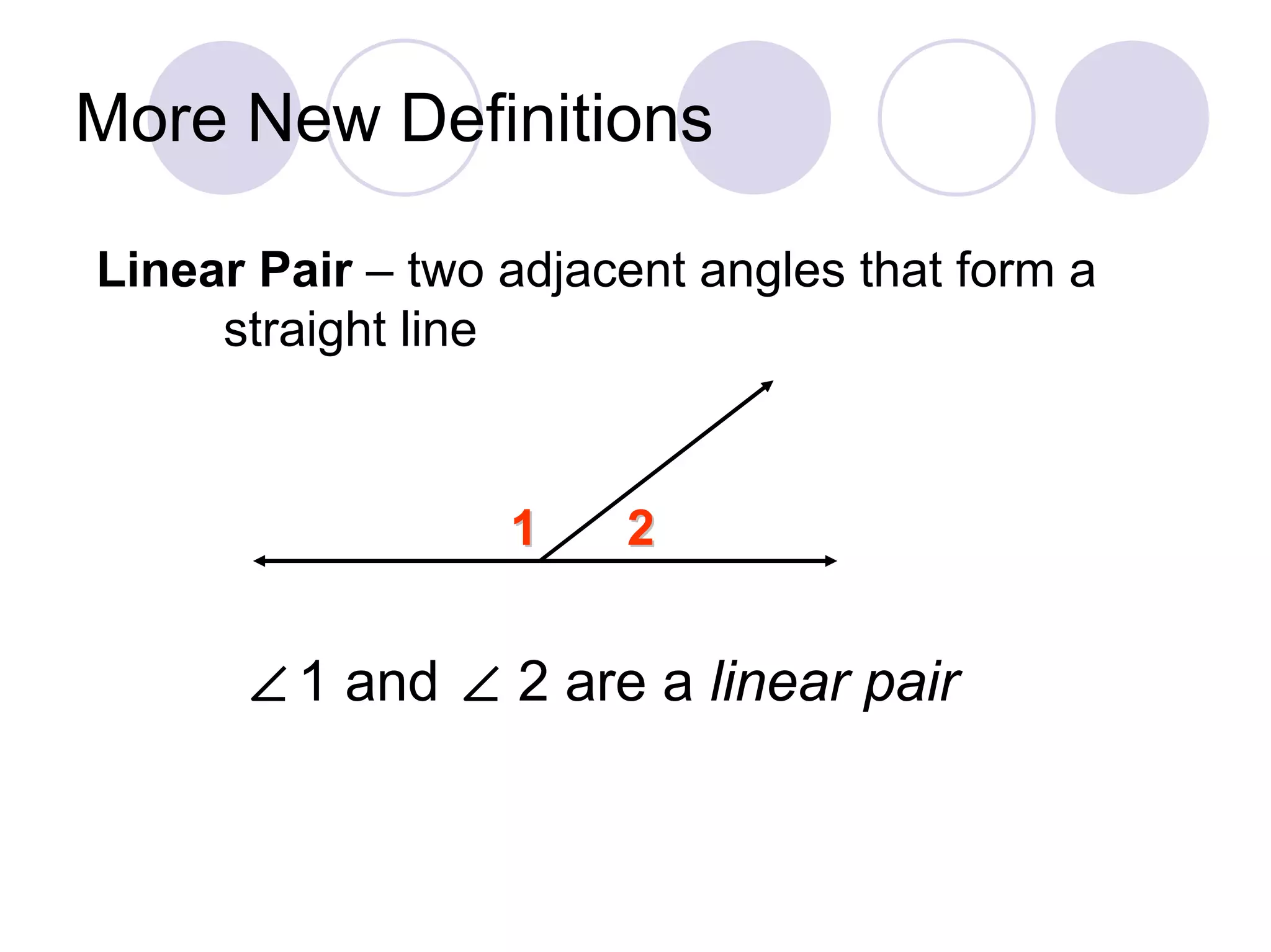
3) It defines congruent angles, adjacent angles, and a linear pair of angles.
