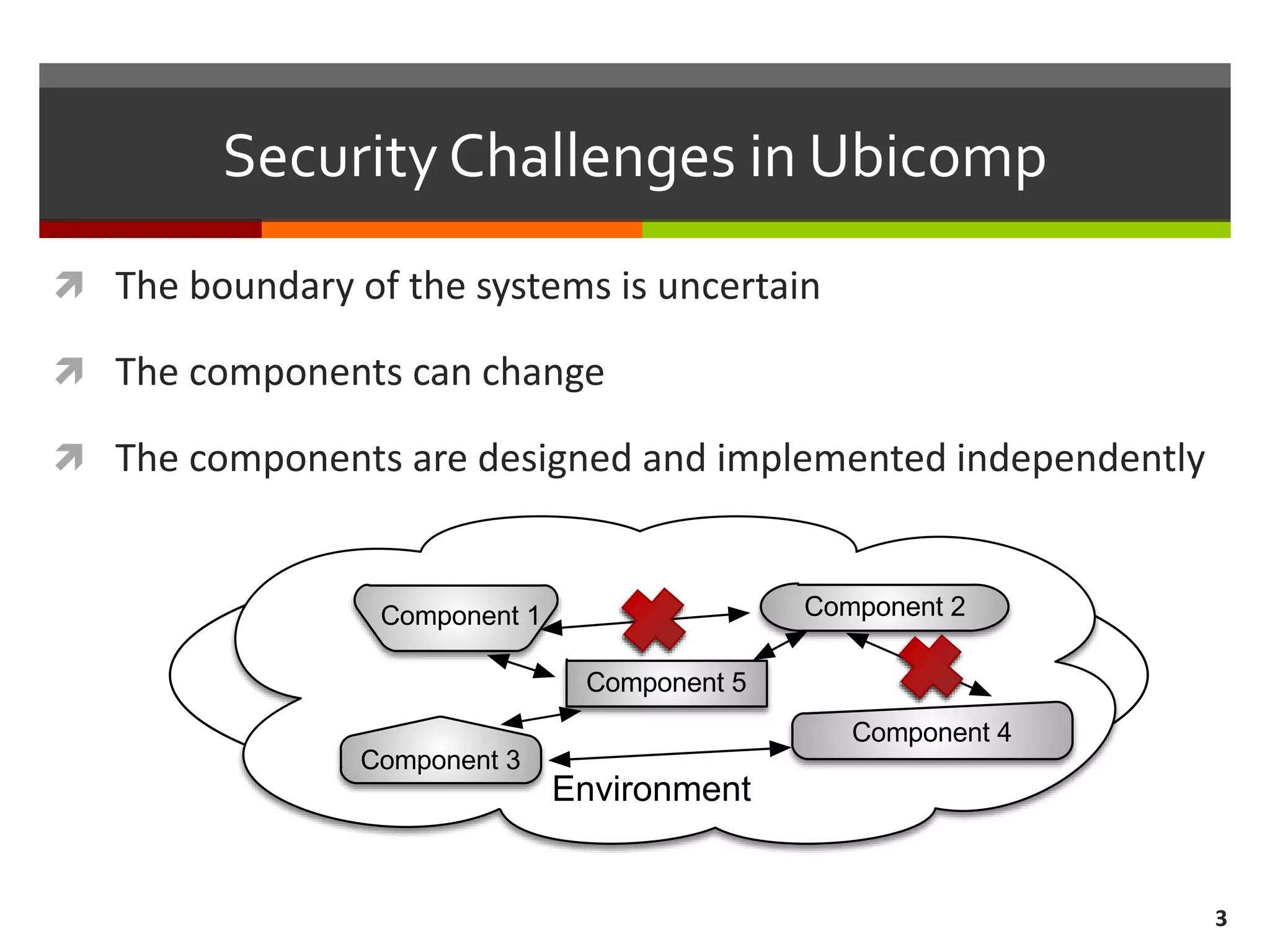
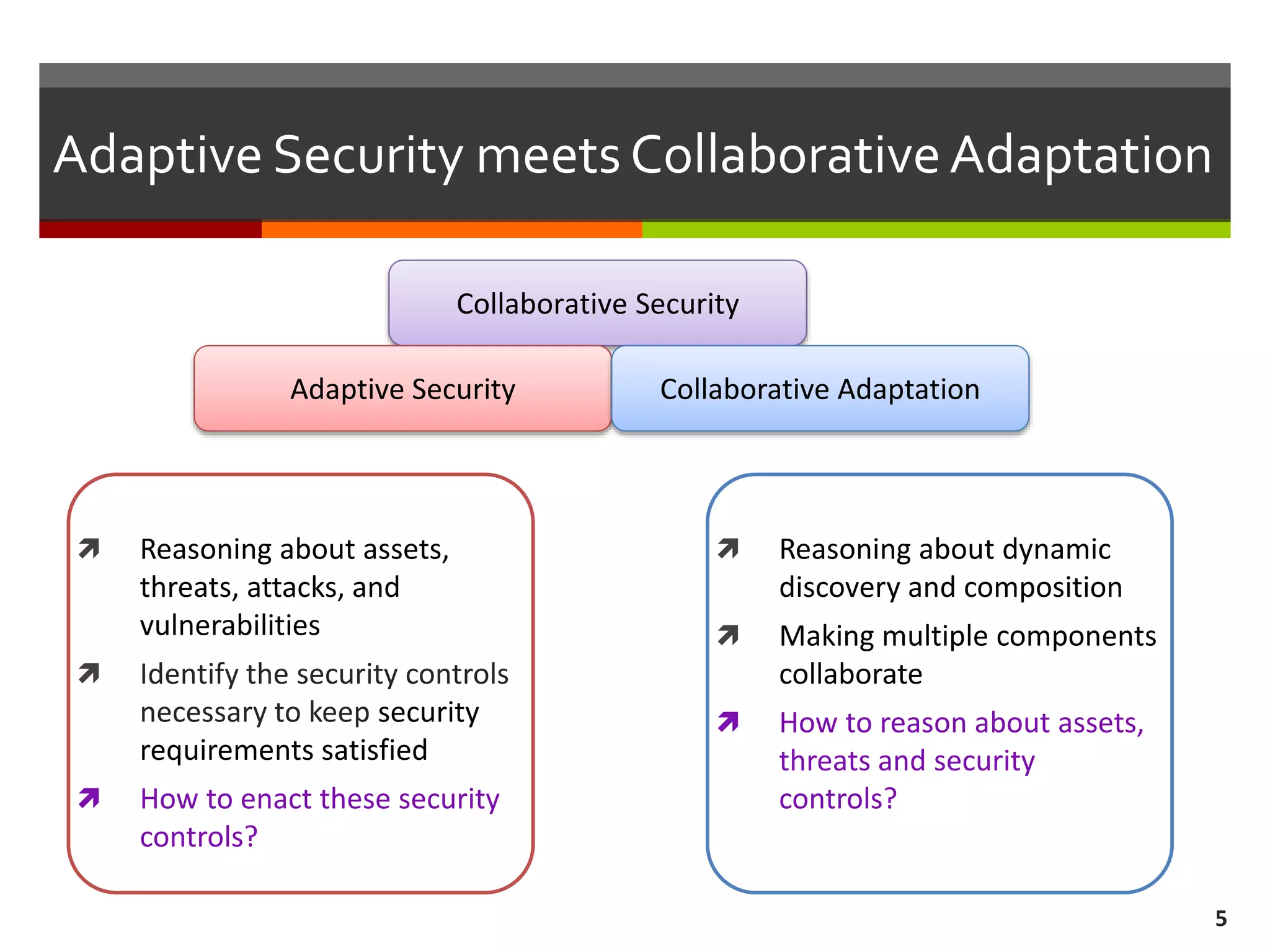
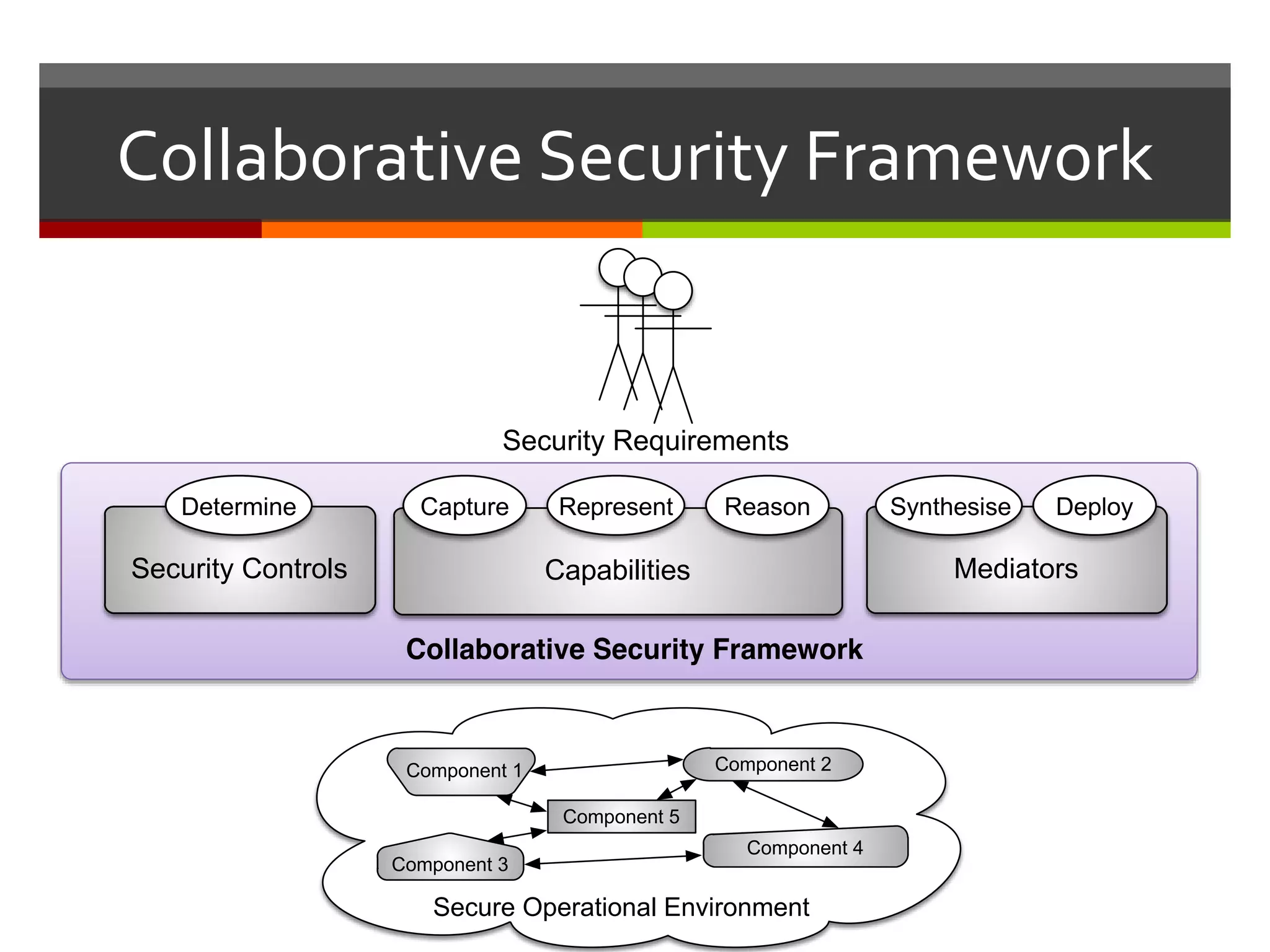
