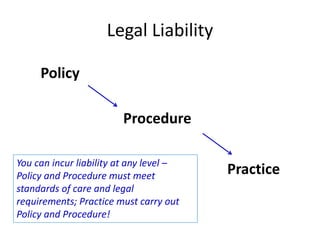
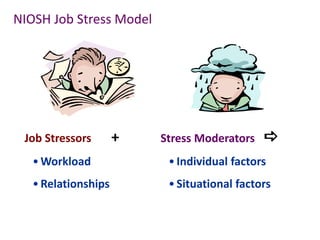
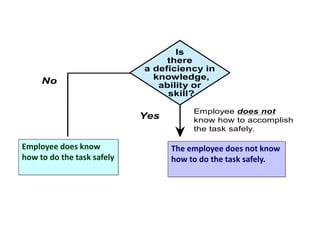
This document discusses effective safety supervision. It begins by outlining four goals: 1) describing why enforcing policies is a supervisor's job, 2) defining "adequate supervision" and how supervisors can meet this requirement, 3) describing supervisor responsibilities for holding employees accountable, and 4) discussing tools for employee motivation. It then discusses what leadership is and is not, defining leadership and different leadership styles. It emphasizes the importance of communication, consistency, and building trust between supervisors and employees. Finally, it discusses supervisor responsibilities including providing training, resources, and discipline when needed to ensure a safe work environment and secure compliance with safety rules.