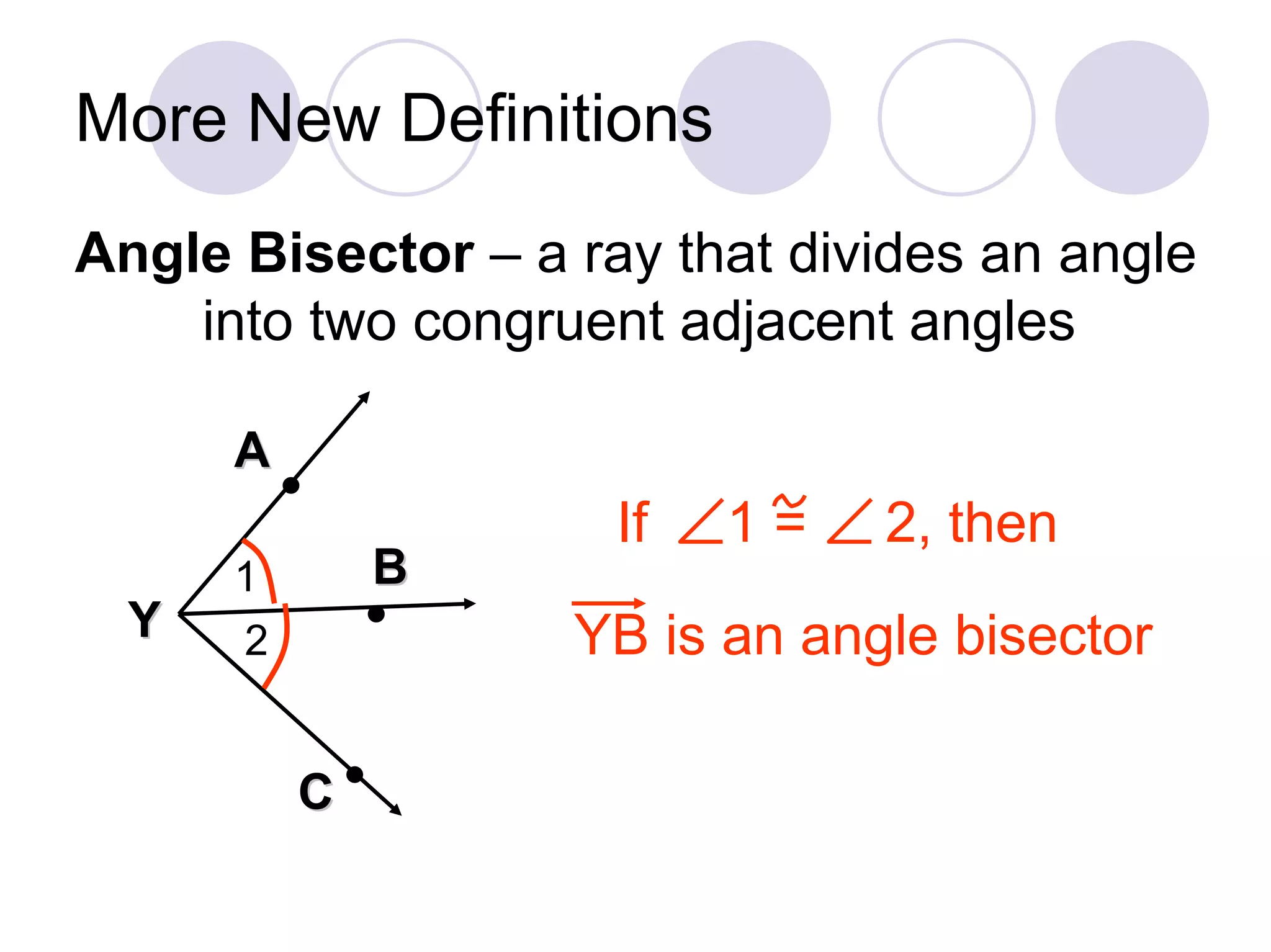
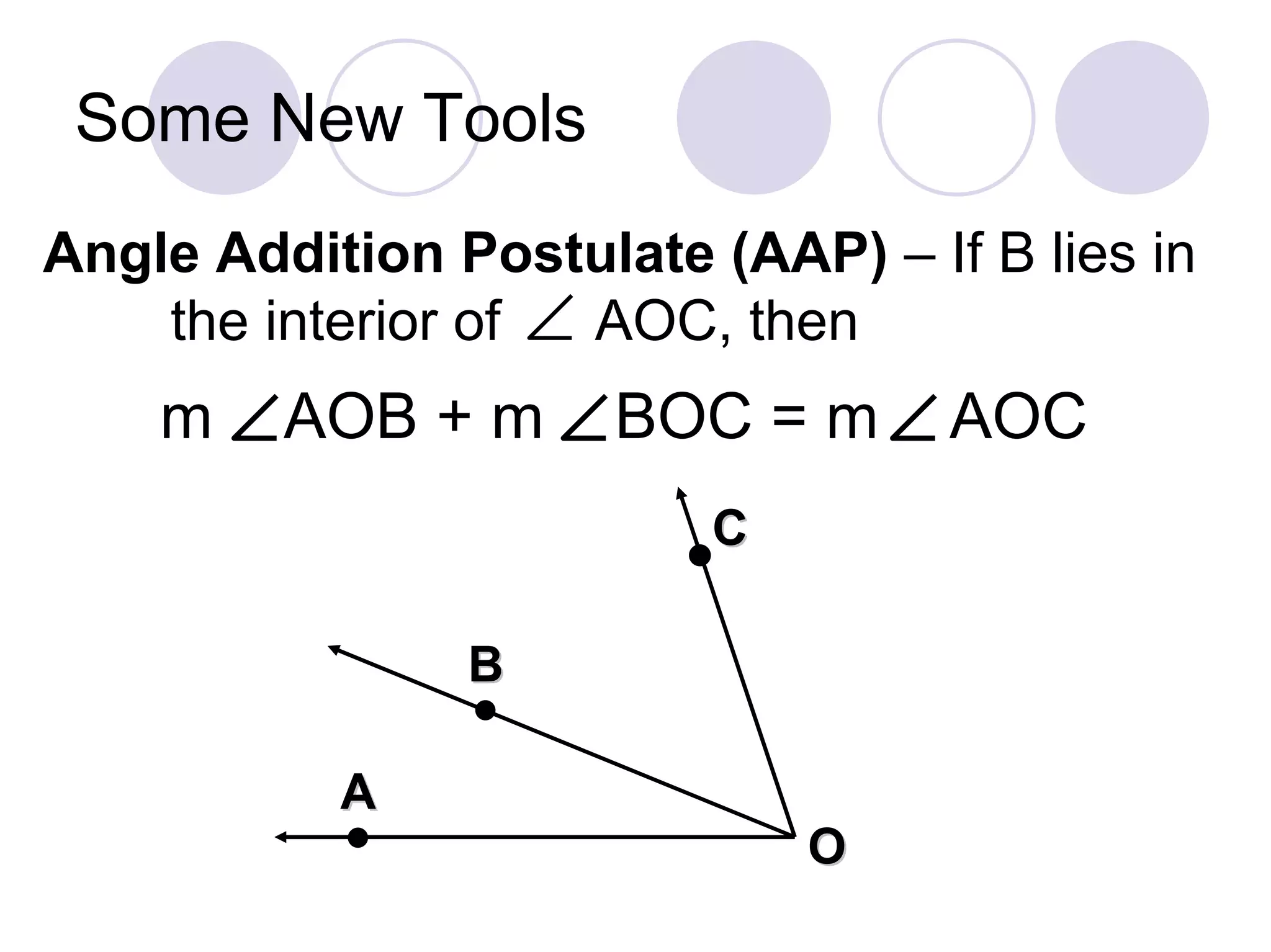