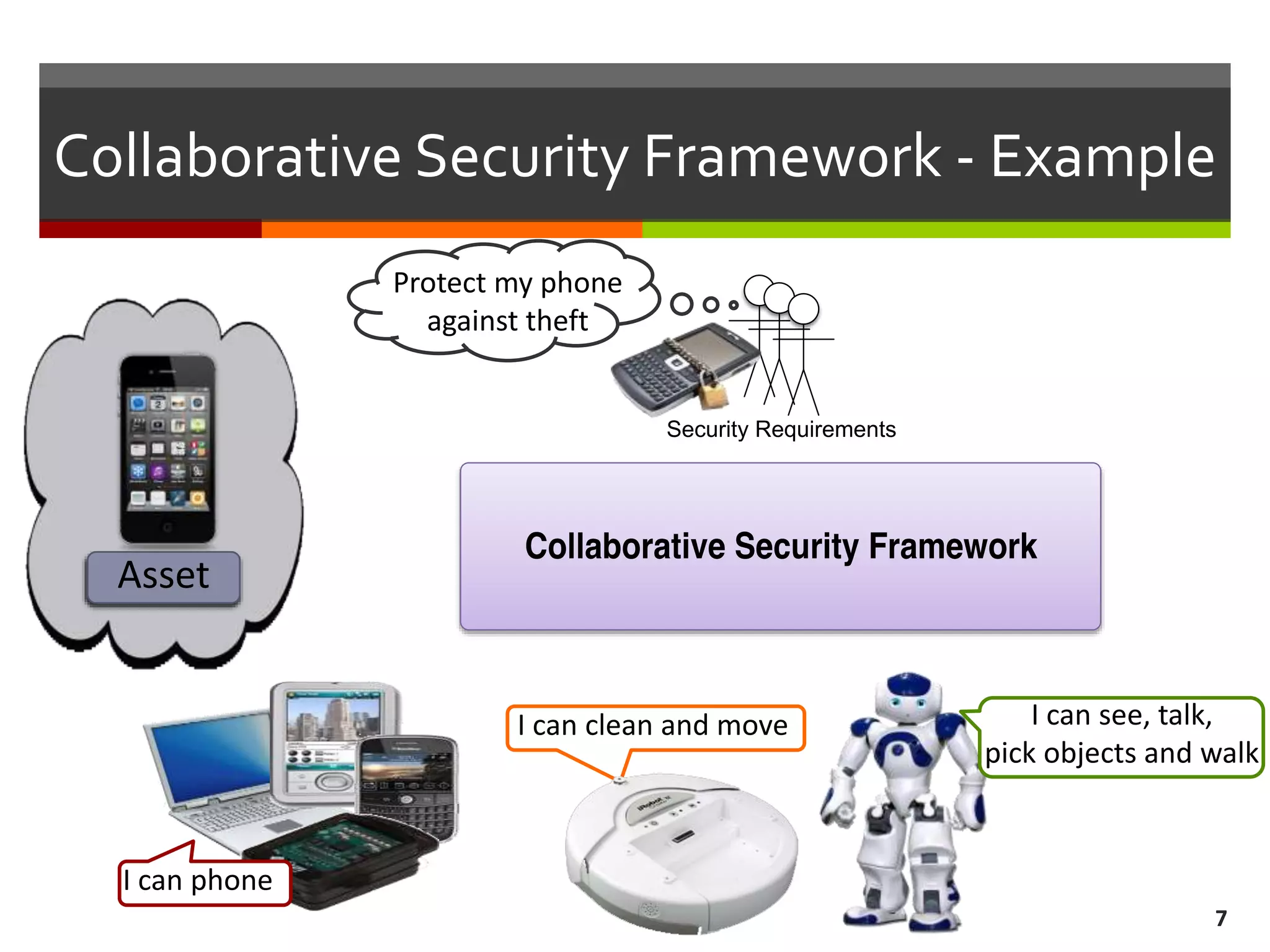
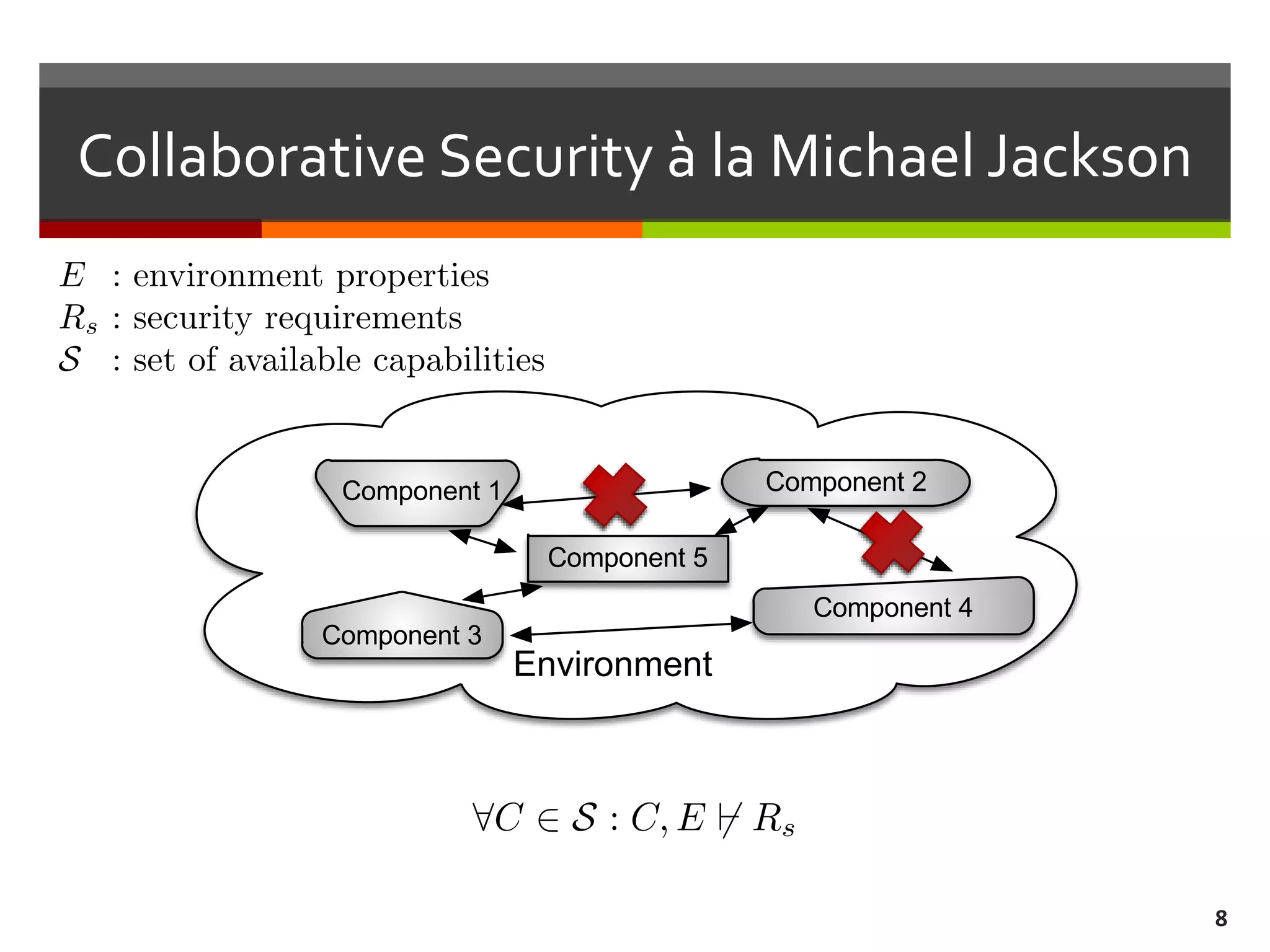
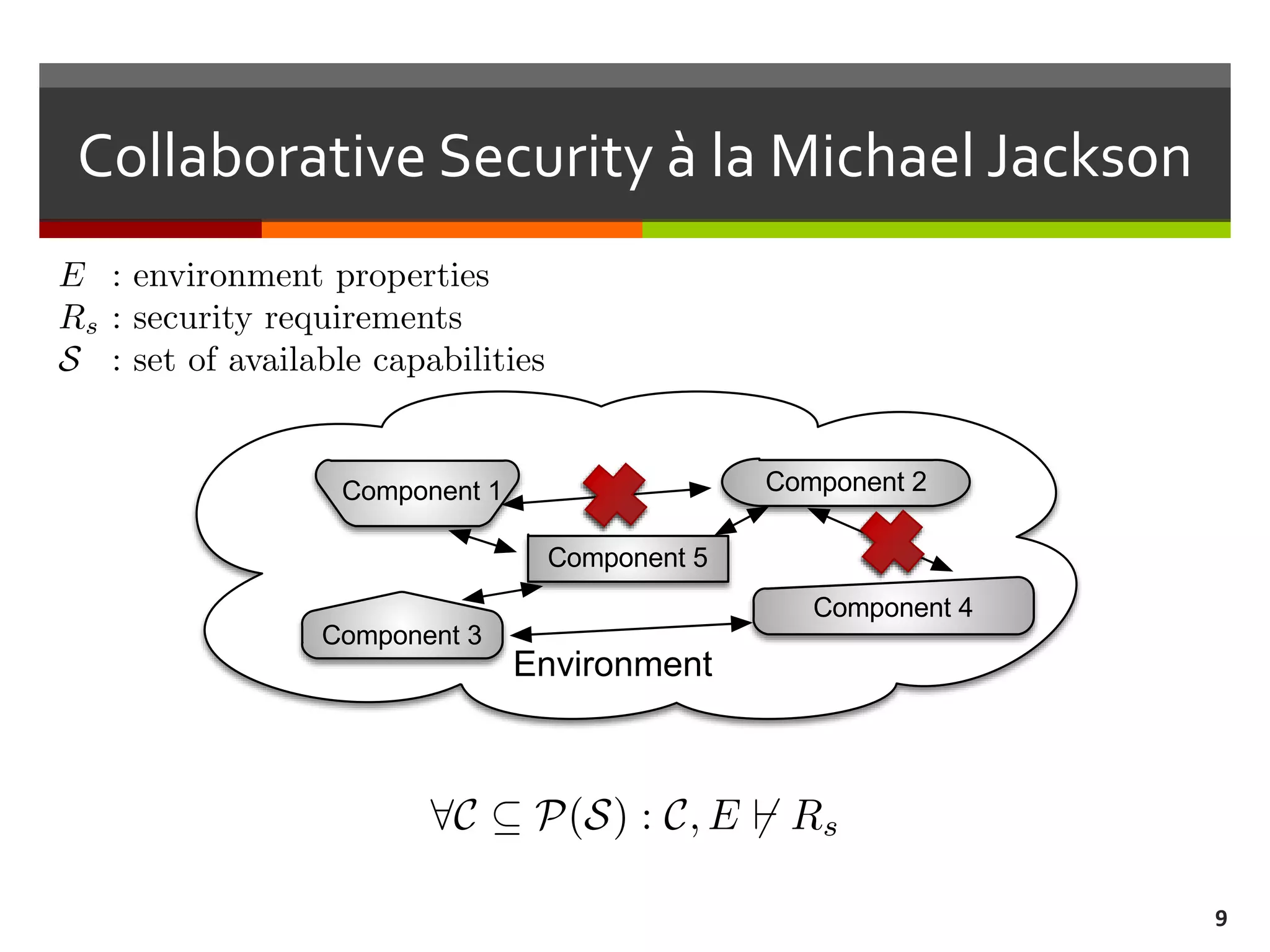
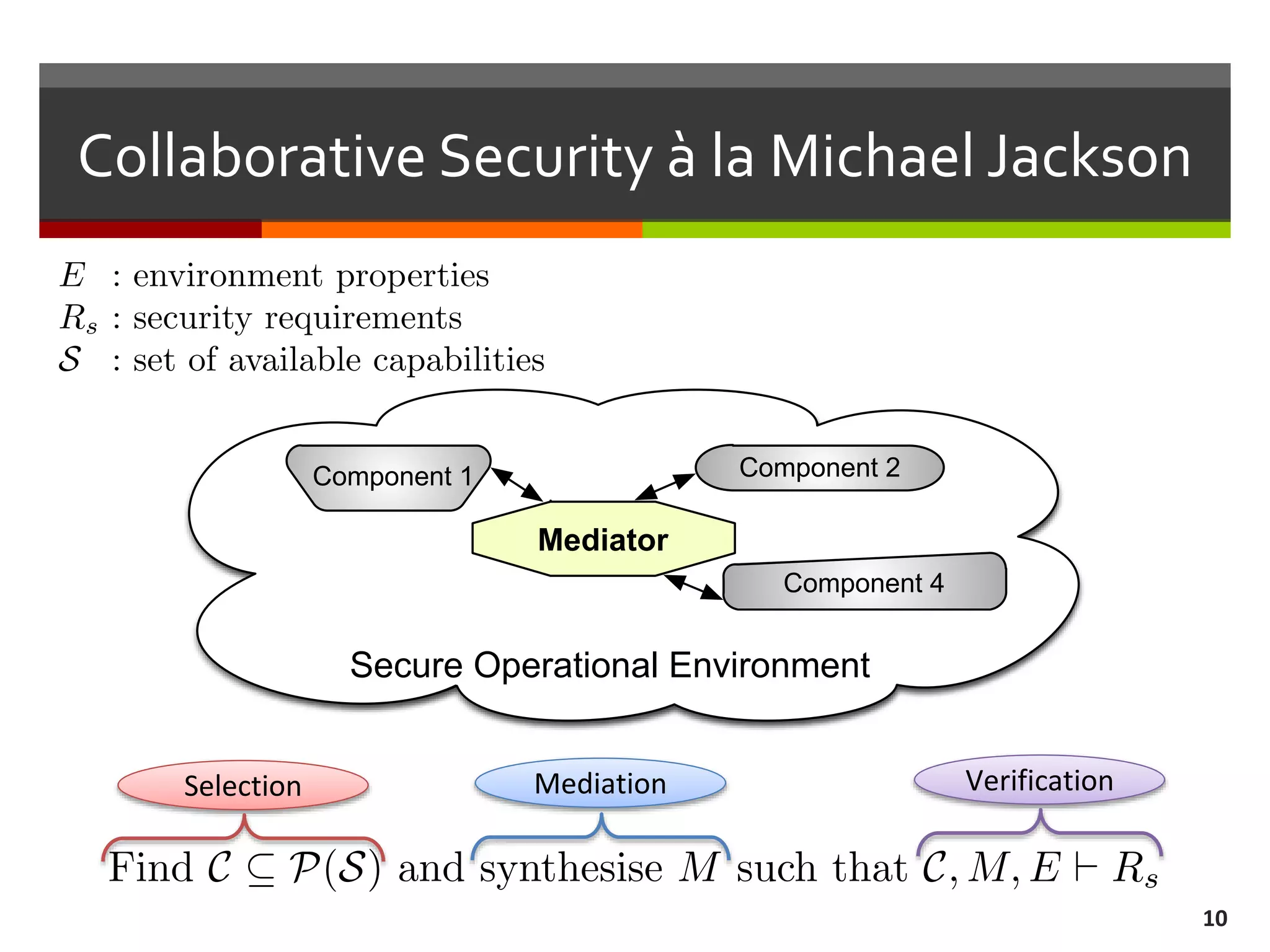
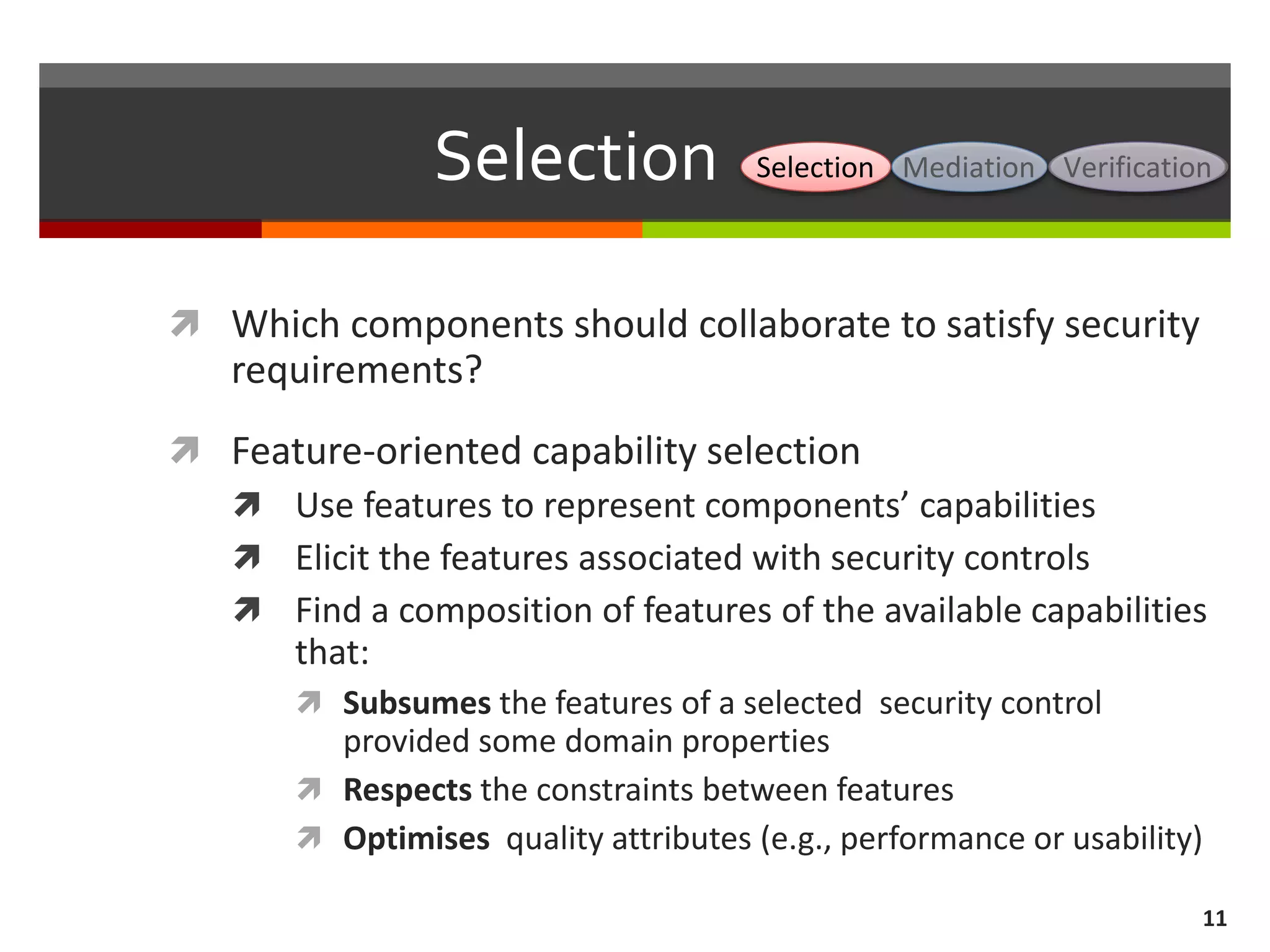
The document discusses the concept of requirements-driven mediation for collaborative security in complex, software-intensive systems. It emphasizes the need for multiple components to work together to adapt to security challenges and changes in the environment, highlighting features such as mediator selection and verification of collaboration to ensure security requirements are met. The paper outlines a research agenda focused on selection, mediation, and verification of security capabilities in collaborative environments.