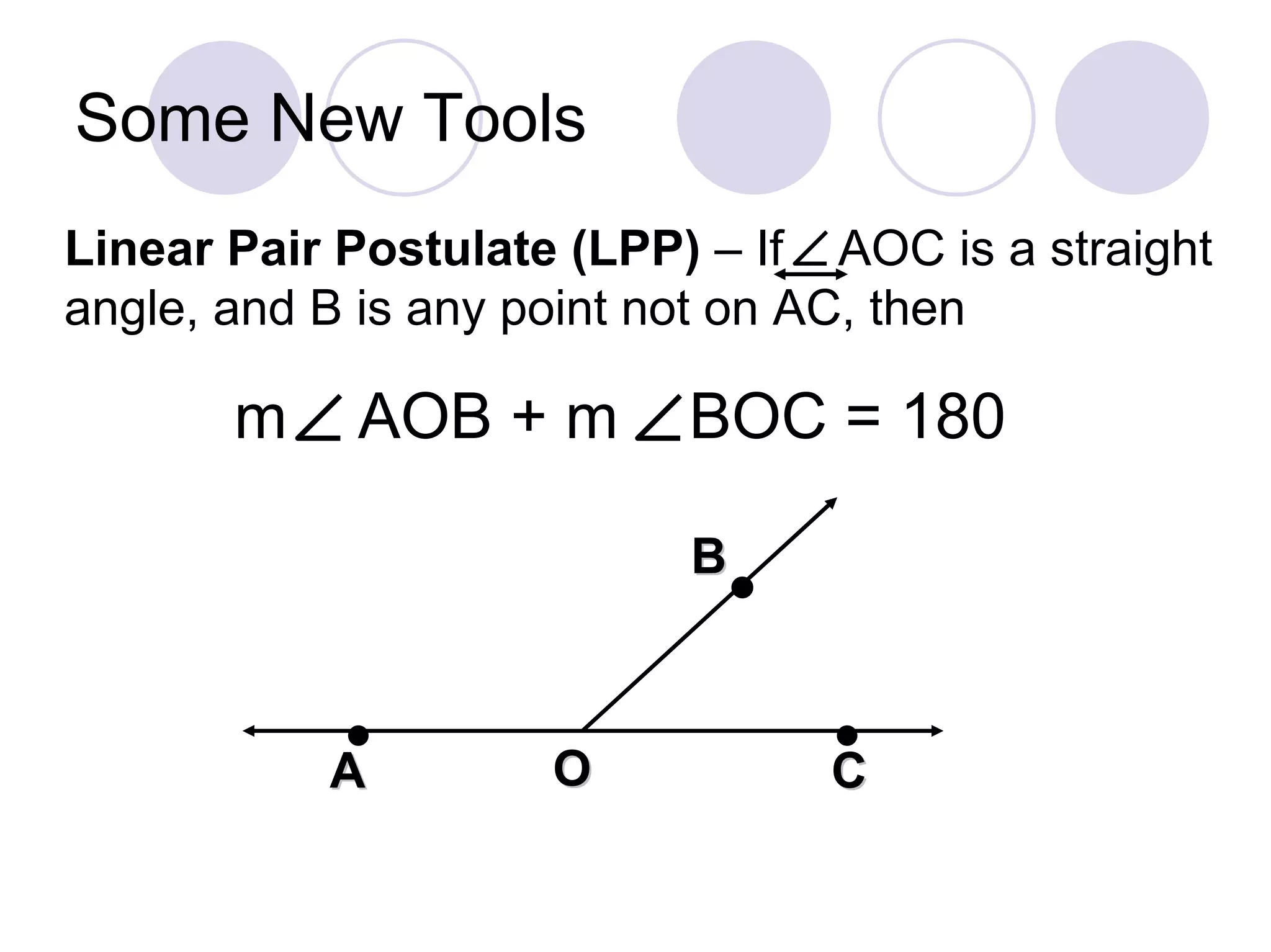
4) It introduces the angle bisector, angle addition postulate, and linear pair postulate as tools for working with angles.